
PIF4 plays a conserved role in Solanum lycopersicum
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchScott Hayes, [email protected]
The adoption of Arabidopsis thaliana as a model plant in the early 1980s led to a revolution in plant molecular genetics. Its diminutive size, rapid generation time and small genome made Arabidopsis a fantastic tool, allowing us to build a complex picture of the genetic…
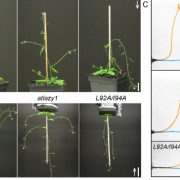
Switching the direction of stem gravitropism by altering two amino acids in AtLAZY1 (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a fascinating twist to the gravitropism story, Yoshihara and Spalding have managed to make a plant with shoots that don’t ignore gravity, but actually respond in the entirely inappropriate away. The LAZY genes were first identified from a rice mutant with a decreased response to gravity. In Arabidopsis…
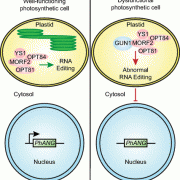
Research update: GUN1 hit the mark in 2019
Plant Science Research Weekly
Chloroplasts are able to sense and respond to environmental signals. They send retrograde signals that inform the nucleus about their developmental stage and integrity. In response, the nucleus adjusts gene expression to optimize chloroplast recovery and adaptation. Back in 1993, a screen for genotypes…
Plant Science Research Weekly: December 13
Blog, WWR Full PostThis week we start with a short summary contributed by Charlotte Gommers hghlighting several papers published in 2019 that revealed new insights into an enigmatic plant gene, GUN1.
Research update: GUN1 hit the mark in 2019
Chloroplasts are able to sense and respond to environmental signals. They…
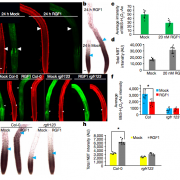
RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signaling (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStem cells are maintained in the stem-cell niche by intercellular interactions and signaling networks in which a peptide hormone, the root meristem growth factor 1 (RGF1), is involved. RGF1 is also important in the control of the size of the meristematic zone and in the stability of the PLETHORA (PLT)…

CSN5 of COP9 signalosome modulates heat-response of Arabidopsis (biomolecules)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCOP9 signalosome (CSN) is a conserved multi-subunit complex in higher eukaryotes that was originally identified as a regulator of plant photomorphogenesis. It functions by regulating ubiquitin-mediated protein stability, through the deneddylase enzymatic acitivity of the CSN5 subunit. CSN5 is encoded…
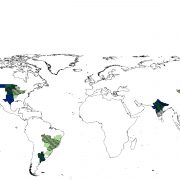
Increasing risks of multiple breadbasket failure under 1.5 and 2 °C global warming (Ag Systems)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop yields are vulnerable to rising temperatures and changes in precipitation. Here, Gaupp et al. model the projected crop yields at 1.5 versus 2.0 degrees of additional warming, as part of the HAPPI experiment (perhaps a misnomer: Half a degree Additional warming, Prognosis and Projected Impacts).…
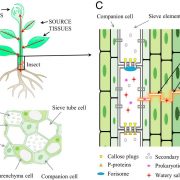
Perspective: Challenging battles of plants with phloem-feeding insects and prokaryotic pathogens (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of plant defense response is built upon the responses that occur in leaves. Many pathogens colonize the phloem system, which is both nutrient-rich and provides an easy conduit for spreading through systemically through the plant body. These phloem-inhabiting prokaryotic pathogens…

Unraveling cis and trans regulatory evolution during cotton domestication (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPolyploidization leads to a myriad of changes in gene expression and organization of genomes and can supply the material for speciation, adaptation, and morphological innovation. The most cultivated cotton species, Gossypium hirsutum, is an allotetraploid species (AD genome) containing two subgenomes…

