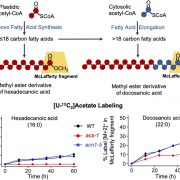
The Fate of Acetate During Hypoxia
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUnder hypoxia, Acetyl-CoA Synthetase (ACS), an enzyme that synthesizes acetyl CoA, recovers carbon that would otherwise be lost from the plant as ethanol. Plastid-localized ACS metabolizes cellular acetate and contributes to the de novo biosynthesis of fatty acids and Leu. On the other hand, a peroxisome-localized…
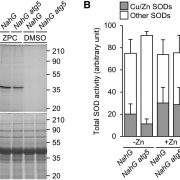
Autophagy Maintains Zinc Pools under Zinc Deficiency
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideZinc (Zn) is a metallic element that is essential for all living organisms. Zn serves as a catalytic or structural cofactor in a large number of enzymes including alcohol dehydrogenase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and regulatory proteins such as transcription factors containing Z-finger domains. Accordingly,…
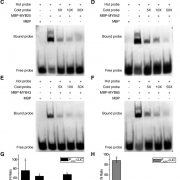
MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Secondary Metabolism
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSecondary cell walls play important roles in providing long-distance water transport, mechanical support, and plant defense. The main components of secondary cell walls are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. The synthesis of lignin monomers involves the phenylpropanoid pathway, which is also shared…
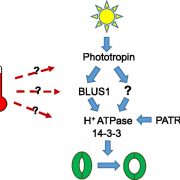
Temperature Signaling in Guard Cells
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe elucidation of plant temperature signaling networks is confounded by the fact that commonly measured physiological outputs of temperature change (e.g., stem elongation and flowering time) can be temporally and spatially distant from the temperature perception event, requiring intercellular, intertissue,…
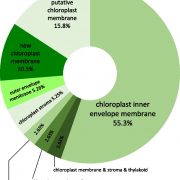
Cold-Induced Proteomic Changes in the Chloroplast Envelope
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideAs a cold-hardy species, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), is a useful model for the investigation of the molecular and physiological mechanisms underlying cold acclimation in plants. Chloroplasts harbor the enzymatic machinery required for photosynthetic CO2 fixation, starch production, nitrite and…

Shared Genetic Control of Root Traits across Taxa
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideRoot system architecture (RSA) plays a crucial role in plant productivity and tolerance to environmental stresses. The maize (Zea mays) root system, composed of the embryonic primary root and variable numbers of seminal roots, as well as postembryonic shoot-borne and lateral roots, is both different…

Auxin and Microtubule Array Patterning
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe Arabidopsis hypocotyl is a valuable model for studying axial growth phenomena in flowering plants owing to its dramatic cell elongation in the absence of cell division and its sensitivity to environmental cues. When grown in the dark, a hypocotyl rapidly elongates, using the energy reserves in the…

The Nuclear Envelope and Stomatal Dynamics
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideEukaryotic nuclei are double membrane-bound organelles with distinct inner nuclear membranes (INM) and outer nuclear membranes (ONM). The site where the INM and ONM meet forms the nuclear pore, where nucleocytoplasmic transport occurs. Spanning the INM and the ONM are protein complexes known as “linkers…

Natural Variation in the Amylose Content of Starch
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideStarch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants. It occurs as semi-crystalline, insoluble granules consisting of two Glc polymers: amylopectin and amylose. Amylopectin, the major polymer, gives rise to the semi-crystalline matrix of the granule. Amylose is believed to reside in amorphous regions…

