
Genome-scale fluxome of Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 using transient 13C-labeling data (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySynechococcus elongates UTEX 2973 (also known as Synechococcus 2973) has the fastest doubling time of known cyanobacteria, completely replicating itself in just over two hours. This fast growth rate makes it an interesting platform for industrial applications. Hendry et al set out to understand what…

Opinion: Capsaicinoids: Pungency beyond Capsicum (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyYou probably saw this article being discussed in your favorite news channel (in the UK, coverage spanned from the Daily Mail to the Guardian). In an Opinion article, Naves et al. discuss the genetics, biochemistry, ecology and health-benefits of capsaicinoids (the “heat” in chili pepper), and consider…
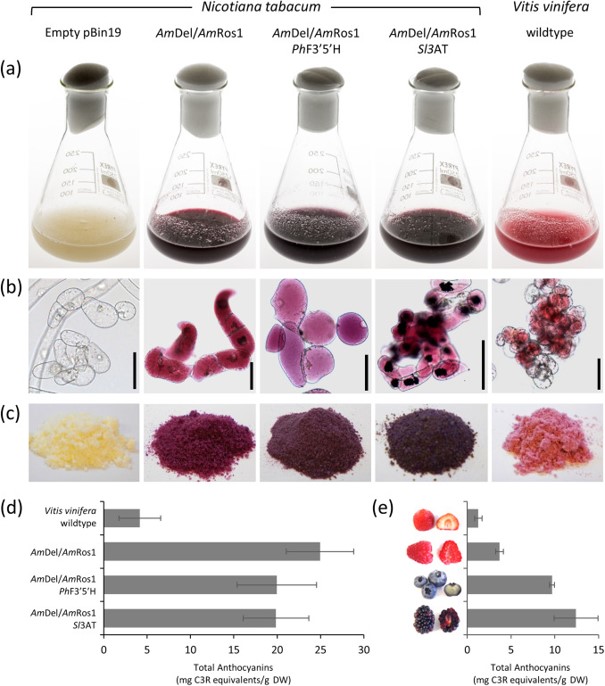

Colour bio-factories: Towards scale-up production of anthocyanins in plant cell cultures (Metabolic Engineering)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAnthocyanins are common plant pigments that provide dietary benefits, leading to an increase in their use as food coloring agents. However, purifying anthocyanins from current plant sources (such as waste grape skins, red cabbage, and berries) is expensive and creates a variable product. Modifying biosynthetic…
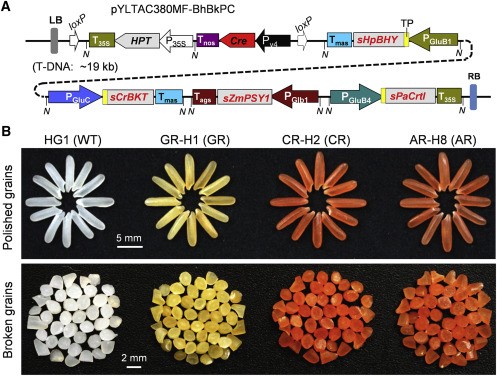
From Golden Rice to aSTARice: Bioengineering astaxanthin biosynthesis in rice endosperm (Molecular Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyZu et al., have successfully harnessed the power of synthetic biology to increase the nutritional content of rice by overexpressing only four synthetic genes in rice endosperm. Here, the authors have created a colorful gradient of carotenoid-enriched rice by expressing two, three, and then four genes…
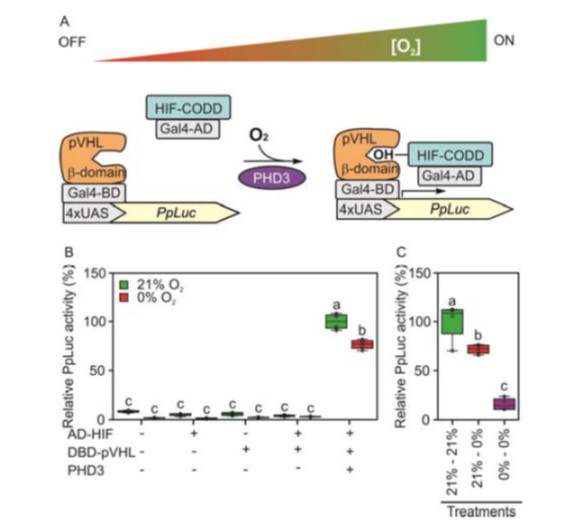
A synthetic oxygen sensing device for plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can die from a lack of oxygen (hypoxia), which contributes to the devastating losses caused by flooding. Iacopino et al. set out to develop a more specific method for detecting oxygen levels in plants, based on the mammalian Hypoxia Inducible transcription Factor HIF. HIF is hydroxylated by…

Plant Synthetic Biology 101
Plantae Webinars, Research, Research Skills, Webinars1 Comment
/
Plant Synthetic Biology 101
Recorded November 2018
About This Webinar
Synthetic biology is an emerging discipline that seeks to apply engineering principles to biology. But what does this actually mean? How does it differ from what has come before? And what challenges are presented by pursuing…
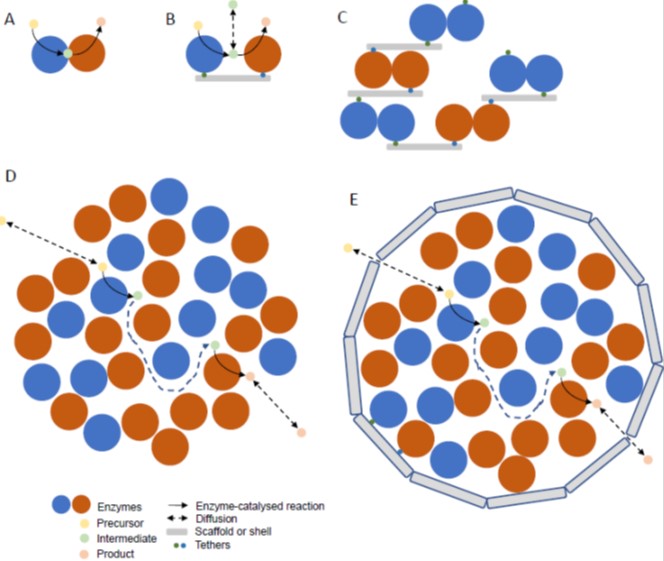
Update: Engineering of metabolic pathways using synthetic enzyme complexes
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Nicholas Smirnoff, University of Exeter. This article is part of the forthcoming Synthetic Biology focus issue.
Plants provide a source of enzymes for metabolic engineering to produce valuable or useful products in micro-organisms or can themselves be engineered (Andre et al., 2016; Vickery et…
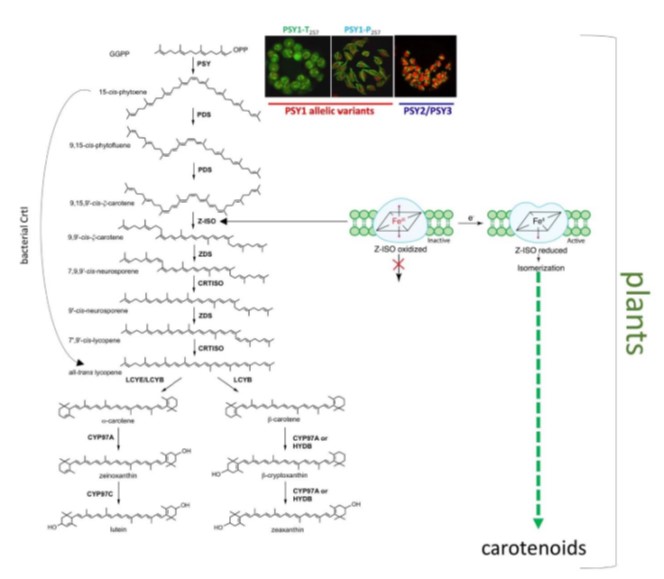
Review: Changing form and function through carotenoids and synthetic biology (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants produce hundreds of carotenoids with functions ranging from photoprotection to signalling, and with important roles in human health as well. Wurtzel describes opportunities arising from applying the tools of synthetic biology to carotenoids. The regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis is complex,…
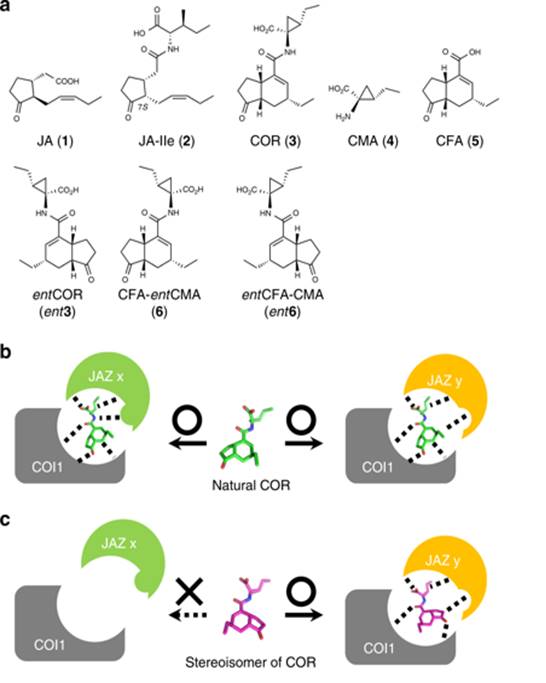
A rationally designed JAZ subtype-selective agonist of jasmonate perception (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany plant hormones have pleiotropic effects, switching on and off multiple, seemingly unrelated processes. As an example, jasmonates both turn on herbivore defense responses and suppress growth. Takaoka et al. have elegantly separated these, by developing a jasmonate mimic that only activates defences.…

