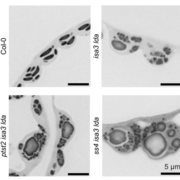
You’ve gotta starch somewhere: Evidence for an alternative starch granule initiation pathway
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants, and in Arabidopsis leaves it forms granules in the chloroplasts to supply energy during the night when photosynthesis is inactive. These semicrystalline granules are made of glucose chains, which can be mostly unbranched (amylose) or highly branched…
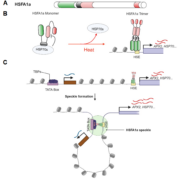
Prion-like domains of sensory HSFs remember heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe heat shock response, a rapid transcriptional response to heat, was first observed nearly 60 years ago, and has long been a paradigm for understanding gene responses to exogenous cues. The family of genes encoding heat shock factors (HSFs) is greatly expanded in plants. These HSFs serve as key regulators…

How a model C4 plant, Setaria viridis, copes with prolonged heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyDue to anthropomorphic global warming, 2024 was the first year during which the global mean temperature was more than 1.5° above pre-industrial levels. Clearly, understanding how high temperatures affect plant physiology is an urgent priority. In this new study, Zhang et al. did a multi-parameter study…
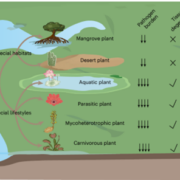
Streamlining the immune system: How plants adapt to reduced pathogen pressure
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough plants are sessile organisms unable to escape pathogen invasions, they are well equipped with defense mechanisms. Cell surface-localized pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) detect extracellular signals and initiate pattern-triggered immunity (PTI), while nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat…
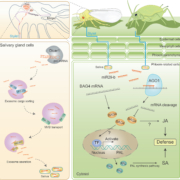
Double attack! Herbivore insects feed on plants and silence their genes
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the natural environment, plants are constantly attacked by animals. Plant immunity is regulated by a network of genes and hormones including salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA). A recent study suggests that herbivore insects threaten plants with concerns more than the bite. Han et al., found…

Plant Science Research Weekly: February 7, 2025
WWR Full PostReview: Genetic engineering for carbon assimilation in plants
Rubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme for photosynthesis, This enzyme poorly discriminates between CO2 and O2, which limits its efficiency. To work around this and make carbon assimilation…
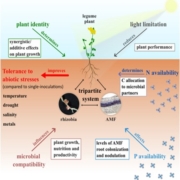
Review. Unraveling plant-microbe interaction dynamics: Insights from the Tripartite Symbiosis Model
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants naturally interact with a diverse array of microorganisms, which influence their fitness in various ways. However, understanding these plant-microbe interactions and applying the knowledge in real-world agricultural systems has been challenging. Most experimental research focuses on bipartite…
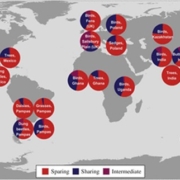
Review: High-yield farming is essential to slow biodiversity loss
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s 2025, and although we live in a world saturated with information, is increasingly difficult to sort fact from propaganda or fiction. This is true in all arenas, including plant science. Calls for strategies to improve crop yields are sometimes met with criticisms that higher yielding crops would…

Capsella rubella: My Fruity Valentine
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyMost shapes in plant organs are pre-determined at the primordial stage and from this point, growth will establish and maintain this shape. Rarely will re-shaping of an organ occur post-organogenesis. However, Hu et al. describe a notable exception in Capsella rubella, a close relative of Arabidopsis…

