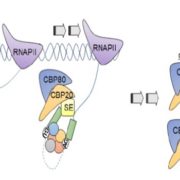
Update: Nuclear Cap-Binding Complex in Abiotic Stress Responses
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Agata Daszkowska-Golec
The nuclear cap-binding 16 complex (nCBC) in higher eukaryotes specifically binds to the monomethylated (7-methylguanosine (m717 GpppN)) cap structure at the 5¢ end of freshly transcribed mRNA. In addition to protecting mRNAs from degradation by exonucleases, the nCBC functions…
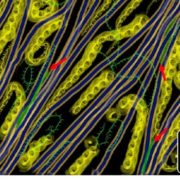
Update: Diffuse growth of plant cell walls
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Daniel J. Cosgrove
Introduction
The primary wall of a growing cell is a versatile, subtle and dynamic structure, with unique properties and functions in the life of the plant (Burton et al., 2010). When a cell grows, its wall stretches irreversibly as the cell enlarges in volume. Cells can start…
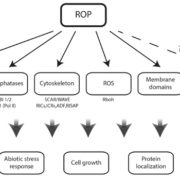
Update: ROP GTPases structure-function and signaling pathways
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Gil Feiguelman, Ying Fu, and Shaul Yalovsky
Introduction
Rho of Plants (ROP) proteins also known as RACs are the plant specific subfamily of Rho small GTP binding proteins, referred to here as small G proteins (Zheng and Yang, 2000; Brembu et al., 2006; Elias and Klimes, 2012). Like other members…
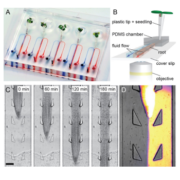
Arabidopsis perfusion platform RootChip reveals local adaptations of roots
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRoots are essential plant organs that need to respond and adapt to dynamic environments. It is still unknown if these adaptations are based on systemic or cell-based responses. Stanley and colleagues created the dual-flow-RootChip, a platform for the heterogeneous perfusion of Arabidopsis roots to…

J. Exp. Bot. Special Issue. The plant cuticle: old challenges, new perspectives ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe cuticle is a cell-wall polymer that protects against desiccation, pathogens and UV light. Domínguez et al. provide an open-access editorial that describes this fine collection of articles covering all aspects of the plant cuticle, from its evolutionary origins to its ecological significance. Within…
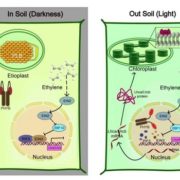
EIN3 and PIF3 interdependently repress chloroplast development in buried seedlings
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDuring embryogenesis, plastids arrest their differentiation as etioplasts (characterized by the distinctive prolamellar bodies, PLBs), and remain poised to complete their differentiation into functioning chloroplasts upon exposure to light. Liu et al. explored the factors that interact to effect this…
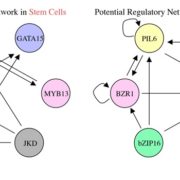
Chromatin accessibility changes between Arabidopsis stem cells and mesophyll cells illuminate cell type-specific
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWhat gives stem cells their plasticity and why are differentiated cells so specialized? Sijacic et al. approach this question by analyzing transcription factor (TF) accessibility to chromatin. Nuclei were isolated from shoot apical meristem (SAM) pluripotent stem cells and fully-differentiated mesophyll…
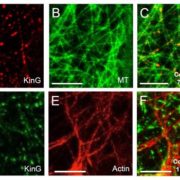
A plant-specific kinesin KinG regulates intra- and intercellular movement of SHORT-ROOT
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSHORT-ROOT (SRT) is a transcription factor that has previously been shown to move between cells and so contribute to developmental patterning. Spiegelman et al. investigated the cellular machinery that contributes to SRT’s movement. Previous work showed that the movement of SRT depends on the endosome…
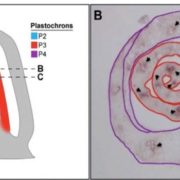
SHORTROOT-mediated increase in stomatal density has no impact on photosynthetic efficiency
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSHORTROOT (SRT) is a transcription factor that contributes to developmental patterning non-cell autonomously, by moving between cells. In leaves, SRT has been shown to contribute to sub-epidermal patterning specified by distance from the vein. Schuler et al. explored whether it also contributes to epidermal…

