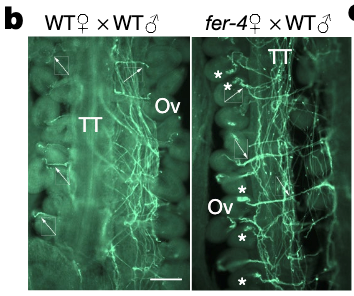
FERONIA controls pectin- and nitric oxide-mediated male–female interaction (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn flowering plants, fertilization occurs when a pollen tube, growing down the transmitting tissue, arrives at the ovule, ruptures, and releases its content of sperm cells. The pollen tube is guided towards the ovule by LUREs, small cysteine-rich secreted peptides. Timely rupturing and sperm release…
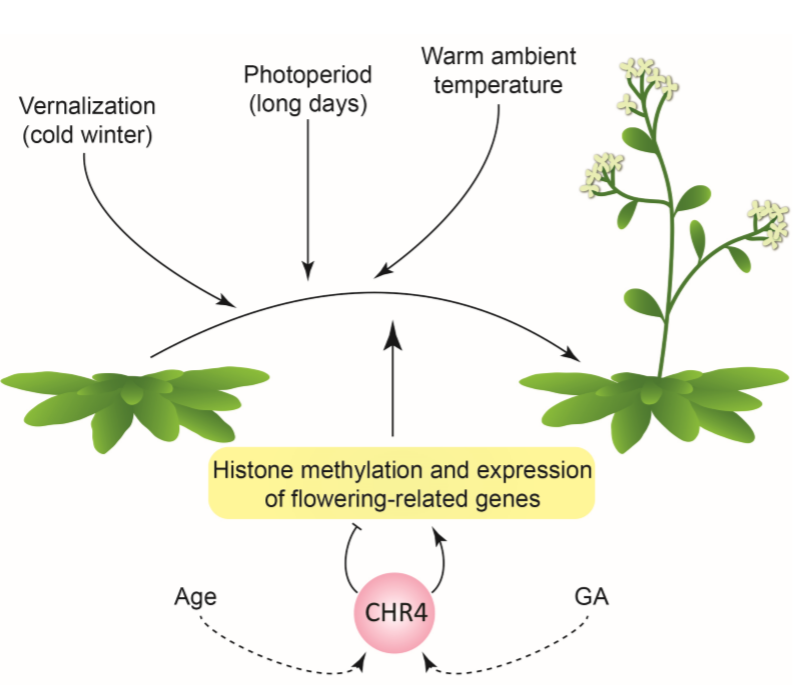
Roles for CHROMATIN REMODELING 4 in Arabidopsis floral transition (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe time at which flowers appear is critical for plant reproductive success. As such, the vegetative to reproductive growth transition is governed by several cues: environmental (photoperiod, temperature) and endogenous (gibberellins, age). Here, Sang et al. used an elegant forward-genetics approach…
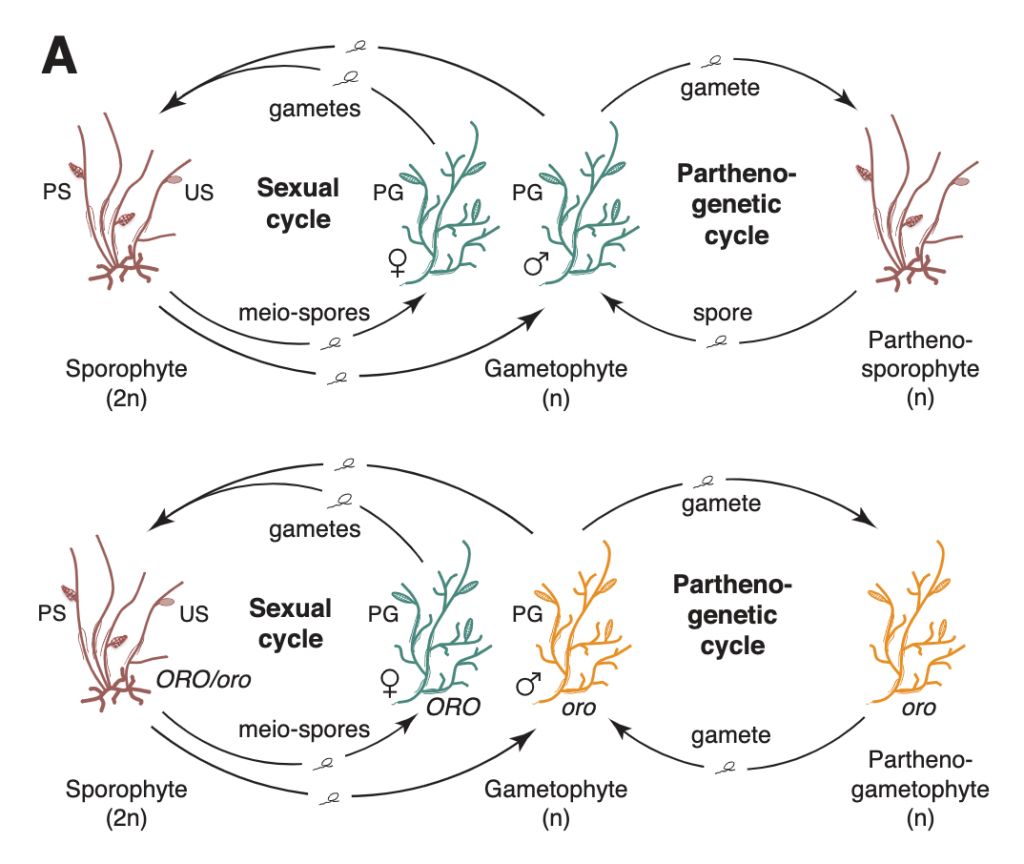
Convergent recruitment of TALE homeodomain life cycle regulators to direct sporophyte development in land plants and brown algae (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLife cycles in sexually reproducing plants and algae alternate between diploid (sporophytic) and haploid (gametophytic) generations. The haploid gametophyte produces gametes that mate to generate the diploid sporophyte, which in turn undergoes meiosis to generate haploid spores. Development must be coordinated…
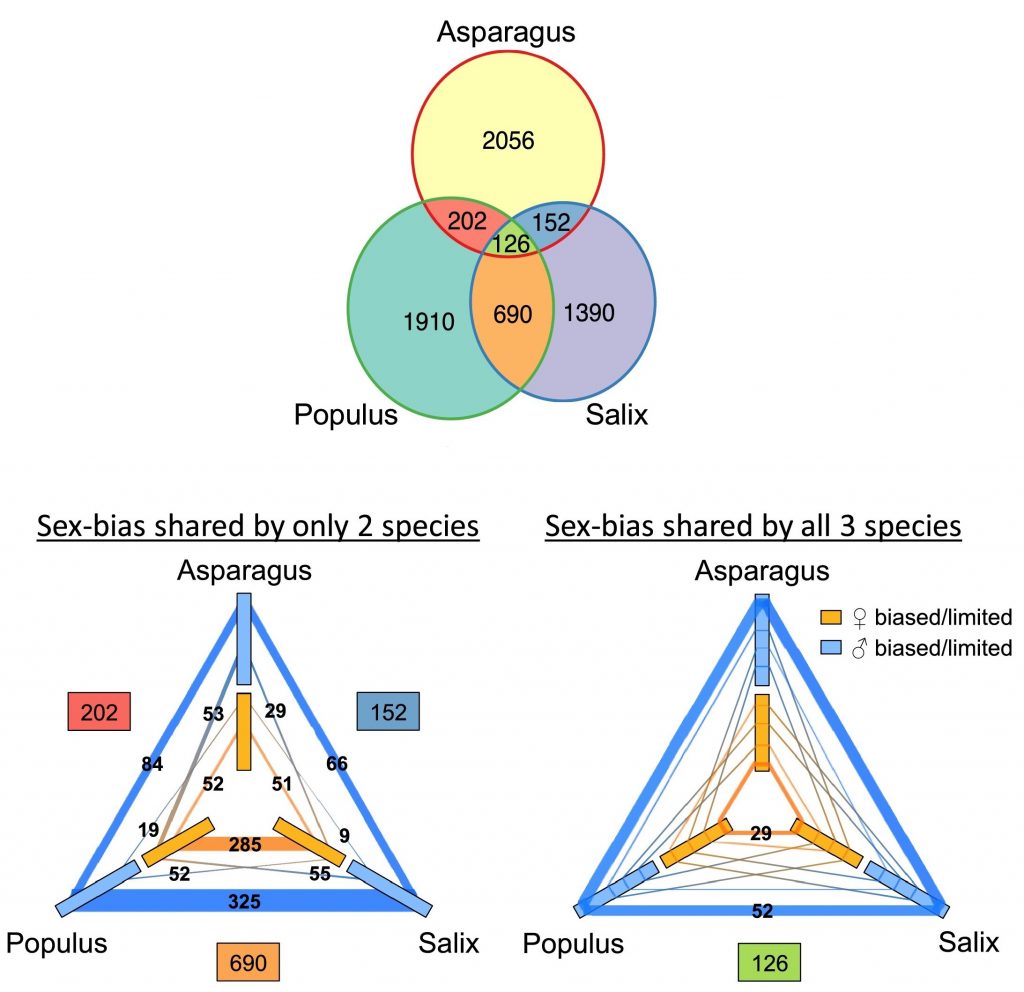
Review: Pathways to sex determination in plants: How many roads lead to Rome? (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough most angiosperms produce both male and female gametes, in some species an individual is either male or female, a property known as dioecy (literally, two houses). Dioecy exists in ~6% of angiosperms and is hypothesized to have evolved several times independently. While much research has been…
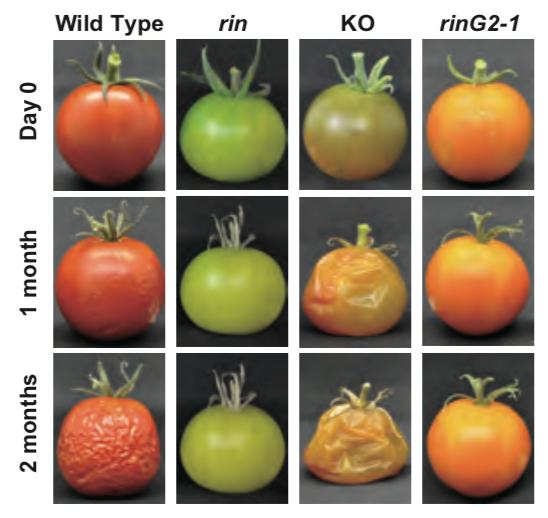

Allelic mutations in the Ripening-inhibitor (RIN) locus generate extensive variation in tomato ripening ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRipened fruits attract animals to eat and disperse seeds, allowing propagation. Slowing down the fruit ripening process is often used commercially to decrease damage during transport and extend shelf life. Molecular (increased pigment, aroma, and flavor) and physiological (softened flesh) changes of…
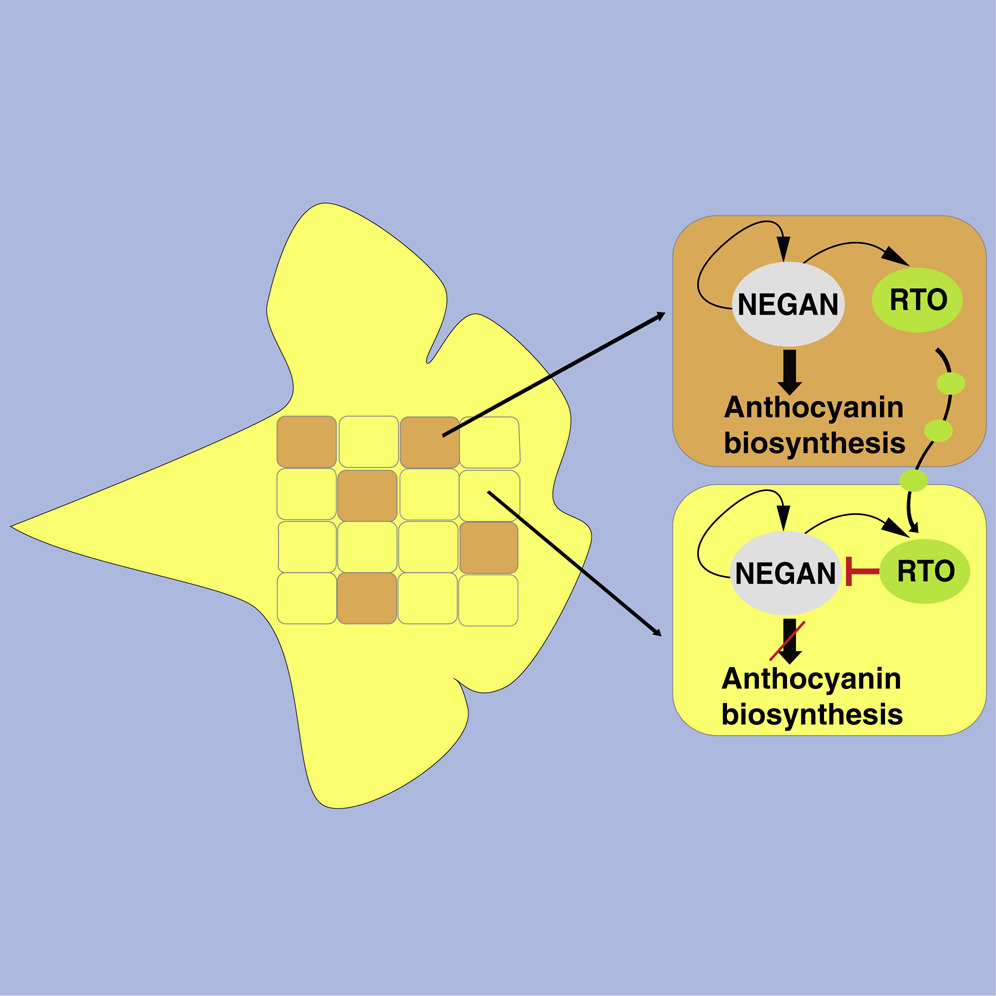
Two MYB proteins in a self-organizing activator-inhibitor system produce spotted pigmentation patterns (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe questions of how patterns are formed is one of the oldest in biology, and even considered by the famous mathematician Alan Turing, who proposed that reaction-diffusion (RD) models underly de novo pattern formation. Briefly, a reaction that takes place in one place sends a signal that leads to a different…
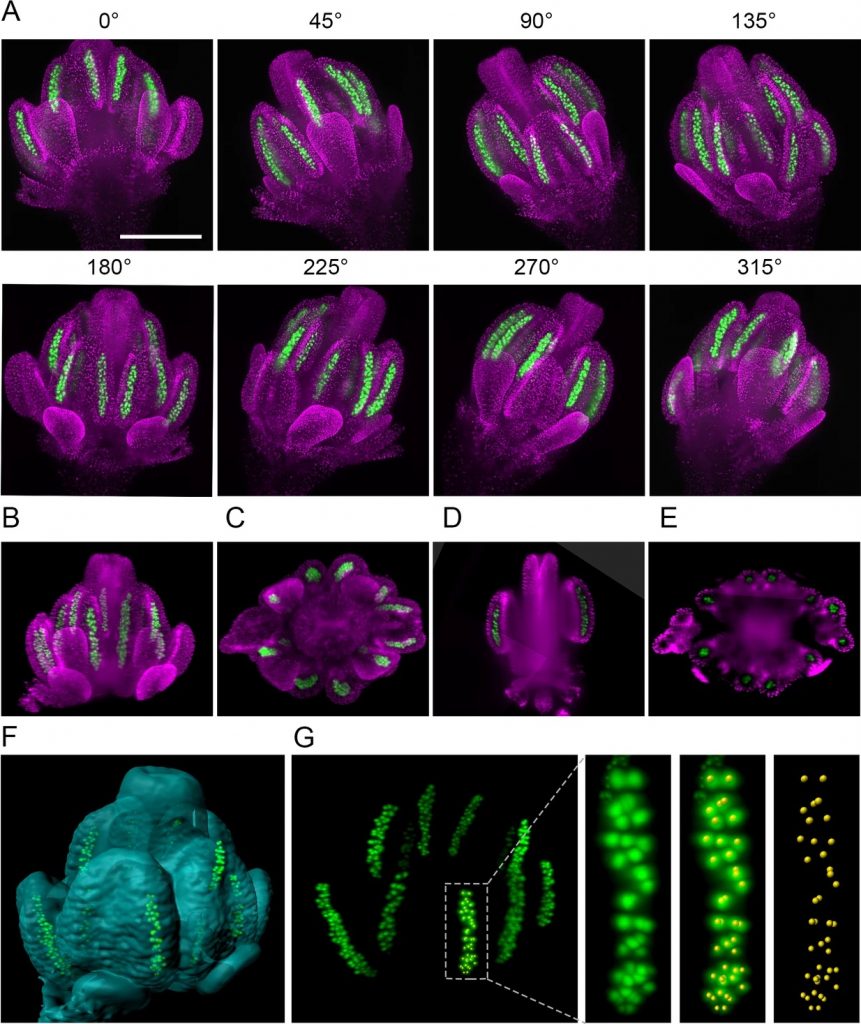
Imaging plant germline differentiation within Arabidopsis flowers by light sheet microscopy (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdvances in microscopy have greatly informed our understanding of fundamental plant processes, but the germline cells in flowers have been hard to image as they are tiny and embedded within other tissues. Valuchova et al. present a method using light sheet fluorescence microscopy that allows live cell…
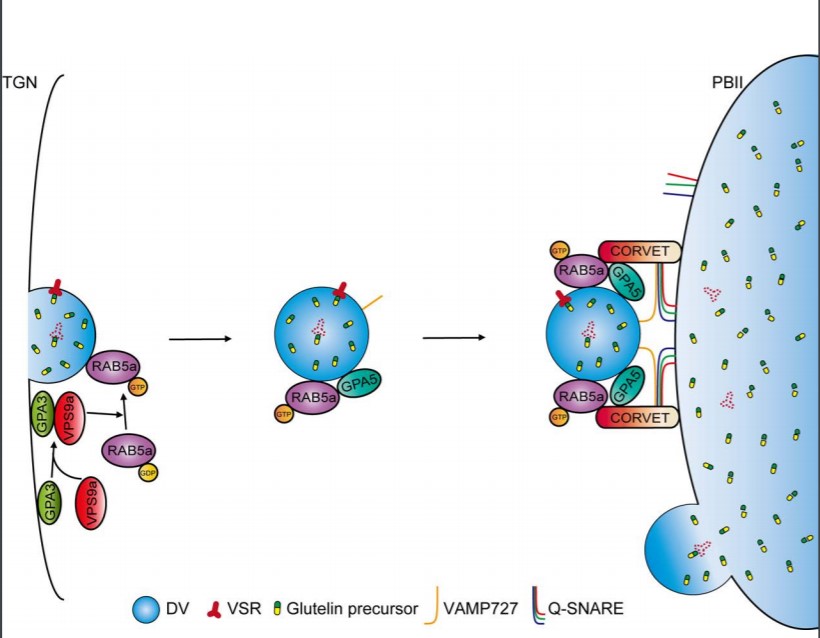
GPA5 encodes a Rab5a effector required for post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStorage proteins secreted into vacuoles during seed development serve as precursors for germination and plant growth. In this paper, Ren et al. identified a regulator, GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION 5 (GPA5) that is involved in protein trafficking into the vacuoles during seed development. The loss…
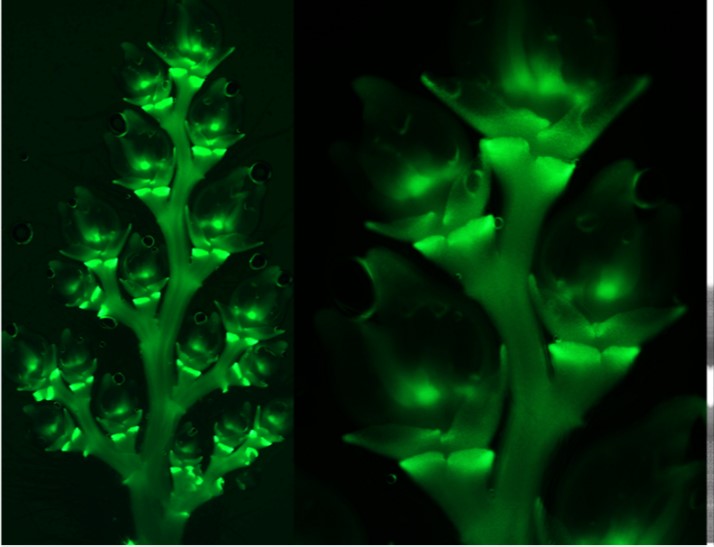
NONSTOP GLUMES 1 regulates spikelet development in rice (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRecently, several genes affecting rice architecture have been identified that may increase yields by increasing the number of grains formed, but as yet the genetic control of rice inflorescence architecture and organ identity is still being worked out. Zhuang et al. identified mutants of the NONSTOP…

