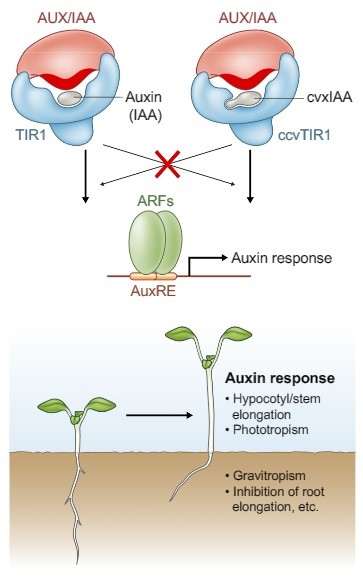
Review: Harnessing synthetic chemistry to probe and hijack auxin signaling (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin has been studied since Charles Darwin observed the phototropic response. More recently, chemical genetic approaches using auxin agonists and antagonists have been applied to studies of auxin. Torii et al. review how synthetic chemistry and chemical genetics have provided insights into and new tools…
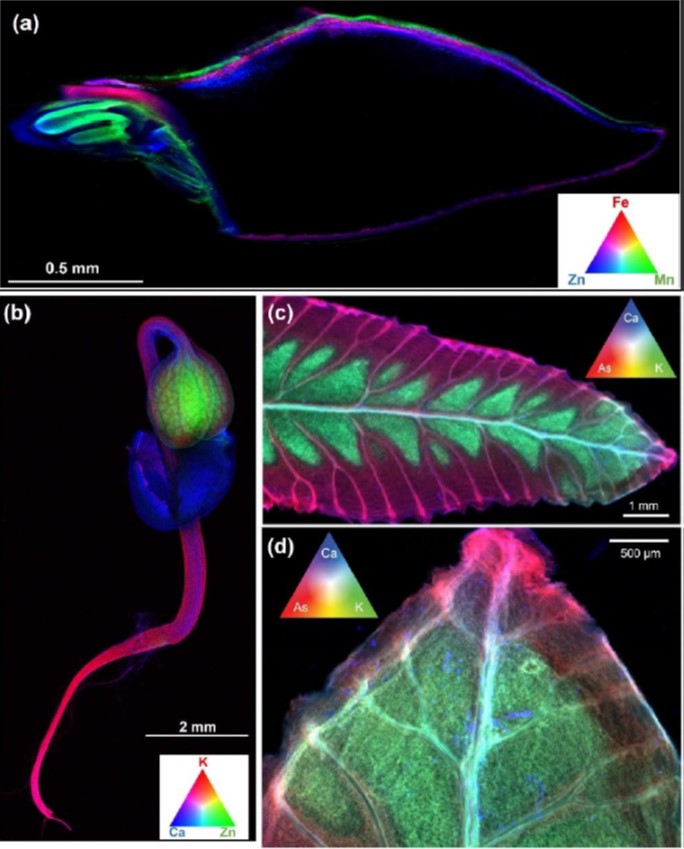
Review: X-ray fluorescence microscopy imaging (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKopittke et al. review the use of synchrotron-based X-ray fluorescence microscopy as a tool to quantify and localize diverse elements in plants. The authors describe how this method can be used to study nutrients in plants and human foods, as well as metal hyperaccumulating plants, and toxic metal(oid)…
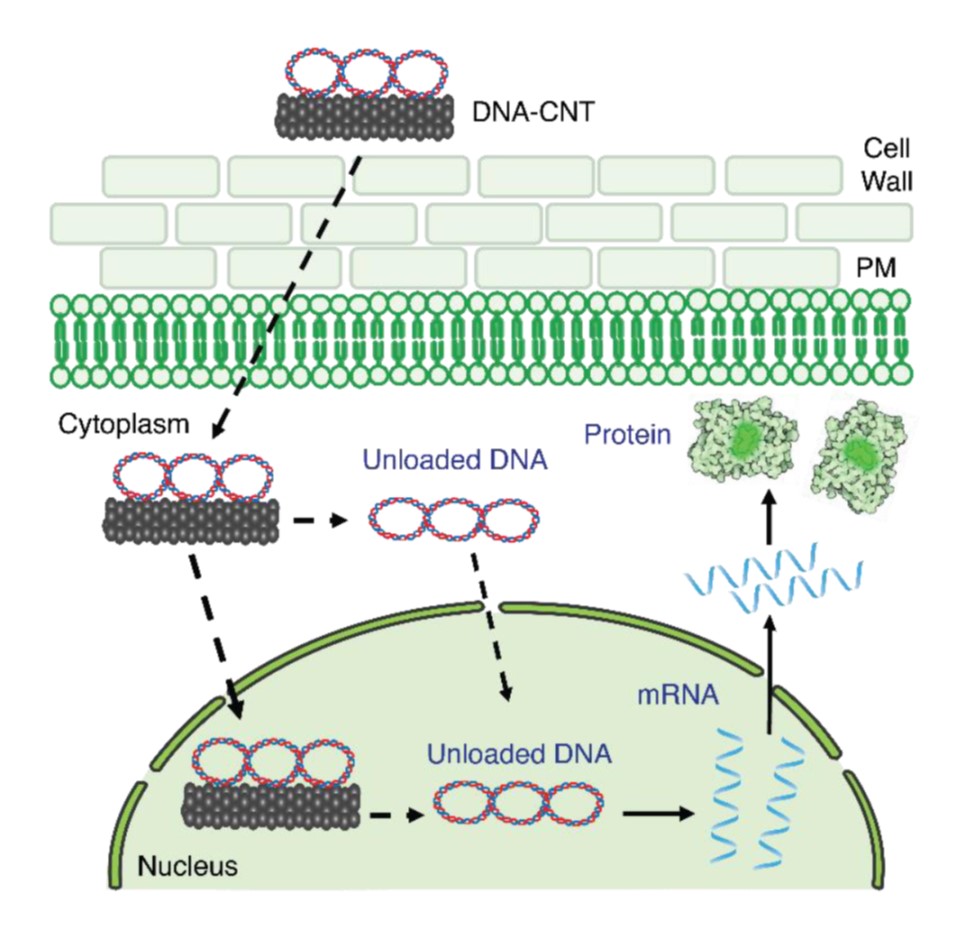
Carbon nanotubes deliver functional genetic material into mature plants without DNA integration
Plant Science Research WeeklyIntroducing DNA or RNA into plant cells remains a challenge. Demirer et al. describe a new method for transient expression studies through delivery of DNA or RNA via carbon nanotubes (CNTs); the size of the nanoparticles is smaller than the exclusion limit for plant cell walls. The authors show that…
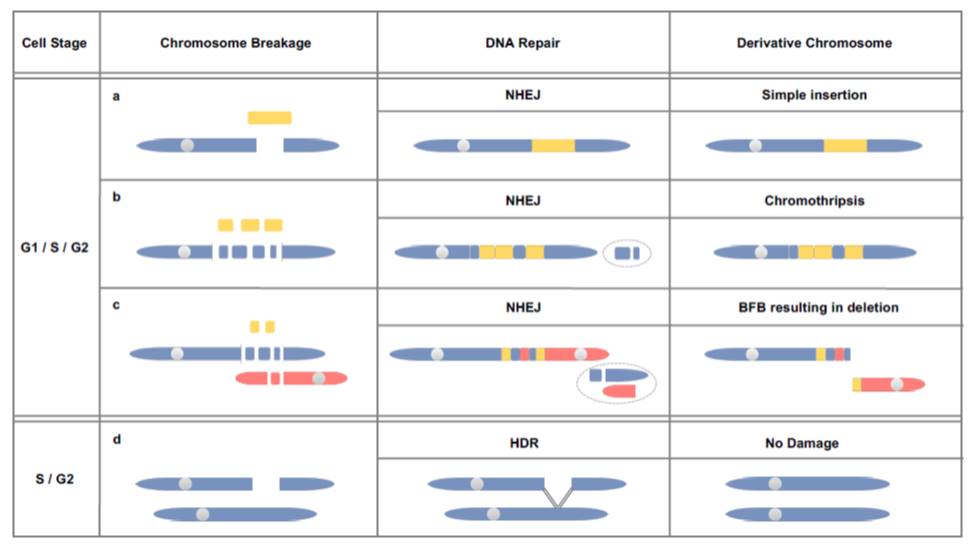
Genome-scale sequence disruption following biolistic transformation in rice and maize (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe two classic approaches to introducing DNA into a plant’s genome are by harnessing Agrobacterium tumefaciens’ fascinating gene-transfer skill, or by shooting the new DNA into the cell using a “biolistic” (gun) approach. Because of Agrobacterium’s restricted choice of hosts, the biolistic…

A single cis-element that controls cell-type specific expression in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMulticellular organisms have different tissues that carry out diverse and specialized functions, and tissue-specific expression is the feature that gives each tissue its specific protein content. Despite its importance, the mechanisms that control spatial patterning is poorly understood. In this work,…
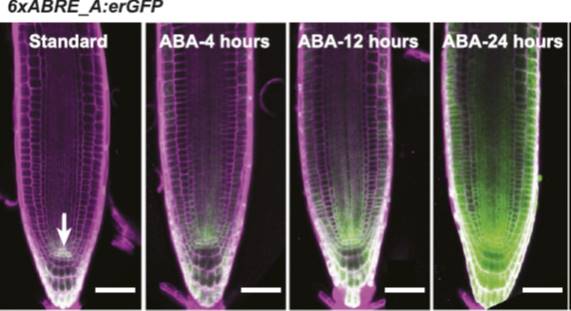
Revealing the Invisible: A Synthetic Reporter for ABA
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsHow do you make the invisible visible? It’s a question that crops up again and again in molecular biology. Abscisic acid (ABA) is one of the most important hormones in plants and is essential for survival in suboptimal conditions. Despite this, we have only a basic understanding of where and when this…
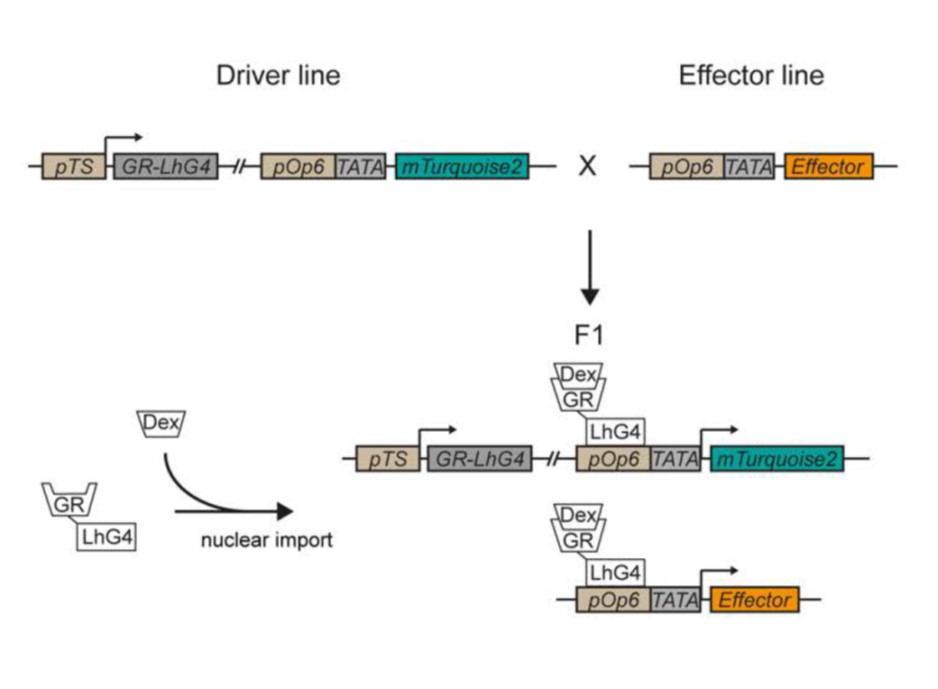
A comprehensive toolkit for inducible, cell type-specific gene expression in Arabidopsis (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene knock-outs and overexpression studies are useful indicators of gene function, but can obscure the gene’s distinct cell-type specific functions. Schürholz and Lopez-Salmeron et al. have developed a set of constructs that allow for precise expression of a gene-of-interest in subsets of cells, accompanied…
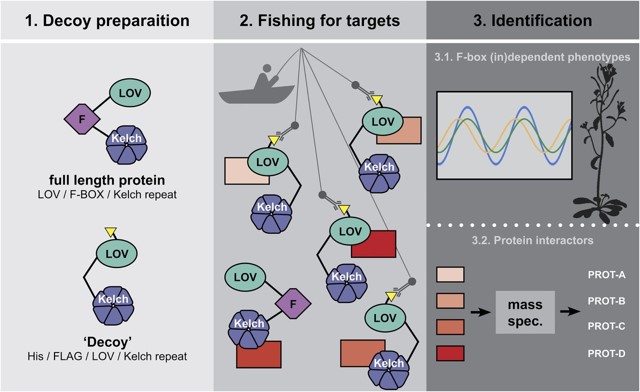
Save Time and Fish for the Clock
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsPlants live by the clock. It helps them to predict day and night as well as upcoming seasons, and to decide when it’s time for reproduction. These predictions depend on oscillating processes that involve gene transcription and protein stability, cycling in a period of, for example, 24 h. Environmental…
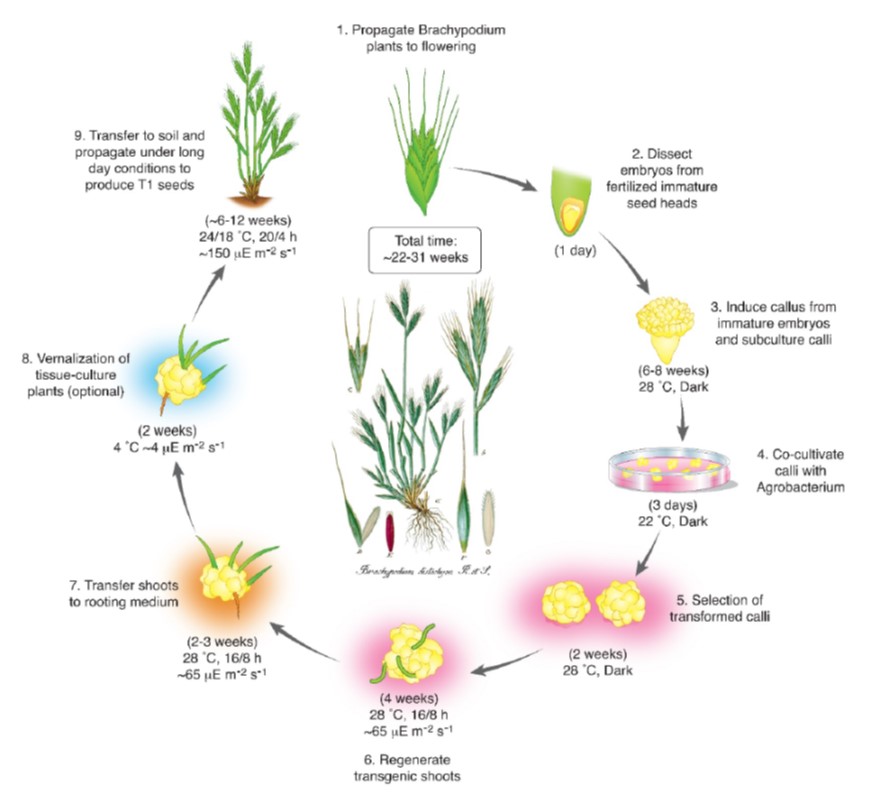
Review. Brachypodium: A monocot grass model system for plant biology (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBrachypodium distachyon is an annual C3 grass that has become an important model species. Scholthof et al. review the genetic tools and resources (sequences and mutants) as well as robust protocols for transformation that have been developed for it. The presence of wild and perennial species within the…

