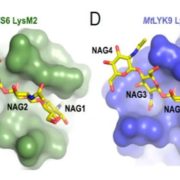
Receptor-mediated chitin perception in legume roots is functionally separable from Nod factor perception ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSmall molecules are crucial for the recognition of friends and foes. For example, Nod factors are N-acetylglucosamine-derived “friend” signals produced by bacterial microsymbionts. Chitin is an N-acetylglucosamine-derived fungal wall polymer that plants perceive as indicating the presence of an enemy. …
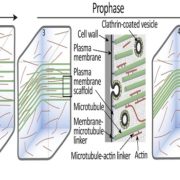
Opinion: Plant cytokinesis: Terminology for structures and processes
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCell division in plants is a structurally beautiful process that involves striking and dynamic changes in the cytoskeleton, endomembranes, and nucleus. However, as authors Smertenko et al. observe, “Current plant cytokinesis terminology was developed using data generated by fluorescence microscopy…

A pair of papers that redefines the pyrenoid, the eukaryotic CO2-concentrating organelle
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPhotosynthesis in aquatic organisms is made difficult due to the low solubility of CO2 in water. Algae such as Chlamydomonas rheinhardtii overcome this limitation through a carbon-concentrating organelle called a pyrenoid. Two papers in Cell redefine our understanding of the pyrenoid structure. Mackinder…
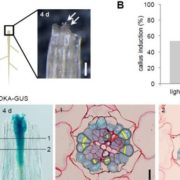
Wounding triggers callus formation via dynamic hormonal and transcriptional changes
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants are known for their ability to regenerate tissues following wounding. Wound repair requires the induction of cell proliferation, leading to the formation of undifferentiated callus at the wound site, followed by cell differentiation. Ikeuchi et al. explored transcriptional changes following wounding…
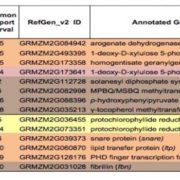
Novel loci underlie natural variation in vitamin E levels in maize grain
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogVitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and related tocochromanol compounds) is a lipid-soluble antioxidant that contributes to numerous cellular activities and confers protection against many diseases, from cancer to cardiovascular disease. The main sources of vitamin E for humans are plant oils, but most crop…

Increasing atmospheric humidity and CO2 concentration alleviate forest mortality risk
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogLiu et al. used models to predict the effects of climate change on tree mortality in 13 temperate and tropical forest biomes across the globe. When only increased temperature and changes in precipitation are considered, mortality increases in most biomes, with higher emissions models leading to increased…
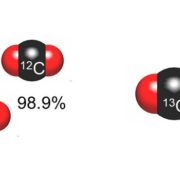
Atmospheric evidence for a global secular increase in carbon isotopic discrimination of land photosynthesis ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCarbon exist in two stable isotopic forms; 99% as 12C and 1% as 13C. The carbon-fixing enzyme Rubisco preferentially fixes 12C, so fossil fuels are enriched for 12C, and since the industrial revolution the atmospheric 13C / 12C ratio has been increasing as the 12C-enriched fossil fuels are reconverted…
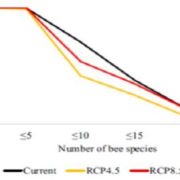
Coupling of pollination services and coffee suitability under climate change
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWith changing climate, crops may need to be relocated to new regions for optimal growth temperatures or precipitation, but temperature and rainfall are not the sole influencers of productivity. Many crops, including coffee, depend on pollinators, which may or may not be available in other regions. Imbach…
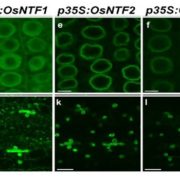
Nuclear transcriptomes at high resolution using retooled INTACT
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogReynoso et al. describe the Isolation of Nuclei from TAgged specific Cell Types (INTACT) in rice. In this method, modified from one described previously in Arabidopsis and tomato, nuclei are labeled with a biotinylated nuclear-envelope anchored protein. Best results were obtained when a rice WIP (WPP-Interacting…

