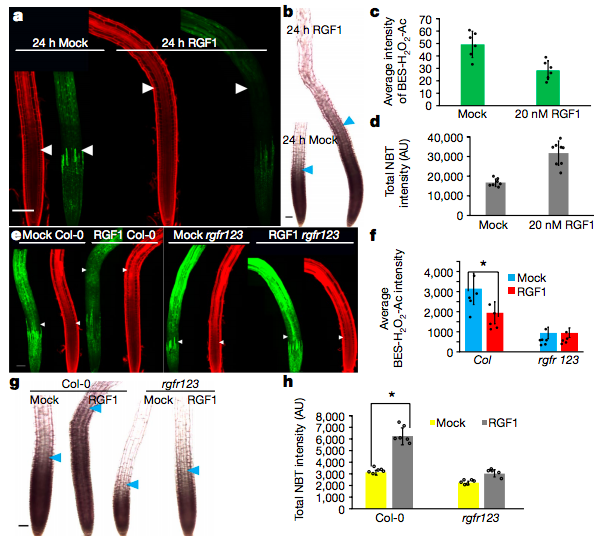
RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signaling (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStem cells are maintained in the stem-cell niche by intercellular interactions and signaling networks in which a peptide hormone, the root meristem growth factor 1 (RGF1), is involved. RGF1 is also important in the control of the size of the meristematic zone and in the stability of the PLETHORA (PLT)…
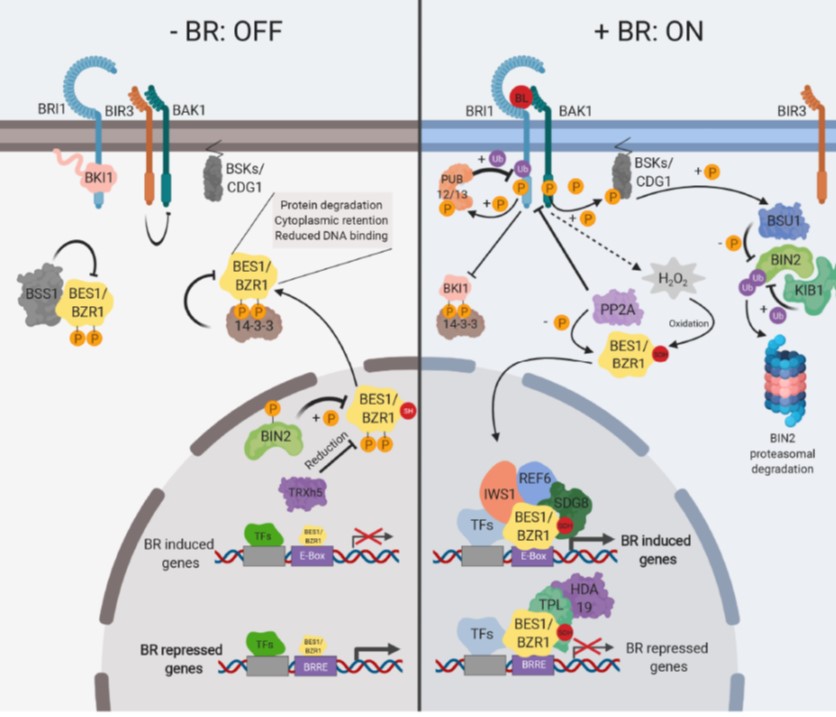
Review. Brassinosteroids: Multi-dimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s been fifty years since the existence of brassinosteroids was shown, and about thirty since the awesome power of Arabidopsis genetics started to reveal the genes involved in its synthesis, perception and signaling. Nolan et al. review the highlights of brassinosteroid research and also more recent…

Review: The role of peptides cleaved from protein precursors in eliciting plant stress reactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough the first signaling peptide identified in plants, systemin, is involved in stress responses, developmentally important peptide signals have largely occupied the limelight. This Tansley Review by Chen et al. summarizes recent insights into peptides with a role in stress responses: wounding, pathogen…

Plant Science Research Weekly: October 18
Blog, WWR Full PostGuest Editor :
Suresh Damodaran
I am a postdoctoral research associate in Dr. Lucia Strader’s lab at WUSTL. My primary area of interest is understanding the role of plant hormones in development. I completed my graduate degree in Dr. Sen Subramanian’s lab at SDSTATE. Twitter: @SureshDamod
Design…

Insect herbivory selects for volatile-mediated plant-plant communication ($) (Current Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in response to insect herbivory. The potential for VOCs to serve as diffusible signals has long been recognized. For example, VOCs can signal neighbors to prime for defense, signal distant parts of the emitting plant, and even attract predatory insects…

A CLE–SUNN module regulates strigolactone content and symbiosis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe symbiosis between plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is conditional. Plants that are limited for phosphate release strigolactones into the soil, promoting changes in the fungi that facilitate the symbiosis. Müller et al. found that a Medicago gene encoding a CLE peptide, MtCLE53, is induced…
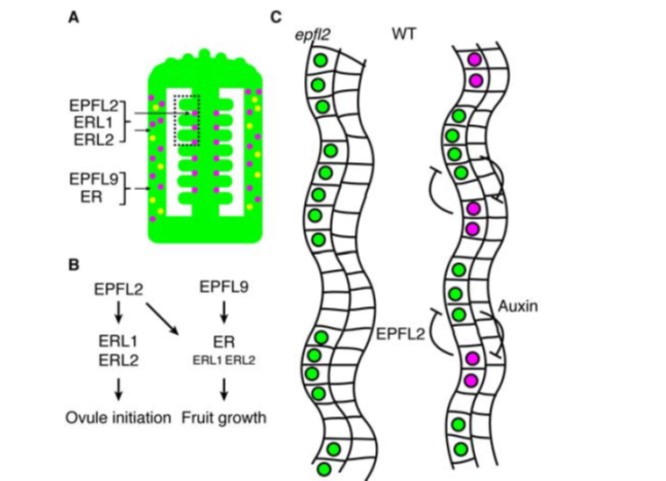
A peptide pair coordinates ovule initiation patterns with seed number and fruit size (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant peptide patterning is popping up everywhere! Now Kawamoto et al. show that a pair of peptides, interacting with receptor proteins, coordinates the placement of ovules in Arabidopsis. They started with a natural variation analysis, which highlighted that several varieties with mutations in the ERECTA…

Review: Structural biology of cell surface receptor–ligand interactions (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn recent months, a flurry of papers have come out that reveal new insights into the structural interactions of cell-surface receptors with each other and with their ligands. This timely review by Moussu and Santiago captures the highlights, in case you haven’t been following along. The review features…
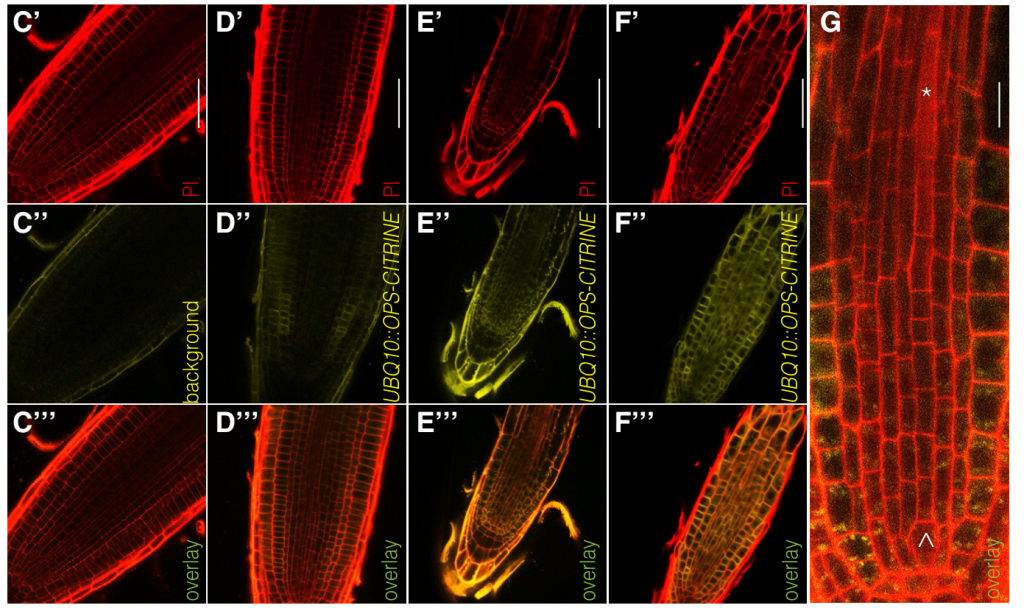
An insulator of CLE-signaling boosts cell-differentiation in protophloem formation
Plant Science Research WeeklyWaddington’s epigenetic landscape, a famous metaphor in developmental biology, depicts how a stem cell progresses from an undifferentiated state to a differentiated one. To some degree this metaphor can also be applied to root cell differentiation. It’s well-known that the CLE-45 peptide and its…

