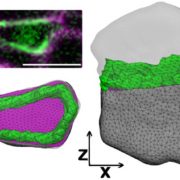
Busted: Finding Cells Whose Division Planes Defy Prediction
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefEvery plant organ, from tuber to tepal, is formed by cells that divide along precisely placed cell plates. While much is known about the molecular biology behind cell plate formation (e.g., Gu et al., 2016), why cells divide where they do is much less clear. Dividing cells have much in common with soap…
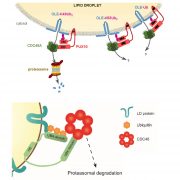
A Lipid Droplet-Associated Degradation System in Plants
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOnce viewed merely as inert packets of metabolic energy that are mobilized during postgerminative growth, lipid droplets (LDs) have emerged as dynamic organelles with important roles in processes ranging from stress responses to hormone signaling (Pyc et al., 2017). LDs consist of a core of neutral lipids…

Tic-Tac-Toe: How TIC and TOC Coordinate Getting Proteins Across the Line
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefMost proteins within a cell are encoded in the nucleus and then translated in the cytosol, but how do they end up where they need to be? With the exception of the few proteins expressed within the chloroplast, the process of shipping nucleus-encoded proteins into the chloroplast is dependent on N-terminal…
Escape from Centromere Land
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAs plant biologists, we do love to consider the physiological adaptations plants have made to being sessile organisms—unlike animals, plants cannot move away from adverse environmental conditions such as high temperature, etc. We commonly consider such responses for organisms, but what about genes?…
CDL1-OST1 Interaction as a Focal Point of Brassinosteroid-Abscisic Acid Hormone Signaling Crosstalk
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants integrate signals in the form of light, humidity, temperature, CO2 concentrations and daily circadian rhythms. In addition, plants encounter pathogens, pests, herbivores and other stressors. Physiological processes like responding to stimuli, plant growth and development are usually governed and…
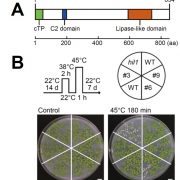
Heat Trims the Fat: HIL1 Functions in Lipid Homeostasis
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGlobal climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our world today. The impact of increasing temperatures can be felt in diverse areas, including human health and disease, natural ecosystems, and food security. In the agricultural sector, deciphering how plants respond to changing environmental…

Modulation of Resistance Genes: Two Paths to Alternaria Resistance in Apple
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApple (Malus x domestica) is a major fruit crop worldwide that faces production losses due to many pathogens. Among them, Alternaria alternata is a fungal pathogen that causes necrotic leaf spots (see Figure), defoliation, and moldy fruit cores and constitutes a serious threat to orchards. Different…

Assembling a Nanomolecular Power Station
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ATP synthase complex of chloroplasts is an elegant example of the union of structure and function at the molecular level (Junge and Nelson, 2015). This enzyme complex consists of an integral membrane CFo component that transports protons and an extrinsic CF1 component that synthesizes ATP (Hahn et…
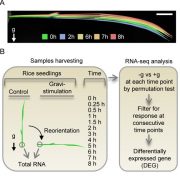
The Dynamic Transcriptome: Using Clustered Time Points to Tease Apart Rice Tiller Angle Control
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGiven the importance of branch angle in determining overall plant form, we know surprisingly little about how those angles are controlled. Branch angle clearly has genetic underpinnings but also responds strongly to light and gravity, as well as to water availability and other stimuli (reviewed in Roychoudhry…

