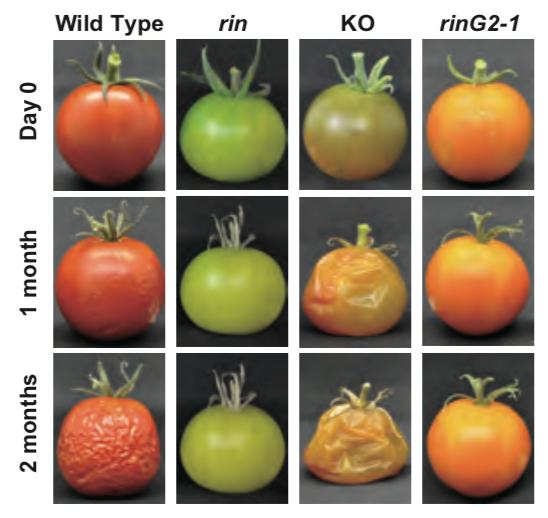

Allelic mutations in the Ripening-inhibitor (RIN) locus generate extensive variation in tomato ripening ($) (Plant Physiol)
Ripened fruits attract animals to eat and disperse seeds, allowing propagation. Slowing down the fruit ripening process is often used commercially to decrease damage during transport and extend shelf life. Molecular (increased pigment, aroma, and flavor) and physiological (softened flesh) changes of…
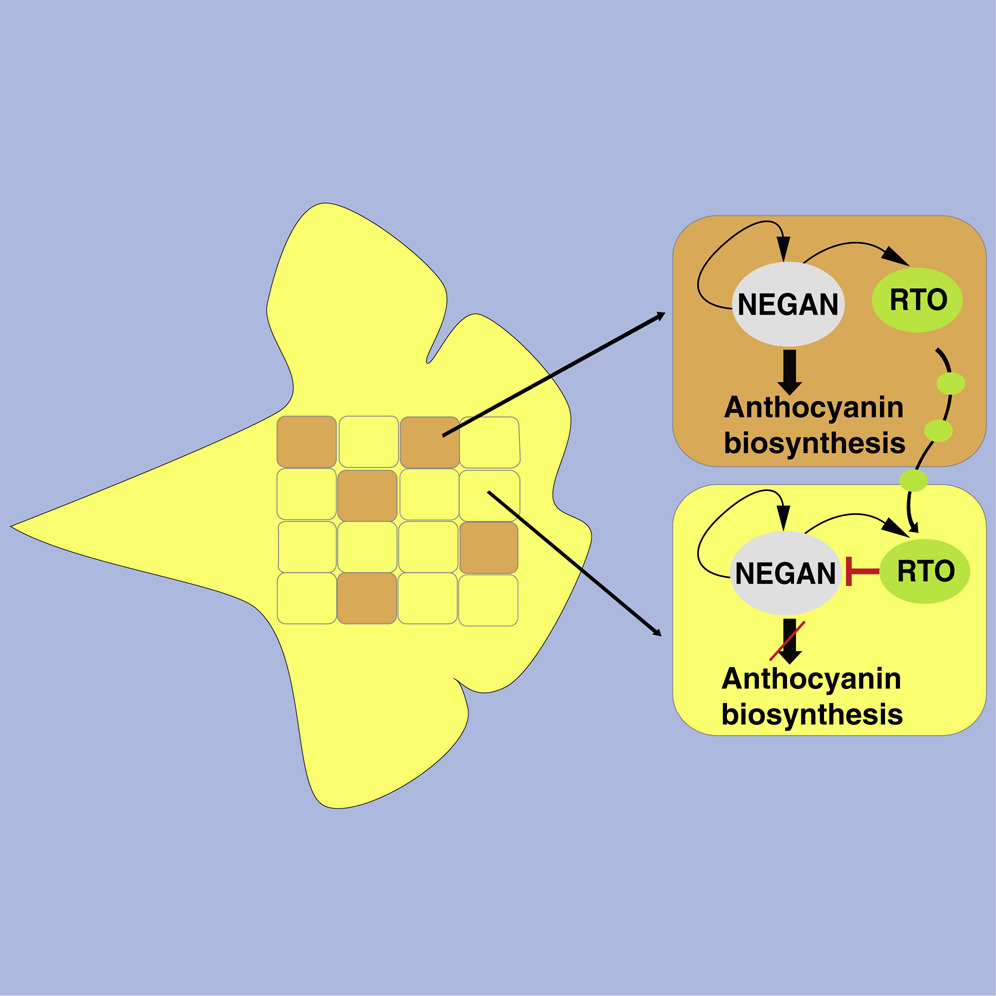
Two MYB proteins in a self-organizing activator-inhibitor system produce spotted pigmentation patterns (Curr. Biol.)
The questions of how patterns are formed is one of the oldest in biology, and even considered by the famous mathematician Alan Turing, who proposed that reaction-diffusion (RD) models underly de novo pattern formation. Briefly, a reaction that takes place in one place sends a signal that leads to a different…
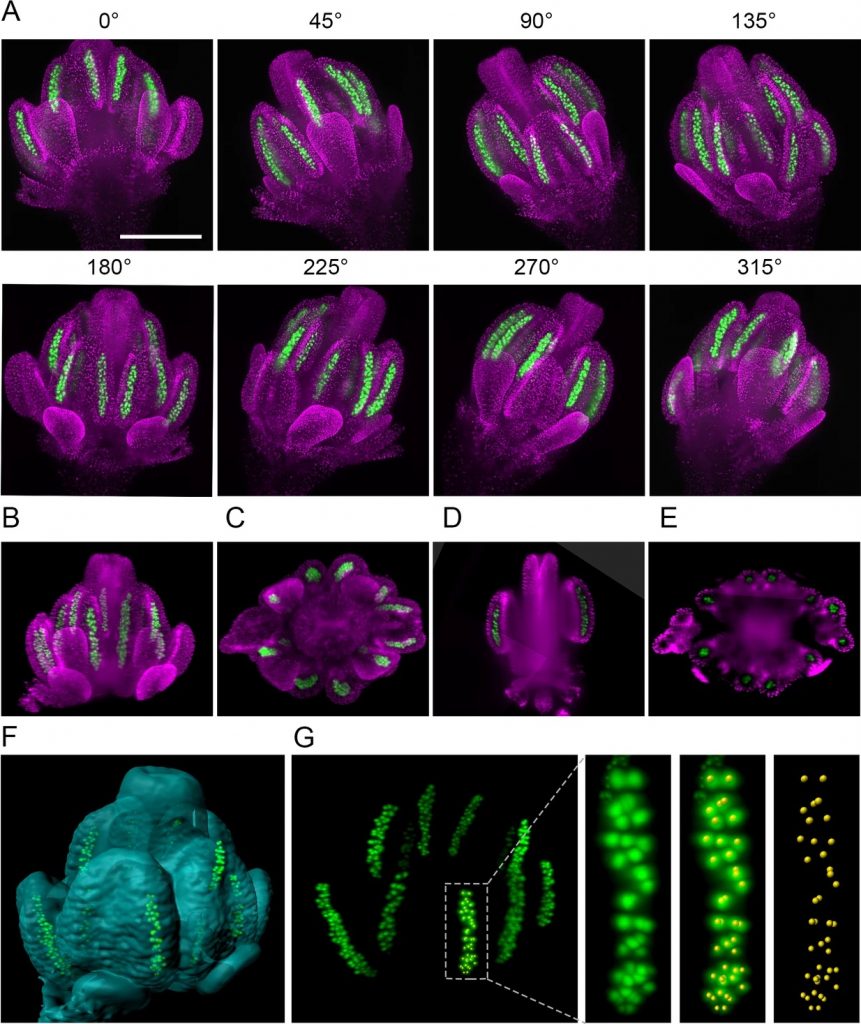
Imaging plant germline differentiation within Arabidopsis flowers by light sheet microscopy (eLIFE)
Advances in microscopy have greatly informed our understanding of fundamental plant processes, but the germline cells in flowers have been hard to image as they are tiny and embedded within other tissues. Valuchova et al. present a method using light sheet fluorescence microscopy that allows live cell…
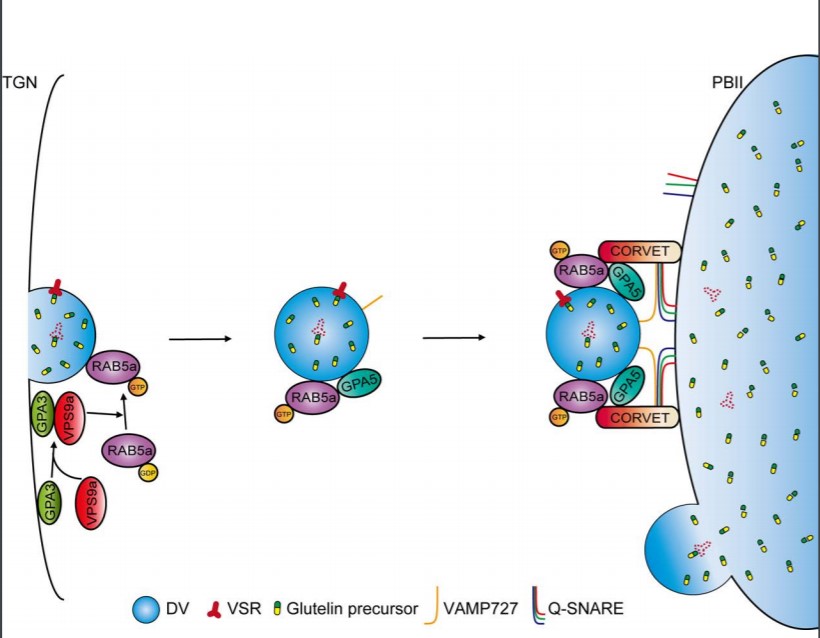
GPA5 encodes a Rab5a effector required for post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins ($) (Plant Cell)
Storage proteins secreted into vacuoles during seed development serve as precursors for germination and plant growth. In this paper, Ren et al. identified a regulator, GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION 5 (GPA5) that is involved in protein trafficking into the vacuoles during seed development. The loss…
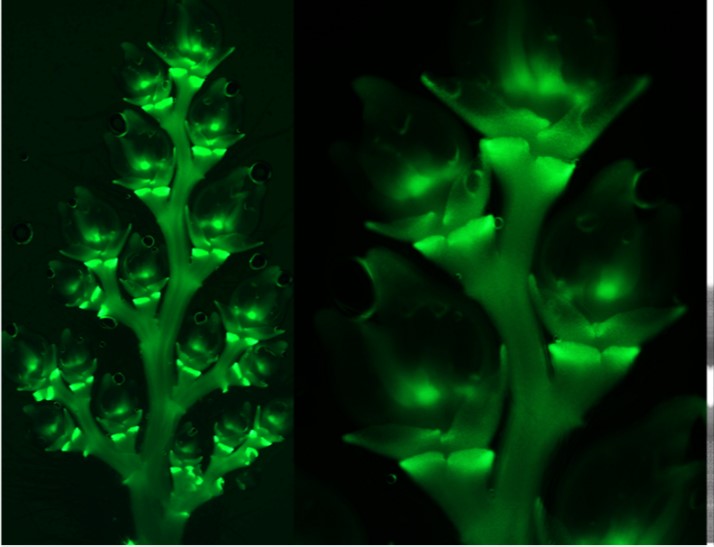
NONSTOP GLUMES 1 regulates spikelet development in rice (Plant Cell)
Recently, several genes affecting rice architecture have been identified that may increase yields by increasing the number of grains formed, but as yet the genetic control of rice inflorescence architecture and organ identity is still being worked out. Zhuang et al. identified mutants of the NONSTOP…

Pollination of Cretaceous flowers (PNAS)
Like something from Jurassic Park, a tiny insect embedded in amber has provided new insights into life millions of years ago. But in this case, the 99 million year old insect shows us that, as Darwin surmised, insects really were important contributors to angiosperm pollination from their origins. In…
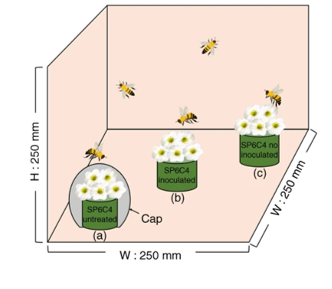
A mutualistic interaction between Streptomyces bacteria, strawberry plants and pollinating bees (Nature Comms)
Some species of Streptomyces bacteria produce antimicrobial compounds that have been shown to enhance plant resistance to pathogens. Kim et al. show that his protection can extend to a pollinator. The Streptomyces defends the plant against Botrytis cinerea and protects the bees against insect pathogens…
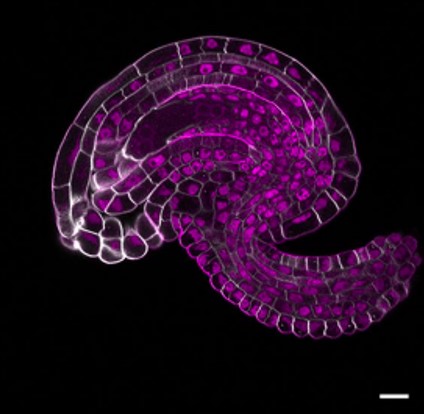
Protocol for rapid clearing and staining of fixed Arabidopsis ovules for improved imaging by confocal laser scanning microscopy (Plant Methods)
This is a very interesting paper that provide a new, fast and easy protocol, with specific step-by-step instructions, for a trustworthy imaging with cellular resolution of fixed Arabidopsis ovules at different developmental stages. The authors combine two previously outlined techniques: clearing of fixed…
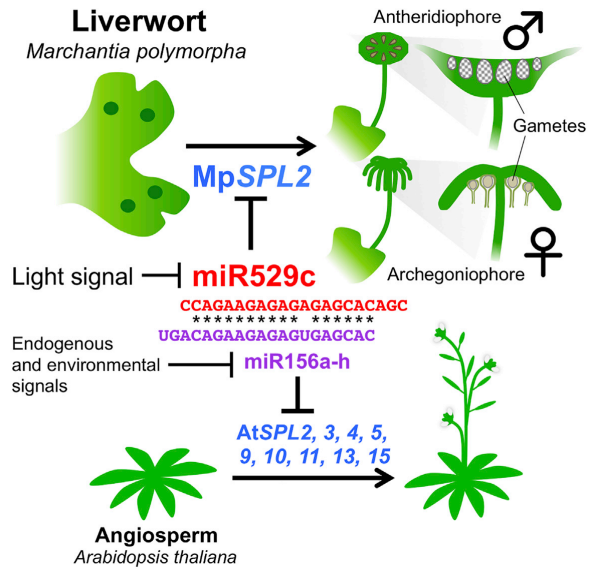
Early origin of miRNA-SPL module in reproductive development revealed by liverwort (Curr. Biol)
In Arabidopsis and other angiosperms, transition to flowering is controlled by a regulatory module that includes transcription factors from the SPL family and a miRNA miR156 targeting them. Marchantia and bryophytes do not make flowers, but there is an equivalent module that includes miR529c and a single…

