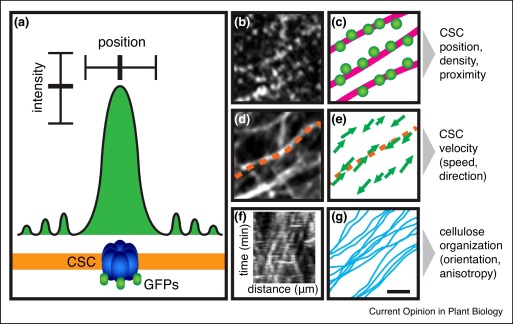
Editorial. Counting what counts: quantitative approaches in plant cell biology (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the new Cell Biology issue of Current Opinion in Plant Biology, editors Haswell and Dixit have chosen to focus on quantitative cell biology, arguing that, “if seeing is believing, then measuring is knowing.” Topics of the issue's reviews span parts of the cell (including cell wall, cytoskeleton,…
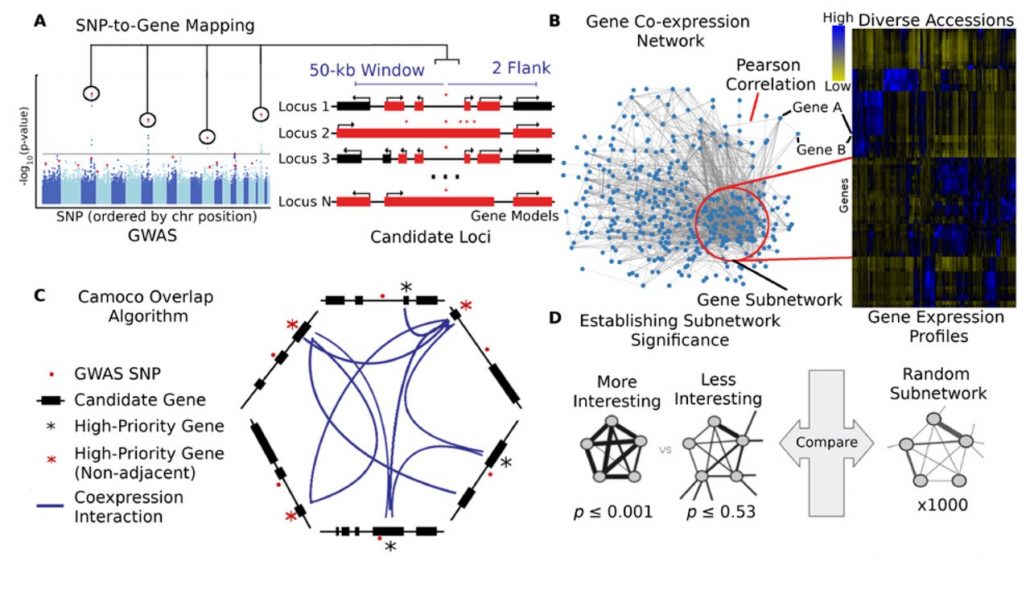
Finding candidate genes in maize with Camoco (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySchaefer and colleagues have developed Camoco (Co-analysis of molecular components), which integrates data from GWAS and co-expression networks to identify high confidence candidate genes associated with a phenotype of interest. To evaluate the program they used GWAS and co-expression data from maize.…
Review: Single-particle tracking for the quantification of membrane protein dynamics in living plant cells (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyReal-time tracking is a hugely powerful way to understand the behaviour of single proteins. Cui et al. review the methods and applications of single-particle tracking (SPT) in plant cells. They describe the applications of variable-angle total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (VA-TIRFM) to…
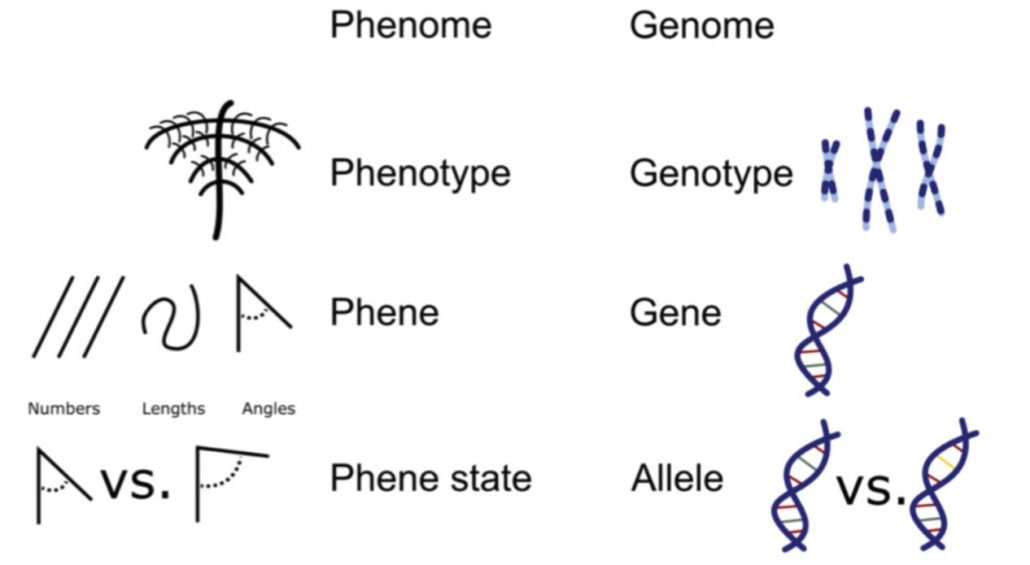
Review. Review. Functional phenomics: An emerging field integrating high-throughput phenotyping, physiology, and bioinformatics (J. Exp. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnderstanding the processes contributing to plant productivity will help to secure food production in the future. Larry York proposes how this can be achieved using functional phenomics. First the ideotype needs to be constructed; the ideotype is a set of phene states that are hypothesized to enhance…
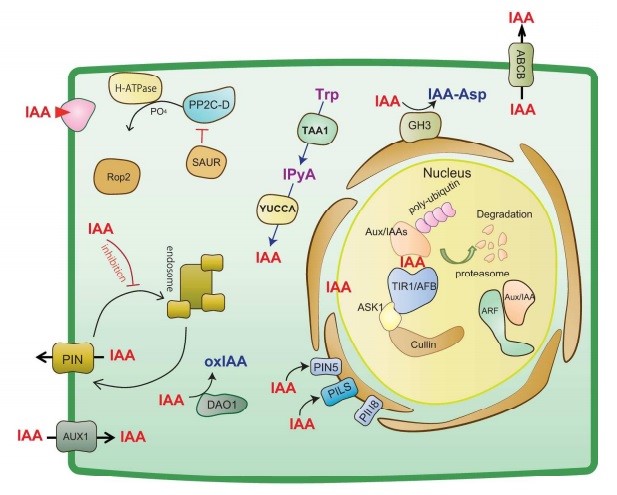
Manipulation and sensing of auxin metabolism, transport and signaling ($) (Plant Cell Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin is involved in a diverse array of developmental processes as well as biotic and abiotic stress responses. The chemical–genetic approach is a powerful tool to decipher the auxin signaling pathway. In this review, Fukui and Hayashi have provided a comprehensive overview about the structure, molecular…

Experimental Reproducibility 101 (Part 2)
BlogThis article is the second of three and is based on a workshop called “Reproducibility for all” presented at PlantBio18 by Benjamin Schwessinger, Sonali Roy, and Lenny Teytelman. In Part 1 (here), the authors describe the importance of having a data management plan, and the value of electronic notebooks.
3.…

Introducing Plant Tracer: A project led by Eric Brenner at Pace University
Blog
Looking at a typical plant, you may not notice that it is moving. Although generally perceived as static, all plants are dynamic, as shown by time-lapse photography. Plant Tracer is the first App-based tool that enables students and scientists to quantify plant movement (circumnutation and gravitropism)…
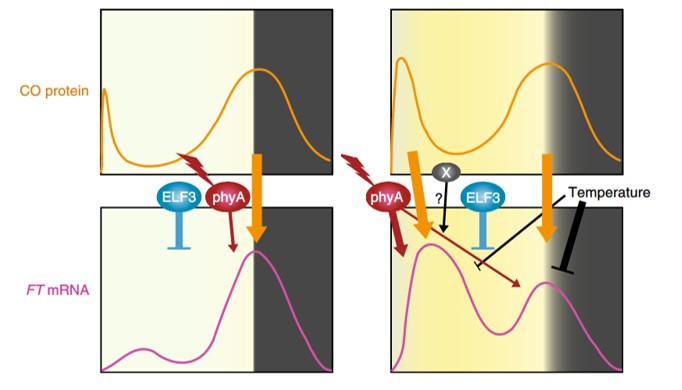
Flowering time in the real world (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere are pros and cons to growing plants in controlled conditions. On the one hand, controlling light, temperature, humidity and other environmental factors should aid reproducibility between experiments and labs. But what if the conditions used profoundly and unexpectedly affect the process you are…
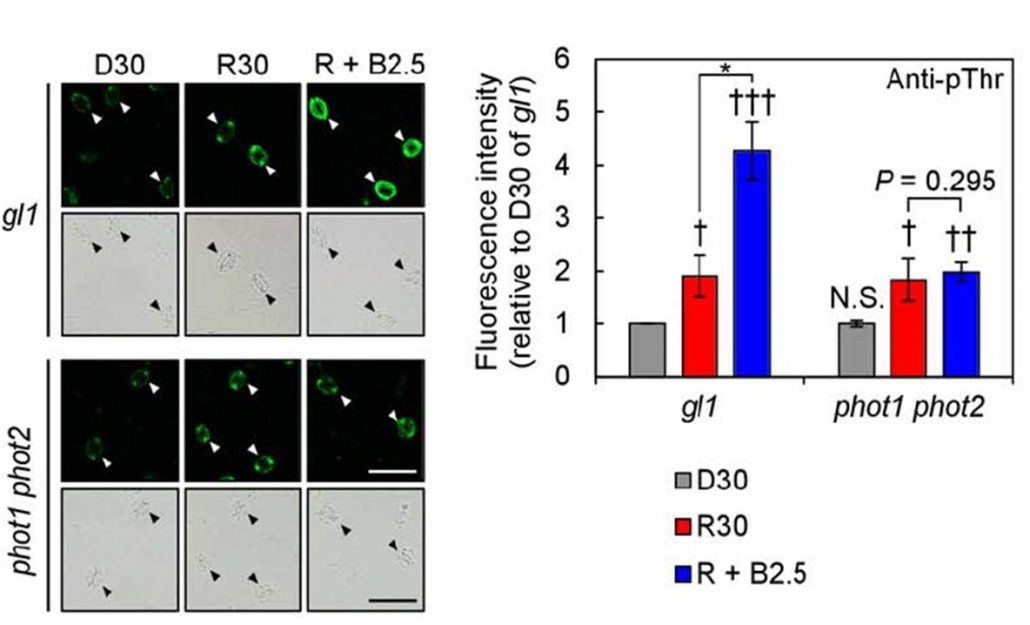
Red Light and the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase in Guard Cells
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideStomatal opening is stimulated by light, including blue and red light. Blue light-induced stomatal opening is fairly well understood: it is mediated by blue-light photoreceptor phototropins (phot1 and phot2). Blue light activates the plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase via phosphorylation of its penultimate…

