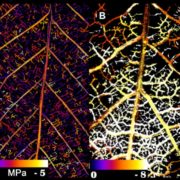
Low Xylem Vulnerability in Oaks
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUnder conditions of drought stress, the continuous column of water in the plant xylem experiences increasing tension caused by declining water potential at the sites of evaporation. Eventually, air is drawn into the water transport system, forming embolisms in the xylem conduits. Although plants have…
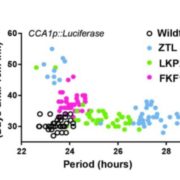
New Insights into the Molecular Biology of Plant Circadian Rhythms
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe circadian clock is an endogenous timekeeper that synchronizes essential biological processes with the outside world. Eukaryotic clocks rely on the ubiquitin proteasome system to target core clock factors for degradation. Altering clock protein degradation can change the period length of the clock.…
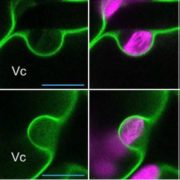
Selective Chloroplast Microautophagy
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideWhen plants are exposed to excessive light, photoinhibition occurs and chloroplasts become damaged. Photodamaged chloroplasts undergo vacuolar digestion through a poorly understood autophagic process called chlorophagy. In general, cell biologists recognize two types of autophagy: macroautophagy and…
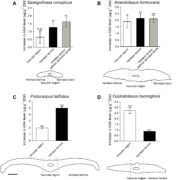
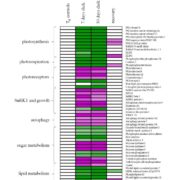
ABA Biosynthesis Occurs in the Mesophyll
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays a critical role in enhancing plant survival during water deficit. While there is no doubt that ABA is a carotenoid derivative and that carotenoid cleavage occurs in the chloroplast, uncertainty remains about which tissues are responsible for synthesizing ABA.…
How Does a Plant Tolerate Prolonged Darkness?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe exposure of plants to prolonged darkness leads to the exhaustion of starch reserves and carbon and energy starvation. In such cases, plants must use alternative nutrient and energy sources to survive. Autophagy is an important mechanism that breaks down proteins and lipids and thereby provides the…
Intra-Organ Regulation of Shade Responses
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlants beneath a canopy compete with neighboring plants for light by triggering various physiological responses, collectively known as shade avoidance syndrome. Because of the selective absorption of red (R) light by plants in the upper canopy, plants in the shade are exposed to low R to far-red (FR)…

A MicroRNA Regulating Lateral Root Growth in Response to Salt
Plant Physiology: On The InsideSoil salinity is a major threat to crop yields around the world. Salt generally damages plants through osmotic stress in the rhizosphere, interfering with water and nutrient uptake and causing cells to be subjected to ionic toxicity Developmental plasticity in the root system is an important strategy…
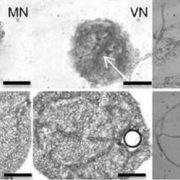
Drugs Triggering Oil Accumulation in a Diatom
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideOils composed of triacylglycerols (TAGs) have a broad range of applications, ranging from foods to biofuels. Microalgae are promising feedstocks for the production of (TAGs) but obtaining high yields of TAGs is challenging. Conte et al. (10.1104/pp.17.01804) have developed a phenotypic assay for the…

Mechanisms of Long-Distance mRNA Movement
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePhloem has long been recognized as a tissue that transports carbohydrates and amino acids. In recent years, however, it has also been found that this tissue serves as a conduit for signals, e.g., mRNAs, small RNAs, proteins, small peptides, and hormones. Several classical studies have shown that certain…

