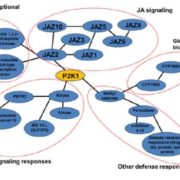
Extracellular ATP Boosts Plant Immunity Via Jasmonate Signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogDamage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are endogenous chemicals that are released from damaged cells and which play a role as “danger signals.”
Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) becomes a DAMP signal after release into the extracellular milieu following cellular damage. Extracellular ATP…
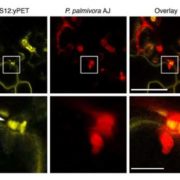
LYS12 LysM receptor decelerates Phytophthora palmivora disease progression in Lotus japonicus
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt might sound odd, but so far it was hard to find a nice pathogen infecting model legume plants. Fuechtbauer and colleagues showed the capacity of an oomycete (Phytophtora palmivora) to infect Lotus japonicus and describe how a LysM receptor, LYS12, is partly mediating this plant-microbe interaction.…
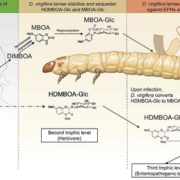
Sequestration and activation of plant toxins protect the western corn rootworm from enemies at multiple trophic levels
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants are attacked by diverse herbivores but have also evolved strategies to resist them. However, highly adapted herbivores exist, including those that have evolved the ability to stabilize, sequester and reactivate plant toxins. This evolved trait has contributed to herbivore defense against higher…
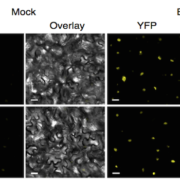
Dual impact of elevated temperature on plant defense and bacterial virulence in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHuot et al. describe how elevated temperature (30 °C) enhances Arabidopsis thaliana disease susceptibility to the bacteria Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000): this includes an increase of bacterial type III secretion suggesting that increased Pst DC3000 virulence at 30°C is linked…

Different gene expression patterns in Arabidopsis grown under different densities
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWhen grown at high density (HD), plants compete for nutrients, water and light. Guo and collaborators characterized Arabidopsis gene expression under two different growth densities: seeds sown at low density (LD), 10 cm apart and high density (HD), 2 cm apart. RNA sequencing analysis showed that only…

VERNALIZATION1 modulates root system architecture in wheat and barley
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog
Root angle determines the rooting depth and was recently associated with the VERNALIZATION1 locus. Using hexaploid wheat, Voss-Fels et al. mapped the root angle to the locus encoding the MADS-box transcription factor, which was previously associated with flowering time. The group found that the lines…
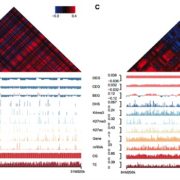
Arabidopsis and crop plants differ in their 3D genome architecture ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThree-dimensional organization of the genome is critical for proper gene expression. Comparison of the extremely compact genome of Arabidopsis with mammalian genomes revealed reduced local intra-chromosomal contacts (also know as Topologically Associated Domains, TADs) and fewer chromatin loops in the…
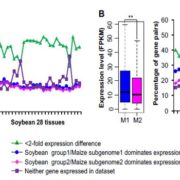
Patterns and consequences of subgenome differentiation provide insights into the nature of paleopolyploidy in plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany plants are polyploid, meaning that instead of the normal, diploid “2n” complement of chromosomes (one from each parent), they have more than 2n. Following whole-genome duplication, redundancy can allow the duplicated regions to diverge or become silenced. In some cases, silencing occurs preferentially…

Increasing leaf vein density in rice results in an enhanced rate of photosynthesis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIncreased leaf vein density is considered to be a key early step in the evolution of C4 photosynthesis. Feldman et al. analyzed five mutants with high vein densities in the C3 crop rice to determine if photosynthetic assimilation was improved. The mutants all had higher photosynthetic rates under…

