
A feedforward loop controls vascular regeneration and tissue repair through local auxin biosynthesis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant cells are entrapped in rigid cell walls, so morphogenesis relies on asymmetric cell division (ACD) and positional cues to regulate tissue patterning. The Arabidopsis phloem is a good system to study tissue patterning due to its relatively simple composition: sieve elements (SEs) and companion cells…
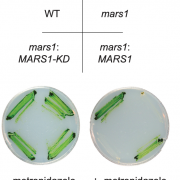
Mars1 kinase signaling in the chloroplast unfolded protein response (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn stressful situations, such as high light and nutrient scarcity, the chloroplast may experience increased proteotoxicity due to a surge in damaging reactive oxygen species. In response, a signal is sent to the nucleus to increase production of many proteins, including proteases and chaperones to help…

The cis-regulatory codes of response to combined heat and drought stress (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs sessile organisms, plants must not only respond to a single stress, but multiple stresses at the same time. To understand the DNA regulatory elements that mediate the transcriptional response to heat, drought and combined heat and drought stress, Azodi et al. utilized the known transcription factor…
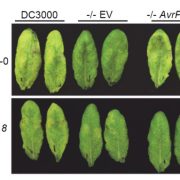
A plant kinase exploited by a bacterial effector (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved a suite of effector proteins that are secreted into plants and aid successful colonization. AvrPtoB is a well-conserved effector of pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae strains that targets multiple plant defense-related proteins and is required for pathogen virulence and bacterial…
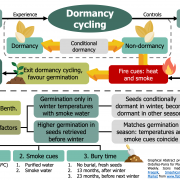
Evidence for physiological seed dormancy cycling in the woody shrub Asterolasia buxifolia and its ecological significance in fire‐prone systems ($) (Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhysiologically dormant seeds shift between dormancy (i.e., unable to germinate), conditional dormancy (i.e., germination restricted to a narrow set of conditions), and non-dormancy (i.e., germination under a wide range of conditions) in response to environmental changes. This mechanism –known as dormancy…

Plant Science Research Weekly: March 27
WWR Full PostReview. Signalling pathways underlying nitrogen-dependent changes in root system architecture: from model to crop species
Nitrogen (N) is one of the seventeen essential nutrients for a plant to complete its life cycle and is one of the most important determinants of productivity of various crops globally.…
Phosphorus sensing in Chlamydomonas by TORC1 subunit LST8
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCouso et al. developed a TOR kinase assay for Chlamydomonas and show how subunit LST8 senses phosphorus availability and modulates cell growth. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00179
By I. Couso, M.E. Pérez-Pérez, M.M. Ford, E. Martínez-Force, L.M. Hicks, J.G. Umen, and J.L. Crespo.
Background:…
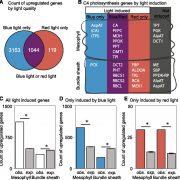
Cell-Specific Light Response in C4 Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn C4 species, the expression of photosynthesis genes is partitioned such that leaf mesophyll and bundle sheath cells accumulate different components of the photosynthetic pathway. The expression of nucleus-encoded photosynthesis genes is modulated both by photoreceptor activity and by a network of…
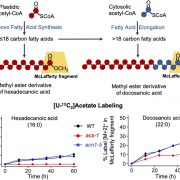
The Fate of Acetate During Hypoxia
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideUnder hypoxia, Acetyl-CoA Synthetase (ACS), an enzyme that synthesizes acetyl CoA, recovers carbon that would otherwise be lost from the plant as ethanol. Plastid-localized ACS metabolizes cellular acetate and contributes to the de novo biosynthesis of fatty acids and Leu. On the other hand, a peroxisome-localized…

