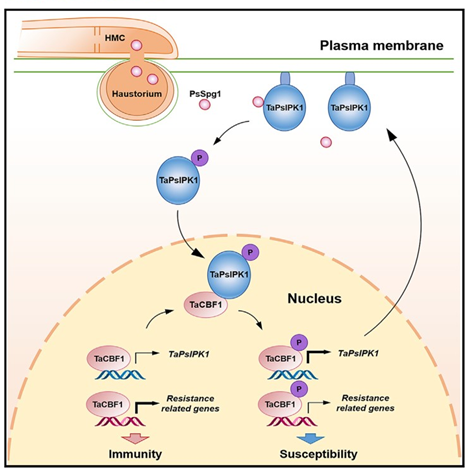
Removing one wheat protein kinase provides resistance to rust fungi (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTolerance against a pathogen can be achieved by either overexpressing a resistance-related gene, or removing a susceptibility-related gene. Overexpression of defense-related genes generally comes with side effects such as decreased growth and yield. On the other hand, a susceptibility factor might have…

Plant Cell Webinar: Highlighting Plant Cell Focus Issue on Biology of Plant Genomes (Part 1)
Blog, Plantae Presents, Research Skills0 Comments
/
Plantae Presents: Ksenia Krasileva, Christine Diepenbrock, and Rory Craig
Special Event: The Plant Cell Focus Issue on the Biology of Plant Genomes
Recorded Wed April 7th – 4 pm EDT, 1 pm PDT 9 pm BST, Thurs April 8th 8 am NZT
Advances in genome sequencing have yielded insights…
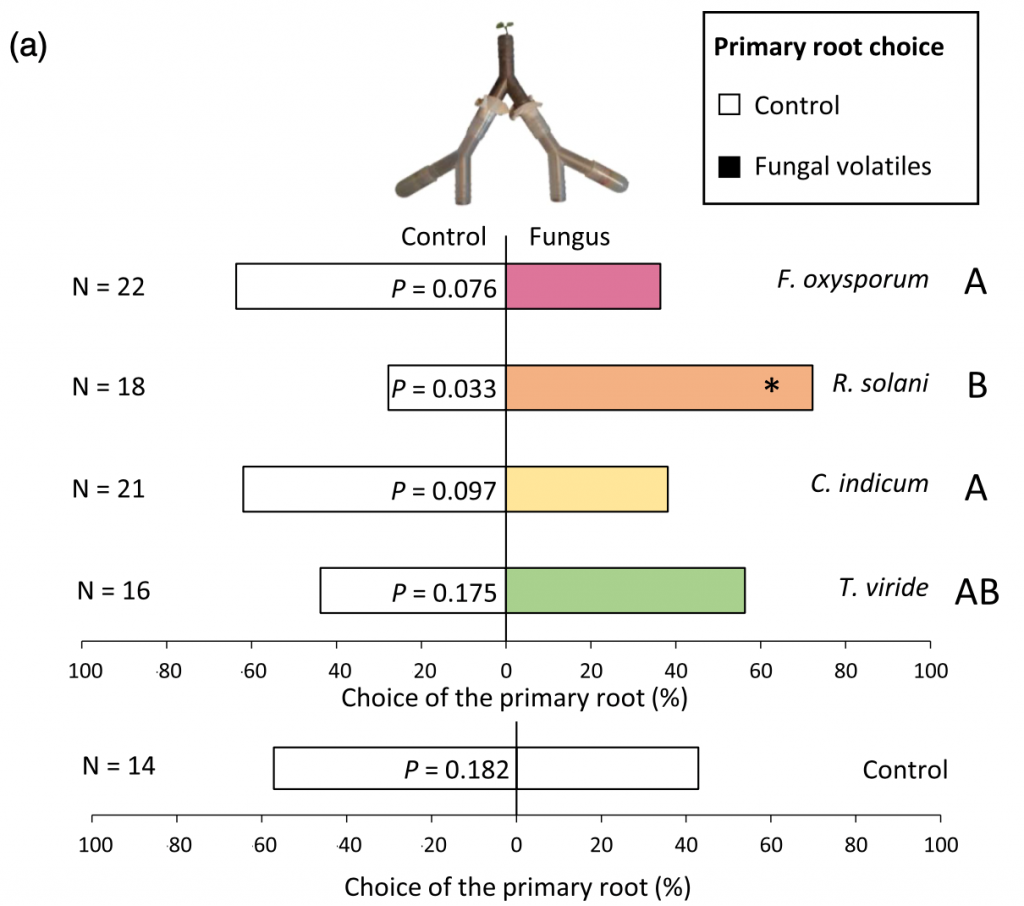
The love potion made by soil-borne fungi (Plant Cell Environ.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe basic requirements for plant growth are water, nutrients, and light. There are many other factors contributing to plant growth, including the interactions between plants and soil microorganisms. Soil microorganisms produce a large array of volatiles that can affect root architecture (e.g., some volatiles…

Plantae Presents: Sophien Kamoun and Phil Carella
Blog, Plantae Presents, Research SkillsPlantae Presents - Sophien Kamoun and Phil Carella
Recorded Wednesday September 16 10am EDT, 4pm CET
Sophien Kamoun: Evolutionary dynamics of NLR immune receptors in plants
Sophien Kamoun is senior scientist at the Sainsbury Laboratory and professor of biology at the University of East Anglia.…
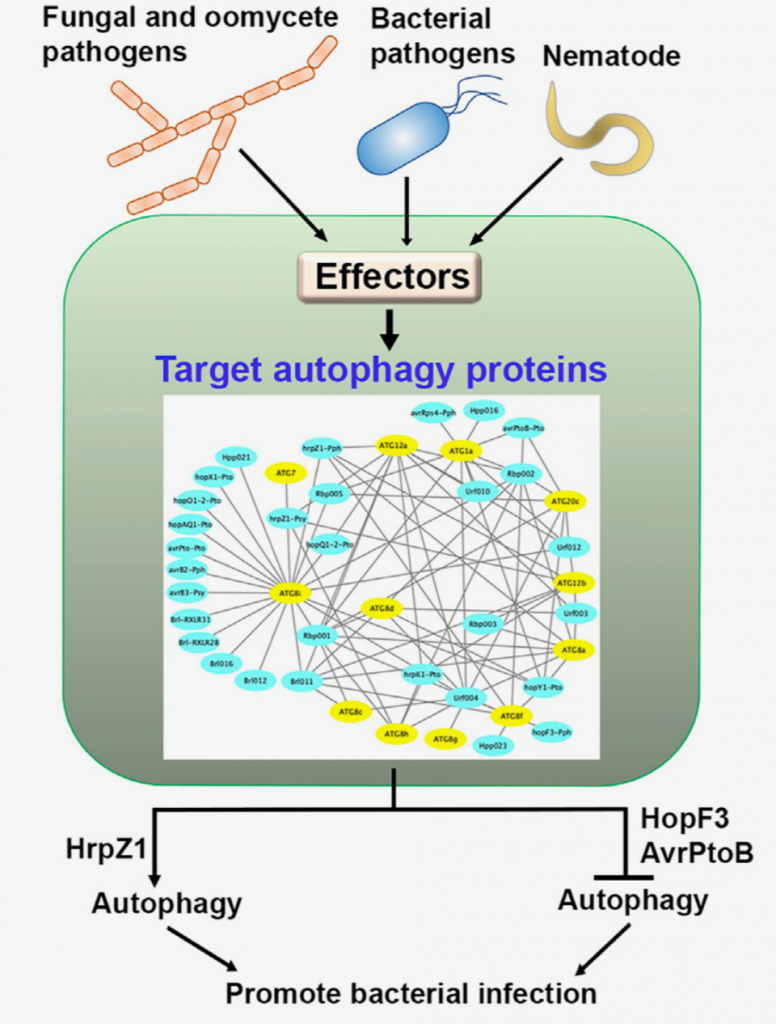
An interactome of plant autophagy proteins and pathogen effectors (Cell Host Microbe) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAutophagy is a regulated process whereby select cytoplasmic components are degraded. It is involved in a variety of biological processes, including defense against pathogens. As such, plant pathogens have evolved mechanisms to target host autophagy machinery to gain virulence. However, we still lack…
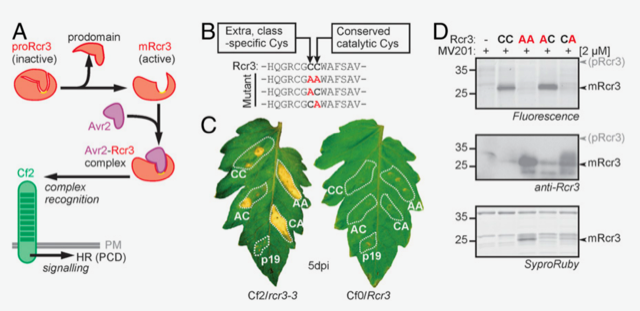
Extracellular proteolytic cascade in tomato activates immune protease Rcr3 (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plant apoplast is a sea of immune-related proteins that facilitate robust defense against pathogens. Rcr3 is a tomato secreted apoplastic protease that contributes to both basal defense and gene-for-gene resistance against pathogens. Rcr3 is activated by the cleavage of its autoinhibitory prodomain,…
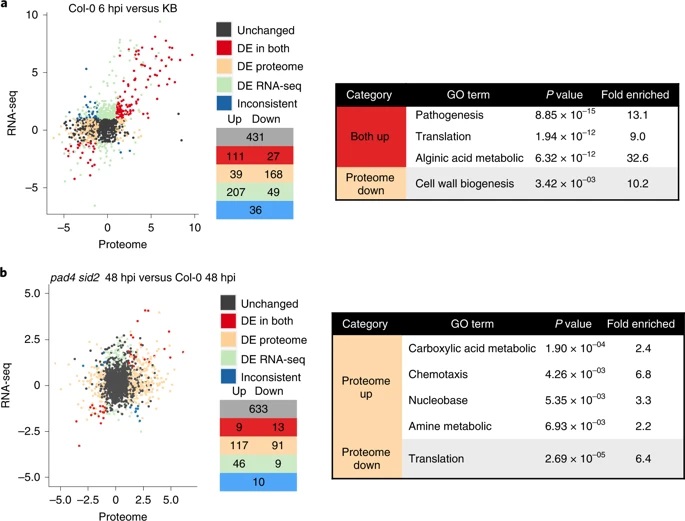
Multidimensional gene regulatory landscape of a bacterial pathogen in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe outcome of a plant-bacteria interaction is determined by the bacterial virulence and plant immune systems. Individually, these systems, and to an extent their interactions, have been well studied. However, certain aspects of their interactions remain elusive, particularly how plant immunity affects…
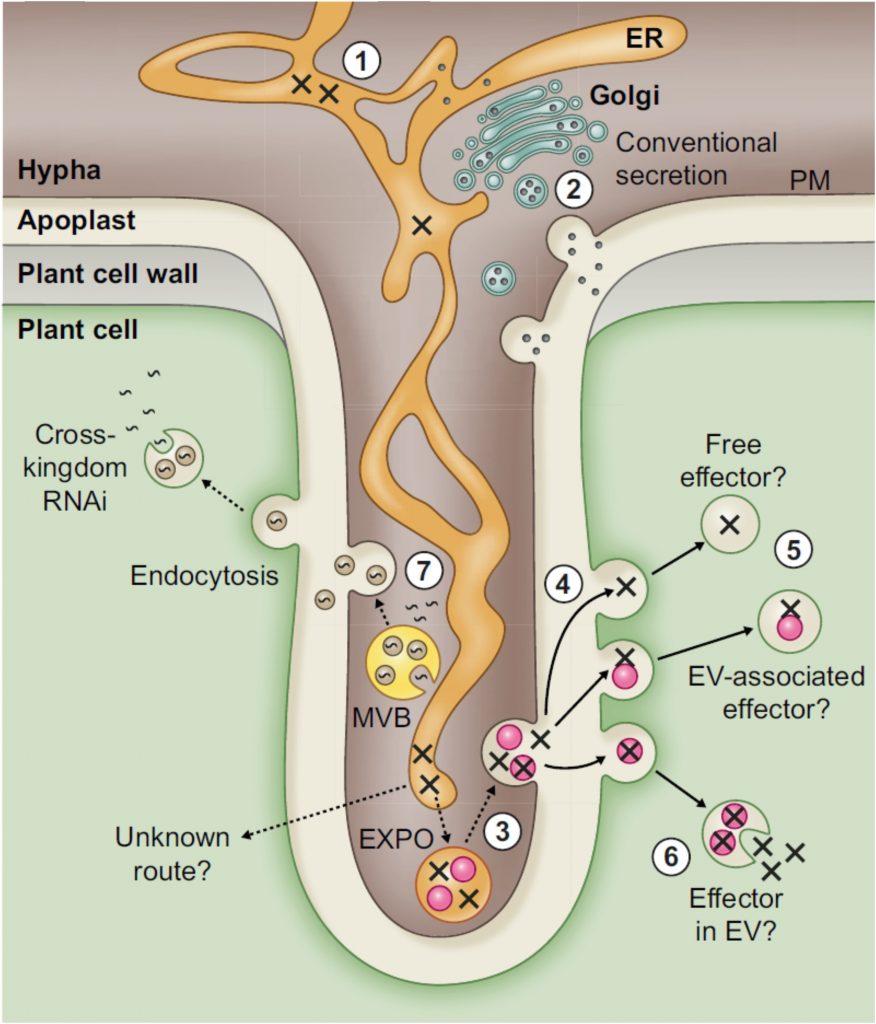
Review: Devastating intimacy: the cell biology of plant–Phytophthora interactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora are plant-destroying oomycetes. Within this genus are several infamous disease-causing agents: P. infestans of the potato late-blight fame, P. sojae of soybean root rot, P. ramorum of sudden oak death, and many other lesser-known species. This fine new review by Boevink et al. explores the…
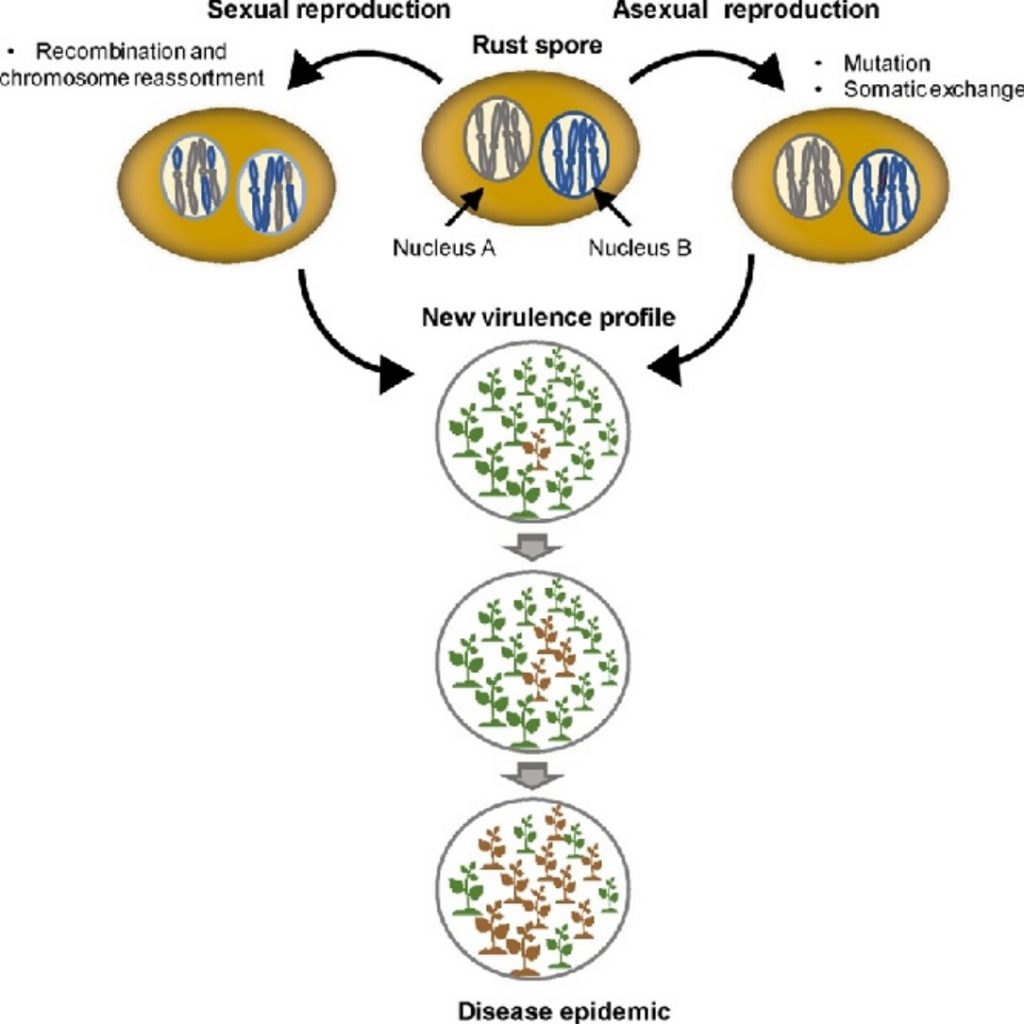
Review: Evolution of virulence in rust fungi — multiple solutions to one problem (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRust fungi are a diverse group (more than 7800 species) of phytopathogenic fungi that cause considerable economic loss. (Coincidently, I’m writing on Robigalia, the Roman “anti-rust” festival, which dates from before we understood that microbes, not gods, cause disease). Figurero et al. have written…

