THE PLANT CELL – TOP ARTICLES OF 2020 based on Altmetric scores
The Plant Cell is pleased to announce our Top 5 of 2020 articles based on Altmetric scores. Altmetrics are metrics and qualitative data that are complementary to traditional, citation-based metrics. They can include (but are not limited to) peer reviews on Faculty Opinions, citations on Wikipedia and in public policy documents, discussions on research blogs, mainstream media coverage, bookmarks on reference managers like Mendeley, and mentions on social networks such as Twitter.
 #1 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
#1 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
Modifying Plant Photosynthesis and Growth via Simultaneous Chloroplast Transformation of Rubisco Large and Small Subunits
 In our September 2020 issue, authors Elena Martin-Avila (The Australian National University), Yi-Leen Lim (The Australian National University), Rosemary Birch (The Australian National University), Lynnette M.A. Dirk (University of Kentucky), Sally Buck (The Australian National University), Timothy Rhodes (The Australian National University), Robert E. Sharwood (The Australian National University), Maxim V. Kapralov (Newcastle University) and Spencer M. Whitney (The Australian National University) show that erasing Rubisco small subunit nuclear synthesis in tobacco provides a new plant chassis for investigating novel Rubisco complexes in a whole plant context via chloroplast transformation of both its large and small subunits in their article: “Modifying Plant Photosynthesis and Growth via Simultaneous Chloroplast Transformation of Rubisco Large and Small Subunits” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00288
In our September 2020 issue, authors Elena Martin-Avila (The Australian National University), Yi-Leen Lim (The Australian National University), Rosemary Birch (The Australian National University), Lynnette M.A. Dirk (University of Kentucky), Sally Buck (The Australian National University), Timothy Rhodes (The Australian National University), Robert E. Sharwood (The Australian National University), Maxim V. Kapralov (Newcastle University) and Spencer M. Whitney (The Australian National University) show that erasing Rubisco small subunit nuclear synthesis in tobacco provides a new plant chassis for investigating novel Rubisco complexes in a whole plant context via chloroplast transformation of both its large and small subunits in their article: “Modifying Plant Photosynthesis and Growth via Simultaneous Chloroplast Transformation of Rubisco Large and Small Subunits” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00288
 #2 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
#2 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
In Vivo NADH/NAD+ Biosensing Reveals the Dynamics of Cytosolic RedoxMetabolism in Plants
 In our October 2020 issue, authors Janina Steinbeck (Institute of Plant Biology and Biotechnology, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster (IBBP)), Philippe Fuchs (IBBP), Yuri L. Negroni (Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation (INRES) and Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität), Marlene Elsässer (IBBP, INRES and Institute for Cellular and Molecular Botany (IZMB)), Sophie Lichtenauer (IBBP), Yvonne Stockdreher (INRES), Elias Feitosa-Araujo (IBBP and Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV)), Johanna B. Kroll (IBBP), Jan-Ole Niemeier (Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität), Christoph Humberg (IBBP), Edward N. Smith (University of Oxford), Marie Mai (Zentrum für Human- und Molekularbiologie (ZHMB)), Adriano Nunes-Nesi (UFV), Andreas J. Meyer (INRES), Michela Zottini (University of Padova), Bruce Morgan (ZHMB), Stephan Wagner (IBBP and INRES) and Markus Schwarzländer (IBBP) show that a fluorescent protein-based biosensing approach allows live monitoring of the tissue heterogeneity and temporal changes of cytosolic NAD redox metabolism in response to environmental changes in their article: “In Vivo NADH/NAD+ Biosensing Reveals the Dynamics of Cytosolic Redox Metabolism in Plants” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00241
In our October 2020 issue, authors Janina Steinbeck (Institute of Plant Biology and Biotechnology, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster (IBBP)), Philippe Fuchs (IBBP), Yuri L. Negroni (Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation (INRES) and Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität), Marlene Elsässer (IBBP, INRES and Institute for Cellular and Molecular Botany (IZMB)), Sophie Lichtenauer (IBBP), Yvonne Stockdreher (INRES), Elias Feitosa-Araujo (IBBP and Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV)), Johanna B. Kroll (IBBP), Jan-Ole Niemeier (Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität), Christoph Humberg (IBBP), Edward N. Smith (University of Oxford), Marie Mai (Zentrum für Human- und Molekularbiologie (ZHMB)), Adriano Nunes-Nesi (UFV), Andreas J. Meyer (INRES), Michela Zottini (University of Padova), Bruce Morgan (ZHMB), Stephan Wagner (IBBP and INRES) and Markus Schwarzländer (IBBP) show that a fluorescent protein-based biosensing approach allows live monitoring of the tissue heterogeneity and temporal changes of cytosolic NAD redox metabolism in response to environmental changes in their article: “In Vivo NADH/NAD+ Biosensing Reveals the Dynamics of Cytosolic Redox Metabolism in Plants” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00241
 #3 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
#3 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
Alternative Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Modes Provide Environment-Specific Water-Saving Benefits in a Leaf Metabolic Model
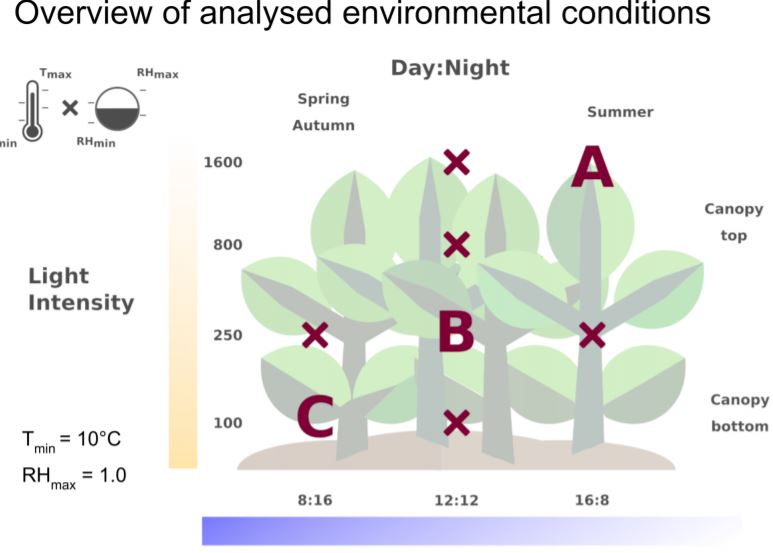 In our December 2020 issue, authors Nadine Töpfer (Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research and University of Oxford), Thomas Braam (University of Oxford), Sanu Shameer (University of Oxford), R. George Ratcliffe (University of Oxford), and Lee J. Sweetlove (University of Oxford) show stoichiometric modelling of leaf metabolism reveals metabolic and morphological determinants for introducing Crassulacean acid metabolism and alternative water-saving flux modes into a C3 leaf in different environments in their article: “Alternative Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Modes Provide Environment-Specific Water-Saving Benefits in a Leaf Metabolic Model” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00132
In our December 2020 issue, authors Nadine Töpfer (Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research and University of Oxford), Thomas Braam (University of Oxford), Sanu Shameer (University of Oxford), R. George Ratcliffe (University of Oxford), and Lee J. Sweetlove (University of Oxford) show stoichiometric modelling of leaf metabolism reveals metabolic and morphological determinants for introducing Crassulacean acid metabolism and alternative water-saving flux modes into a C3 leaf in different environments in their article: “Alternative Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Modes Provide Environment-Specific Water-Saving Benefits in a Leaf Metabolic Model” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00132
 #4 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
#4 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
One C-to-U RNA Editing Site and Two Independently Evolved Editing Factors: Testing Reciprocal Complementation with DYW-Type PPR Proteins from the Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens and the Flowering Plants Macadamia integrifolia and Arabidopsis
 In our September 2020 issue, authors Bastian Oldenkott (University of Bonn), Matthias Burger (University of Bonn), Anke-Christiane Hein (University of Bonn), Anja Jörg (University of Bonn), Jennifer Senkler (University of Bonn), Hans-Peter Braun (Leibniz Universität), Volker Knoop (University of Bonn), Mizuki Takenaka (University of Bonn and Kyoto University) and Mareike Schallenberg-Rüdinger (University of Bonn) show that DYW-type PPR proteins independently evolved in mosses and flowering plants restore RNA editing defects across wide phylogenetic distances in their article: “One C-to-U RNA Editing Site and Two Independently Evolved Editing Factors: Testing Reciprocal Complementation with DYW-Type PPR Proteins from the Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens and the Flowering Plants Macadamia integrifolia and Arabidopsis” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00311
In our September 2020 issue, authors Bastian Oldenkott (University of Bonn), Matthias Burger (University of Bonn), Anke-Christiane Hein (University of Bonn), Anja Jörg (University of Bonn), Jennifer Senkler (University of Bonn), Hans-Peter Braun (Leibniz Universität), Volker Knoop (University of Bonn), Mizuki Takenaka (University of Bonn and Kyoto University) and Mareike Schallenberg-Rüdinger (University of Bonn) show that DYW-type PPR proteins independently evolved in mosses and flowering plants restore RNA editing defects across wide phylogenetic distances in their article: “One C-to-U RNA Editing Site and Two Independently Evolved Editing Factors: Testing Reciprocal Complementation with DYW-Type PPR Proteins from the Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens and the Flowering Plants Macadamia integrifolia and Arabidopsis” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00311
 #5 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
#5 The Plant Cell Article of 2020
The Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens: A Model Organism for Non-Seed Plants
 In our May 2020 issue, authors Stefan A. Rensing (Philipps University of Marburg), Bernard Goffinet (University of Connecticut), Rabea Meyberg (Philipps University of Marburg), Shu-Zon Wu (Dartmouth College) and Magdalena Bezanilla (Dartmouth College) show that P. patens is a powerful model non-seed plant that has made fundamental contributions to diverse fields, including evo-devo and cell biology in their article: “The Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens: A Model Organism for Non-Seed Plants” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00828
In our May 2020 issue, authors Stefan A. Rensing (Philipps University of Marburg), Bernard Goffinet (University of Connecticut), Rabea Meyberg (Philipps University of Marburg), Shu-Zon Wu (Dartmouth College) and Magdalena Bezanilla (Dartmouth College) show that P. patens is a powerful model non-seed plant that has made fundamental contributions to diverse fields, including evo-devo and cell biology in their article: “The Moss Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens: A Model Organism for Non-Seed Plants” https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00828








