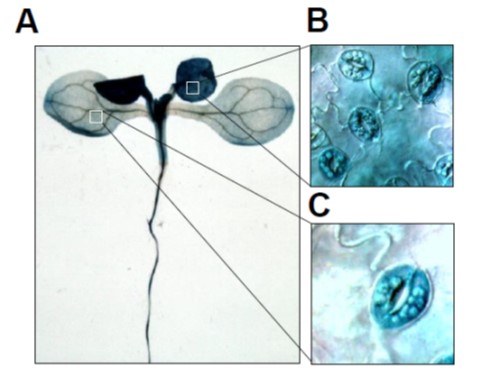
CDL1-OST1 Interaction as a Focal Point of Brassinosteroid-Abscisic Acid Hormone Signaling Crosstalk
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants integrate signals in the form of light, humidity, temperature, CO2 concentrations and daily circadian rhythms. In addition, plants encounter pathogens, pests, herbivores and other stressors. Physiological processes like responding to stimuli, plant growth and development are usually governed and…
NO2 Enhances Pathogen Resistance
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideNitrogen dioxide (NO2) forms in plants under stress conditions, but little is known about its
physiological functions. Using a variety of techniques, Mayer et al. (10.1104/pp.18.00704) have examined the effects of fumigating Arabidopsis with 10 ppm NO2 for 1 h, a treatment that does not cause
visible…
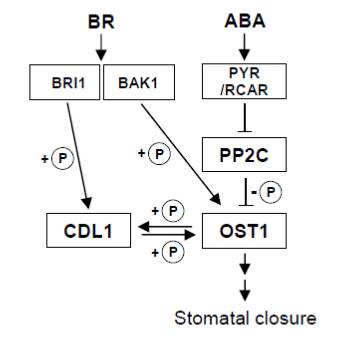
OST1 activation by the brassinosteroid-regulated kinase CDG1-Like 1 in stomatal closure ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs gatekeepers between the outside world and the interior of the leaf, guard cells are extraordinarily sensitive to their environment. Closing keeps out pathogens and keeps in water vapor, but opening is needed to admit CO2. The web of interactions that control stomatal aperture are also correspondingly…
Roles of N-terminal acetylation and N-terminal acetyltransferases in plants (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN-terminal acetylation is a common protein modification completed by ribosome-associated N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs) or plastid-localized NATs. The recent discovery of the plastid-localized NATs upended the traditional model of static, co-translational imprinting of the plant proteome. These…
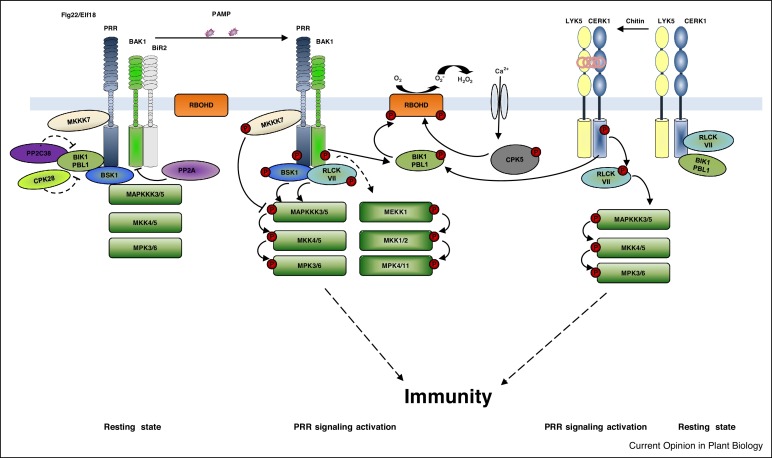
Review: Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling by phosphorylation and ubiquitination (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA key step in pathogen recognition occurs at the cell surface with the interaction between receptor-like kinases (pattern-recognition receptors) and their ligands. This event triggers a signal-transduction cascade that leads to the induction of defense responses. Mithoe and Menke review our current understanding…
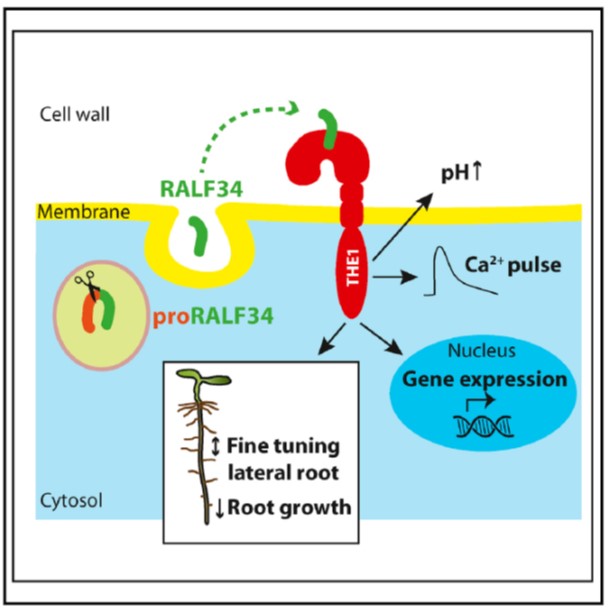
Receptor kinase THESEUS1 is a RALF 34 receptor with roles in lateral root development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRALF peptides were identified nearly 20 years ago, as small peptides that induce rapid alkalinisation of the culture medium when added to cell suspension cultures. Previously, members of the receptor-like kinase (RLK) family including FERONIA (FER) have been identified as RALF receptors. A related…

Role of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Self-Incompatibility
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellChen et.al. demonstrate that phosphatidic acid mitigates S-RNase signaling in pollen by stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton. Plant Cell (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00021
By Jianqing Chen, Peng Wang, Shaoling Zhang, and Juyou Wu
Background: The success of sexual reproduction in flowering…
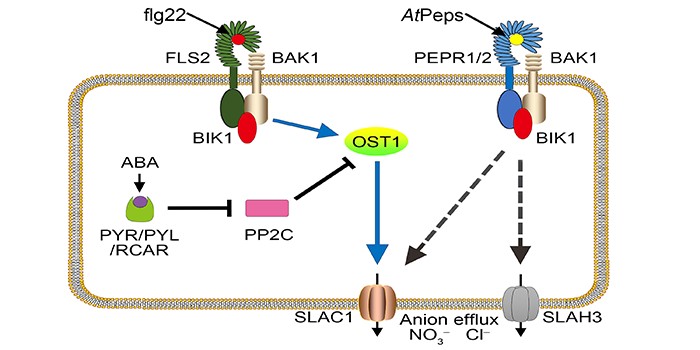
All Roads Lead to Rome: Multiple Pathways Close Stomata in Plant Defense
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZheng et al. reveal that plant endogenous peptides and their receptors initiate stomatal closure to prevent microbes’ entry, thus enhancing plant immunity. The Plant Cell (2018) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00701.
By Xiaojiang Zheng and Sheng Luan.
Background: Unlike animals, plants can’t…
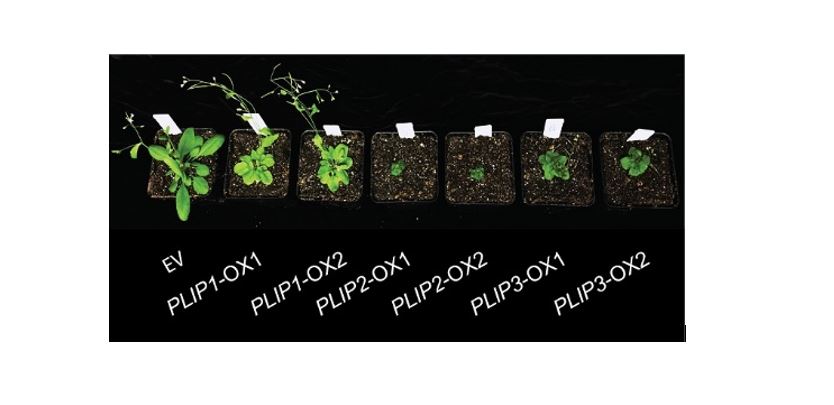

When Lipids Meet Hormones: Plants’ Answer to Complex Stresses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. show that abscisic acid-inducible genes encode lipid degrading enzymes that release polyunsaturated fatty acids from chloroplast lipids as precursors for jasmonic acid production leading to biotic defenses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00250
By Kun Wang and Igor Houwat
Background:…

