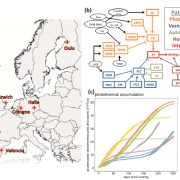
Large-effect flowering time mutations reveal conditionally adaptive paths through fitness landscapes in Arabidopsis thaliana (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have a tendency to think of genes carrying mutations as having a negative impact on fitness, which raises the question of why they might persist in a population. Taylor et al. tested whether large-effect mutations that affect flowering time might not be detrimental in all conditions, by comparing…

Increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduces global vegetation growth (Science Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant scientists know that when the air at the leaf surface is dry, the plant will tend to close its stomata, but we tend to think of this as a relatively localized effect. Yuan et al. have explored the global trends in vapor pressure deficit (VPD; difference between saturated and real water content…

Plant Science Research Weekly: August 30th
Blog, WWR Full PostA modular cloning toolkit for genome editing in plants
Genome editing with the CRISPR/Cas system is now widely used in functional studies across biological sciences including plant biology. Typically, this system involves a DNA nuclease and a guide RNA that directs the nuclease to a specific location…
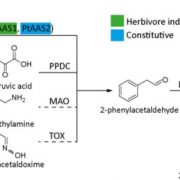
Do all roads lead to 2-phenylethanol in Populus?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchPlants emit scented volatile compounds to attract pollinators, or alternatively, as direct or indirect plant defense mechanisms. Direct defense involves compounds that are toxic, whereas an indirect defense uses volatiles to attract parasitoids of insect herbivores (Unsicker et al., 2009; Maag et al.,…

Turnip Mosaic Virus is Released into Extracellular Space
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTurnip Mosaic Virus (TuMV) is a +RNA virus that belongs to the order Picornavirales. +RNA viruses reorganize the endomembrane system to generate quasi-organelle structures called “viral factories”. In the case of TuMV, these factories are motile vesicles of ~100 nm in diameter that contain the TuMV…

Regulation of Imprinting in Arabidopsis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe seeds of flowering plants consist of three genetically distinct components: the diploid embryo with one genome copy from each of the parents, the triploid endosperm with two maternal copies and one paternal copy, and the seed coat having the same genotype as the diploid mother plant. Balanced parental…

Salicylic Acid Influences Root Meristem Patterning at Low Concentrations
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideHigh exogenous concentrations (>50 µM) of salicylic acid (SA) stimulate systemic acquired resistance (SAR), a vitally important adaptive immunity response that protects against a broad spectrum of pathogens. The transcription of PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENE 1 (PR1) is rapidly induced in leaves upon…

The Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll in Leaves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe biochemistry of photosynthesis and biophysical processes that constrain it are intrinsically linked within the landscape of the inner leaf. Because leaf tissue is heterogeneous in structure as well as photosynthetic capacity, it follows that chlorophyll may also be spatially heterogeneous. Yet, while…

Domestication Affected Root System Architecture in Common Bean
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideComparative analyses of wild and domesticated accessions have previously identified several aboveground domestication-related traits in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Genetic analyses of these traits suggested the presence of several major quantitative trait loci (QTLs) with large effects. However,…

