
Translating to beat the heat
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. investigate protein translation under heat stresss http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/8/1952
By Elizabeth Vierling
Plants can’t move to avoid unfavorable growth conditions, such as insufficient water availability or extremes of temperature. When plants are confronted with stressful…
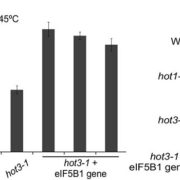
Some Like it HOT: Protein Translation and Heat Stress in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ability to acclimate to high temperatures that are normally lethal is common to virtually all organisms on the planet. A short exposure to milder heat stress informs organisms that they should ready themselves in case they experience even warmer conditions. Acquired thermo-tolerance in plants is…

Plant Cell Editorial: Journal Impact, Brave New World
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News0 Comments
/
Latest news on The Plant Cell significance and editorial policies
"Larivière et al. (2016) advocate publishing frequency distribution plots of the citations to provide a clearer view of the underlying data. We agree that showing the underlying frequency distribution of citations “echoes the reasonable…
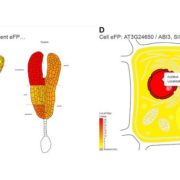
So Much Data, So Little Time: ePlant Steps into the Breach for Plant Researchers
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ever-increasing amount of data available to researchers has come with similarly increasing cognitive loads in efforts to use these data. Even when data sets are stored in well-curated databases, it can be time-consuming to master the specific tools harbored at each site and cumbersome to move between…
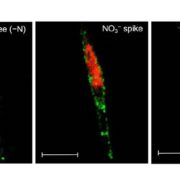
An Emerging Model Diatom to Study Nitrogen Metabolism
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCarbon and nitrogen metabolism are intricately linked in all organisms and are tightly regulated to maintain growth, homeostasis, and other cellular activities. In plants and algae, photosynthesis provides both carbon skeletons and the reductant needed for assimilation of inorganic NO3¯ by nitrate reductase…
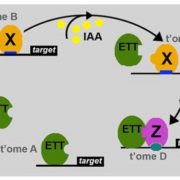
A Genome-wide Approach to Understanding a Non-Canonical ARF
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe canonical auxin-response pathway in plants begins with auxin sensing by F-box proteins, triggering degradation of AUX/IAA proteins that act as transcriptional repressors via their interaction with sequence-specific DNA-binding AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS (ARFs; reviewed in Weijers and Wagner, 2016). Recently,…

Recognizing featured Plant Cell first authors, July 2017
Blog, Careers, Profiles of Plant Scientists, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Author ProfilesElizabeth Henry, featured first author of Direct and Indirect Visualization of Bacterial Effector Delivery into Diverse Plant Cell Types During Infection
Current Position: Postdoctoral Scholar, Discovery and Project Support in Crop Efficiency and Seed Growth, Biologics R&D at Bayer Crop Science.
Education:…
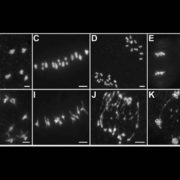
Crossover Guard: MEICA1 Prevents Meiotic Mishaps
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefDuring meiosis, recombination between allelic sequences on pairs of homologous chromosomes forms crossovers; these crossovers help make sure that the homologs segregate accurately (reviewed in Zhang et al., 2014). However, cells must suppress recombination between non-allelic sequences, as ectopic recombination…

Exploring Maize Leaf Architecture from Different Angles
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOrnamental grasses with a sprawling growth habit may be welcome in the garden, but grasses such as maize (Zea mays) give the highest yields when they exhibit upright leaf architecture, allowing them to be planted at high density while maximizing their exposure to sunlight. The maize leaf is composed…

