
A Peptide Hormone Receptor Controls Seed Size and Yield
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideLeucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLK) are one of the largest gene families in plants. Research over the past decade has implicated LRR-RLKs and their selective interactions with secreted peptide hormones in a myriad of developmental processes. A conserved LRR-RLK with a burgeoning list…
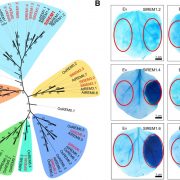
Remorin and Plant Death
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideProgrammed cell death (PCD) in plants is closely associated with a wide variety of biological processes, including cell differentiation, aleurone layer formation, tapetum degradation, leaf and fruit resistance, pathogen invasion and abiotic stresses. Plant PCD is a complex genetically programmed mechanism,…

Roots, Bacteria, Ethylene, and Rhizosheath Formation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe rhizosheath, the sticky part of the rhizosphere, is the layer of soil that adheres to roots upon excavation of the root system. The stickiness of the layer arises from mucilage and other substances secreted by roots, soil microbes or both. Rhizosheaths preferentially form in drier soil and are…

Durotropic Growth of Pollen Tubes
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUpon germination, the vegetative pollen cell forms a long tubular protrusion, the pollen tube, which rapidly elongates through the pistil and transports the enclosed immobile sperm cells toward the egg and the central cell for double fertilization. To reach the female gametophyte, growing pollen tubes…
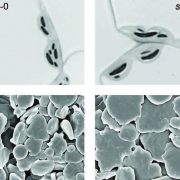
Secret Talents: STARCH SYNTHASE 5—Not an Enzyme, but Very Active!
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAbt et al. found that Arabidopsis SS5, a protein homologous to typical starch-synthesizing enzymes, is itself enzymatically inactive, but rather has an important role in the starch granule initiation process. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00946
By Melanie R. Abt and Samuel C. Zeeman, Institute…

Review Single-cell genomics and epigenomics: Technologies and applications in plants ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants (embryophytes) are by definition multicellular, but we seek to understand them as the sum of the activities of individual cells. Much of this knowledge rests on information obtained through grinding up tissues made up from several cell types. This review by Luo et al. describes methods for plant…
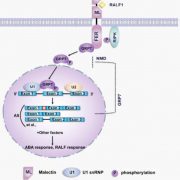
RALF1-FERONIA complex affects splicing dynamics to modulate stress responses and growth in plants (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlternative splicing is a process that can produce two or more transcript isoforms from a single gene and can increase protein diversity. FERONIA (FER) is a receptor-like kinase that serves as a receptor for the rapid alkalinization factor (RALF) peptides that regulate multiple cellular activities in…

Divide to heal: auxin regulates wound-induced cell division in roots (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmong the stresses that sessile plants face, wounding is peculiar as it can be caused by both biotic and abiotic sources. While studies of wounding in animal systems have largely focused on the repair mechanisms, less is known about wound healing in plants. In an attempt to throw light on this, Hoermayer…
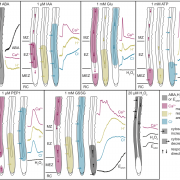
Dual-sensing genetically encoded fluorescent indicators, ABA and second messenger dynamics (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponses to a changing environment require an interplay between primary and secondary messengers. Hormones like abscisic acid (ABA), auxin etc. act as a primary messengers, whereas molecules like Ca2+, reactive oxygen species (ROS), other cations and anions act as a secondary messenger. In this paper,…

