Transcriptome Studies of Deepwater Rice
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideRice (Oryza sativa) paddies frequently become submerged during the rainy season in some parts of South and Southeast Asia, such as Bangladesh, India, Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia. Submergence stress is harmful to plants. In addition to causing O2- and CO2-deficient conditions by restricting environmental…
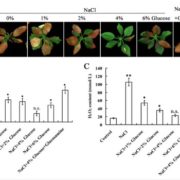
Apple Hexokinase Mediates Response to Salinity Stress
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideAbiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, low temperature, and flooding usually lead to sugar accumulation. It has been reported that the accumulation of Glc, Suc, and Fru under high salinity plays an important role in carbon storage, osmotic regulation, and homeostasis, as well as scavenging of free…
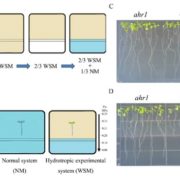
Brassinosteroids and Hydrotropism
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSoil water availability is a major constraint for crop growth throughout the world. Hydrotropism, the bending of roots in response to moisture gradients, enables plants to take better advantage of available soil water. In contrast to gravitropism and phototropism which have been studied extensively,…
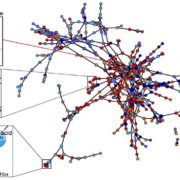
Mycorrhiza-Triggered Networks in Leaves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideOne effect of mycorrhizal fungi is to stimulate the plant immune system, leading to induced systemic resistance (ISR). Thus, mycorrhizal fungi influence the interactions between plants and aboveground herbivores. The molecular mechanisms underlying these types of beneficial microbe-plant interactions…
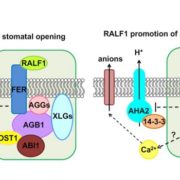
FERONIA-RALF and G Proteins in Guard Cell Response
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogHeterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins are composed of Ga, Gb, and Gg subunits and function as molecular switches in signal transduction. In Arabidopsis, there is one canonical Ga (GPA1), three extra-large Ga (XLG1, XLG2, and XLG3), one Gb (AGB1), and three Gg (AGG1 to 3) subunits. Despite…
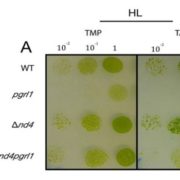
Mitochondria Affect Photosynthetic Electron Transport
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogPhotosynthetic eukaryotic organisms rely on two organelles, chloroplasts and mitochondria, for the synthesis of the molecules NAD(P)H and ATP that fuel their metabolism. These two organelles are commonly thought of as two separate entities but the results of Larosa et al. (10.1104/pp.17.01249) suggest…
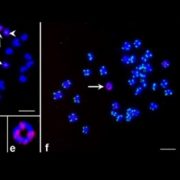
Herbicide Resistance in Common Waterhemp
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe herbicide glyphosate is widely used in agriculture, especially on glyphosate-resistant (GR) transgenic crops. The widespread adoption of GR crops across the globe and an overreliance on glyphosate as a single means of weed control has spawned many GR weed species. Glyphosate inhibits the 5-enopyruvlyshikimate-3-phosphate…
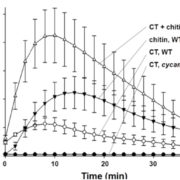
Cellotriose Induces Increases in Cytoplasmic Calcium
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogThe root-colonizing endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica, which was originally isolated from the rhizosphere of two woody shrubs in the Indian Thar Desert, colonizes the roots of a broad host range, including the model plant Arabidopsis. P. indica does not cause pathogenic symptoms, but promotes root…
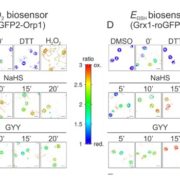
Hydrogen Sulfide’s Role in Stomatal Closure
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research Blog Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an important gaseous signaling molecule in plants that participates in stress responses, development, and stomatal closure. In plants, H2S is enzymatically produced by cysteine desulfhydrase in the catalyzed conversion of cysteine to pyruvate, H2S, and NH3+. In Arabidopsis…

