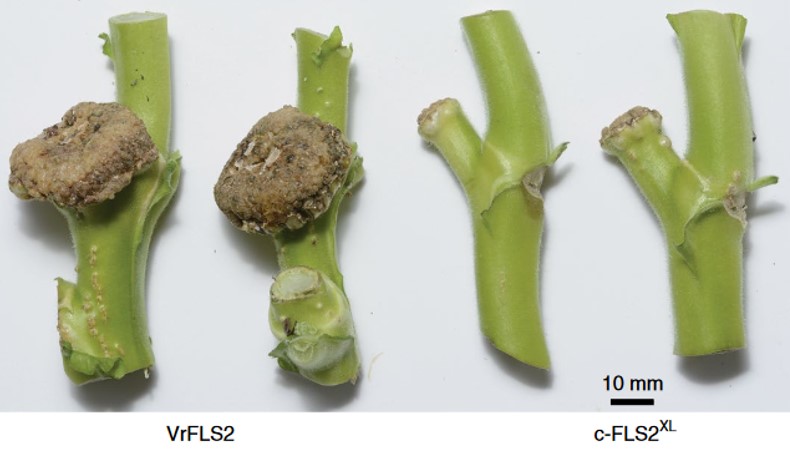

Perception of Agrobacterium tumefaciens flagellin by FLS2XL confers resistance to crown gall disease (Nature Plants)
FLS2 is a well-characterized cell-surface receptor that recognizes a short epitope found on most bacterial flagellin proteins. The plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens, causative agent of crown gall disease, deviates strongly at this epitope region, and so is generally not recognized by FLS2 receptors,…
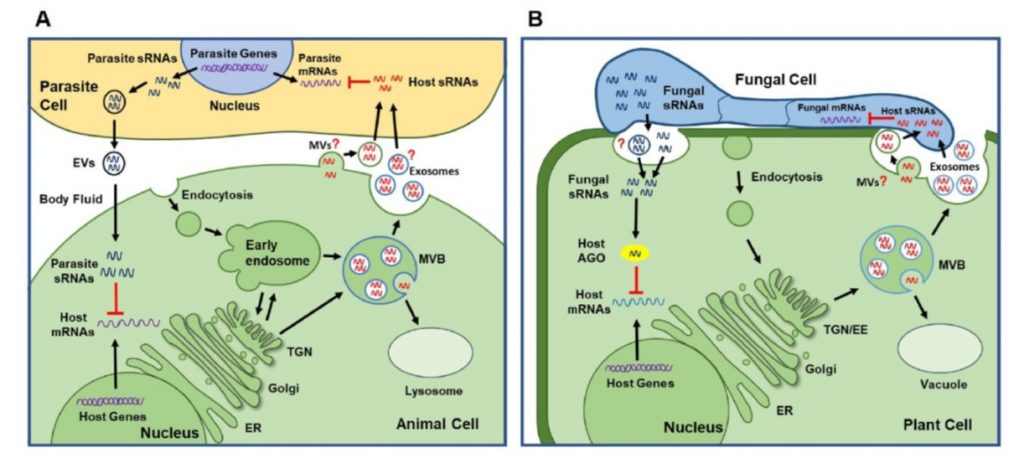
Review. Small RNAs and extracellular vesicles: New mechanisms of cross-species communication and innovative tools for disease control (PLOS Pathogens)
We have only recently begun to appreciate the phenomenon of cross-species or cross-kingdom small RNA transfer, and its applications. Using examples from plants and animals, Cai et al. summarize how some pathogens have evolved the capacity to introduce small RNAs into their host to suppress host defense…
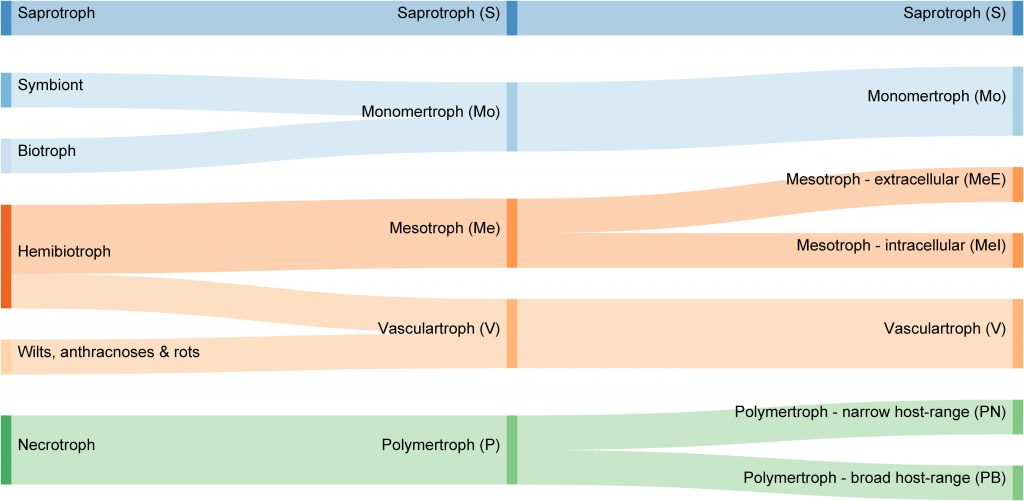
A proposed new classification scheme for fungal and oomycete pathogens based on carbohydrate-active enzymes (Front. Microbiol)
Filamentous pathogens (fungi and oomycetes) use a variety of tactics to obtain nutrients from plants. Classically, they have been categorized as biotrophic ("eating" living tissues), nectrotrophic (eating dead tissues) or hemibiotrophic (biotrophic followed by heterotrophic). Hane et al. point out that…
Pathogenic bacteria target plant plasmodesmata to colonize and invade surrounding tissues (Plant Cell)
Plasmodesmata are regulated channels that connect adjacent cells, allowing movement of metabolites, RNA, proteins, and pathogens. Plants close their plasmodesmata as part of their immune response, but this closure can be interfered with by pathogens. Aung et al. examined the repertoire of effector proteins…

Resistant tomato restricts colonization and invasion by the pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum at four organismal levels (J Exp Bot)
Ralstonia solanacearum is a pathogenic bacterium that infects many important crop species, including tomato. Following invasion into the roots, the bacteria move upwards into the shoot and cause dramatic wilting. Previous studies have identified moderately and highly resistant lines. Here, Planas-Marquès…
Medicago-Sinorhizobium-Ralstonia co-infection reveals legume nodules as pathogen confined infection sites developing weak defenses (Curr. Biol.)
The pathogenic bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum enters roots through wounds and also at root tips. It can also infect legume nodules. Benezech et al. investigated how this infection occurs, and how it is affected by and affects nitrogen fixation. The authors found that nodules are as permissive of Ralstonia…
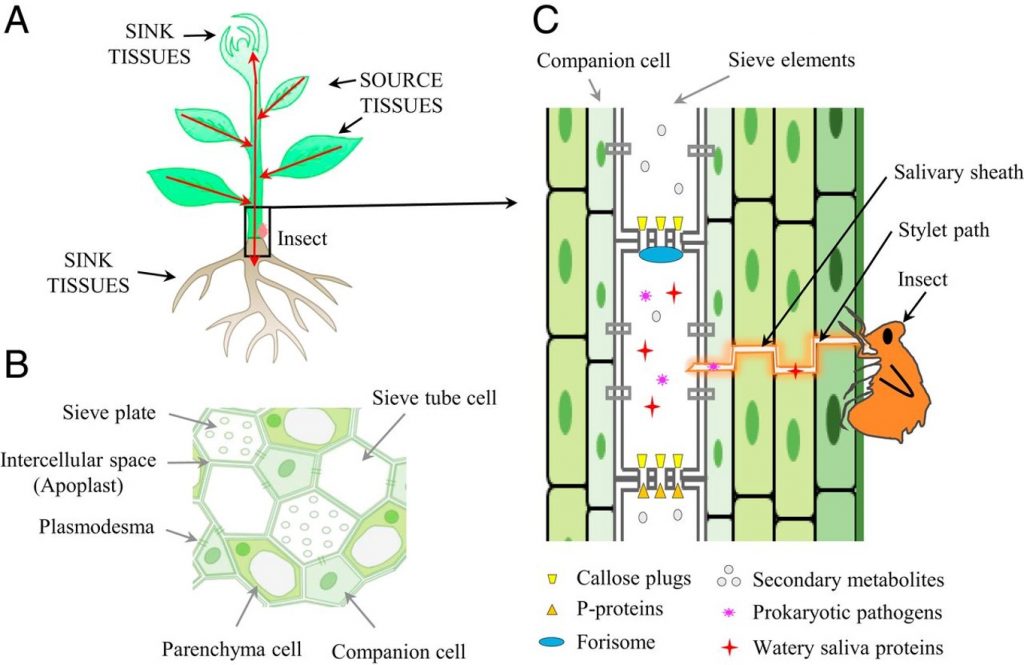
Perspective: Challenging battles of plants with phloem-feeding insects and prokaryotic pathogens (PNAS)
Much of our understanding of plant defense response is built upon the responses that occur in leaves. Many pathogens colonize the phloem system, which is both nutrient-rich and provides an easy conduit for spreading through systemically through the plant body. These phloem-inhabiting prokaryotic pathogens…

Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato ($) (Nature Biotech)
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria. As agents that weaken or destroy pathogens, they have shown therapeutic promise in human and plant disease treatment. Wang et al. studied the effect on pathogenic Ralstonia solanacearum of different phages individually and in combinations in the rhizosphere…
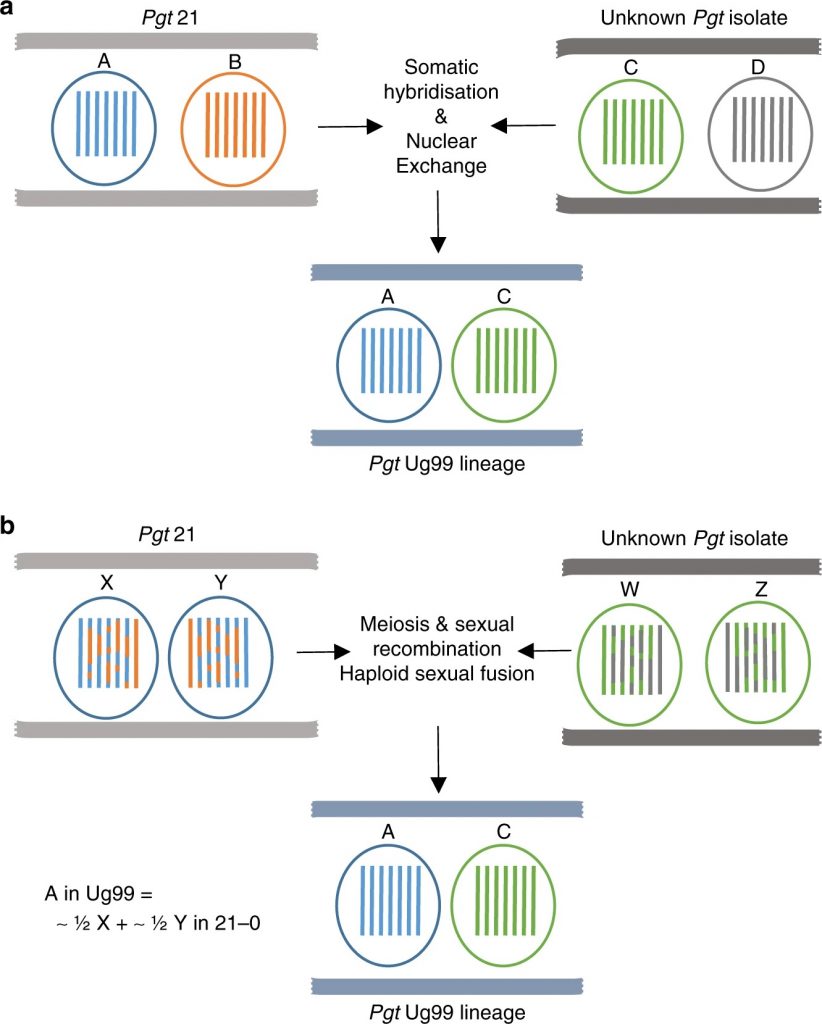
Emergence of the Ug99 lineage of the wheat stem rust pathogen through somatic hybridization (Nature Comms)
The Ug99 strain of wheat stem rust pathogen Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici (Pgt) emerged in Uganda in 1999 and presents a significant threat to global wheat production. Genetic analysis indicates it is distinct from other Pgt races. Li et al. set out to understand its origins. Puccinia graminis are…

