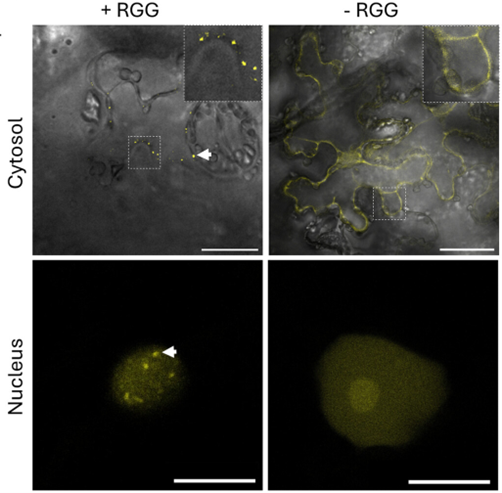
Artificial condensates can boost metabolic engineering
Plant Science Research WeeklyNicotiana benthamiana is widely used to reconstruct complex, multi-step metabolic pathways for research or industrial purposes. This is enabled by rapid and high-level protein expression after agroinfiltration. Within cells, as well as membrane-bound organelles, nonmembrane-bound biomolecular condensates…
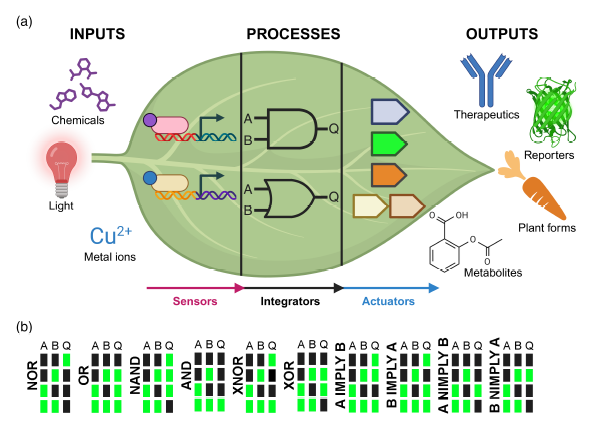
Review. Genetic switchboards: Rewiring plant traits with synthetic circuits
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe expression of a transgene in plants can impose a significant stress, sometimes referred to as metabolic burden. Synthetic gene circuits offer a precise approach to engineering plant traits by regulating gene expression through programmable operations. This review by Lloyd et al. examines the core…

Review: Synthetic algal genomes
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs photosynthetic organisms, algae can harness solar energy to do useful things, from environmental cleanup to producing fuels and other beneficial molecules. This review by Goold et al. provides an overview of how algae can be valuable platforms for synthetic biology and metabolic engineering through…
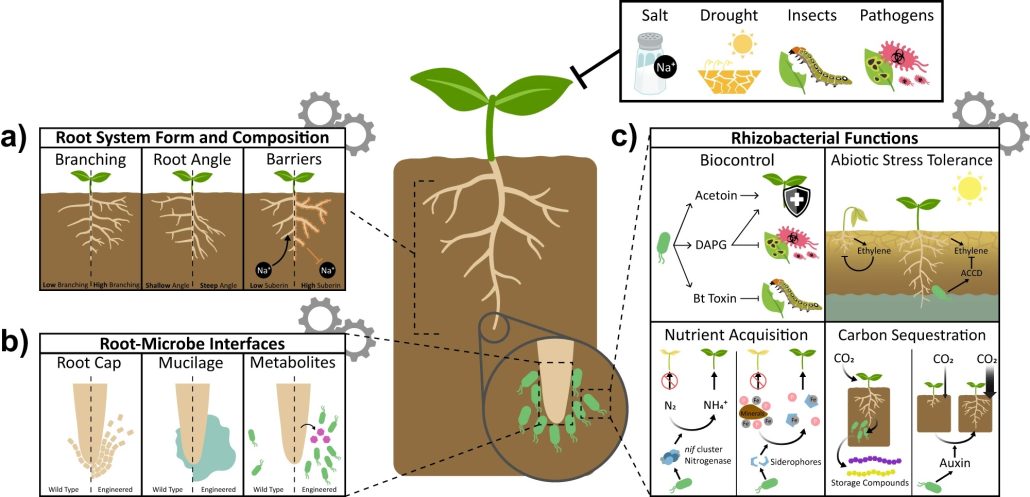
Review: SynBio takes on roots and the rhizosphere
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is an excellent introduction to how synthetic biology can be used to program plants for climate resilience by engineering them to respond predictably and in ways beyond those that evolution has explored, through the use of controllable synthetic gene circuits. Ragland et al. describe how precise…
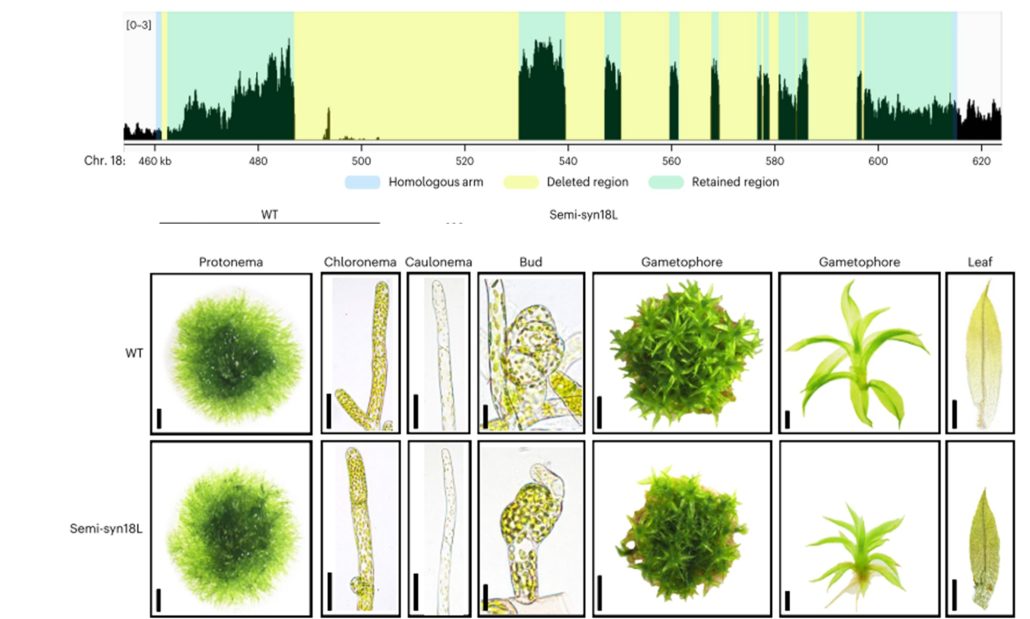
Moss phenotype unaffected by removal of repetitive sequences from genome
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenome complexity in multicellular organisms is often associated with repetitive sequences from Transposable Elements (TEs). TE function, importance for genome integrity, and dispensability have not been completely characterized. In prokaryotes and simple eukaryotes, genome synthesis (production of…
Review: Scripting a new dialogue between diazotrophs and crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyAll organisms need nitrogen to produce nucleic and amino acids, but nitrogen-limitation is common for many plants. Although nitrogen is very abundant in the atmosphere, most is inaccessible due to the triple bond that renders N2 relatively inert. Tremendous crop yields in recent decades are attributable…

Regulated and optimized control of insect pheromone biosynthesis in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyInsect sex pheromones, volatile molecules used to attract mates, are used commercially to disrupt breeding behavior of insect pests and can be a good alternative to harmful pesticides. These pheromones have been produced in plants at a low amount and shown to be released as volatiles, but their production…
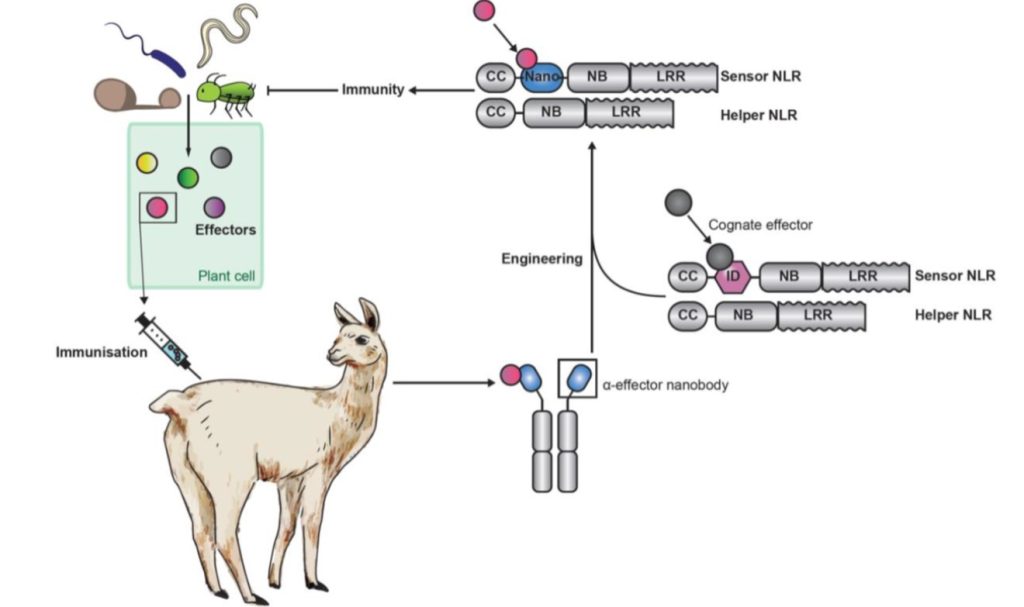
Bioengineered “pikobodies” confer plant disease resistance
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe vertebrate adaptive immune system is truly an evolutionary marvel. With its ability to mix-and-match segments of immunoglobulin genes, a nearly unlimited diversity of antigens can be recognized. Plants lack this ability, greatly limiting the number of antigens (and pathogens) any individual can recognize.…

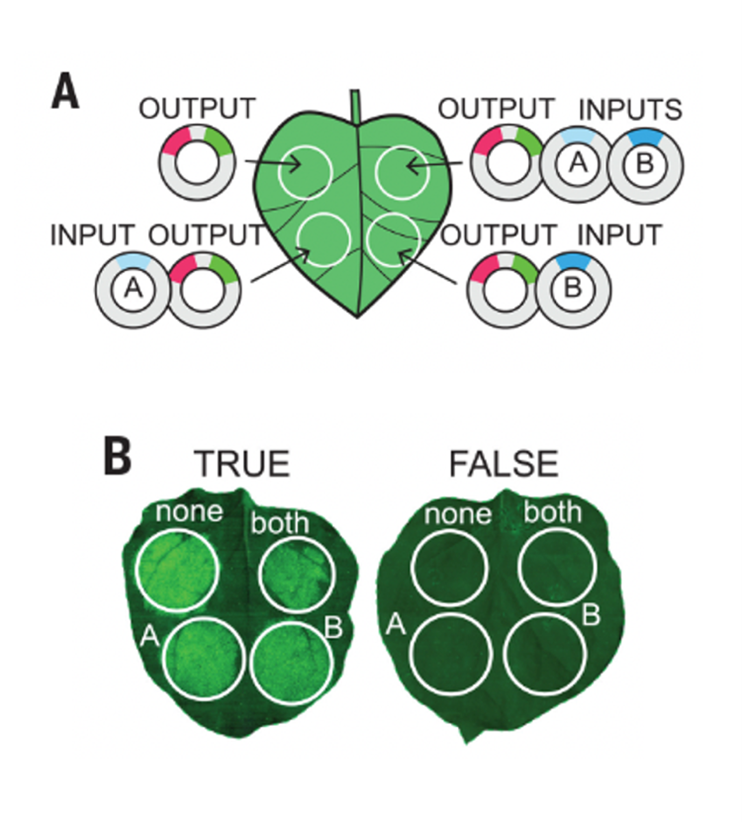
Synthetic genetic circuits as a means of reprogramming plant roots (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklySynthetic genetic circuits offer a promising method to achieve beneficial changes in plant phenotypic traits. By combining different activator or repressor transcription factors (TFs) , the expression of target genes may be fine-tuned according to Boolean operations. Here, Brophy et al. describe a method…

