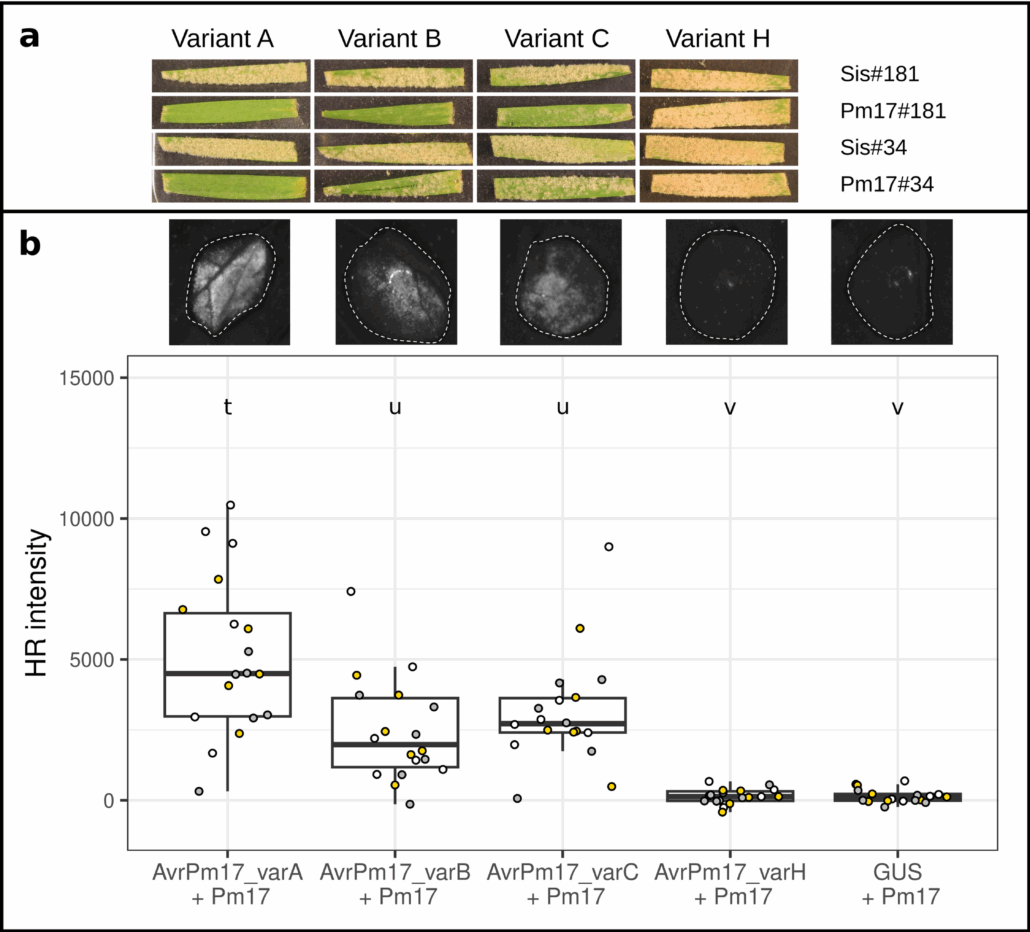
Molecular epidemiology of European wheat powdery mildew
Plant Science Research WeeklyAt the height of the Covid pandemic, epidemiologists carried out mass sequencing of the circulating virus populations to track their movements and the emergence of new variants. Such molecular epidemiological studies are rarer for plant pathogens but can be equally effective in learning about their patterns…
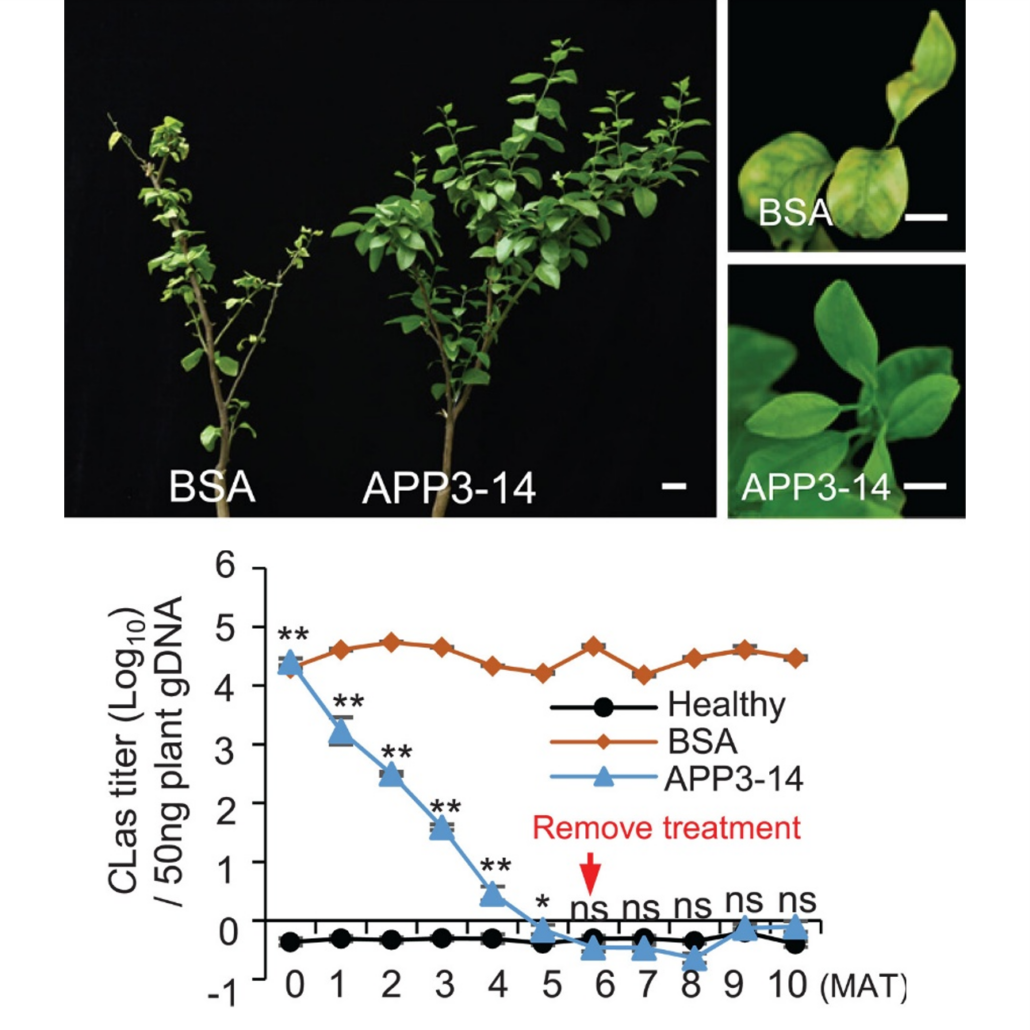
Stopping citrus greening with peptide therapy
Plant Science Research WeeklyCitrus greening disease (also known as Huanglongbing) has had a huge impact on citrus fruit production worldwide, with Florida particularly hard hit. The disease is caused by insect-vector-spread bacteria, including Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas). There is some genetic variability in susceptibility,…
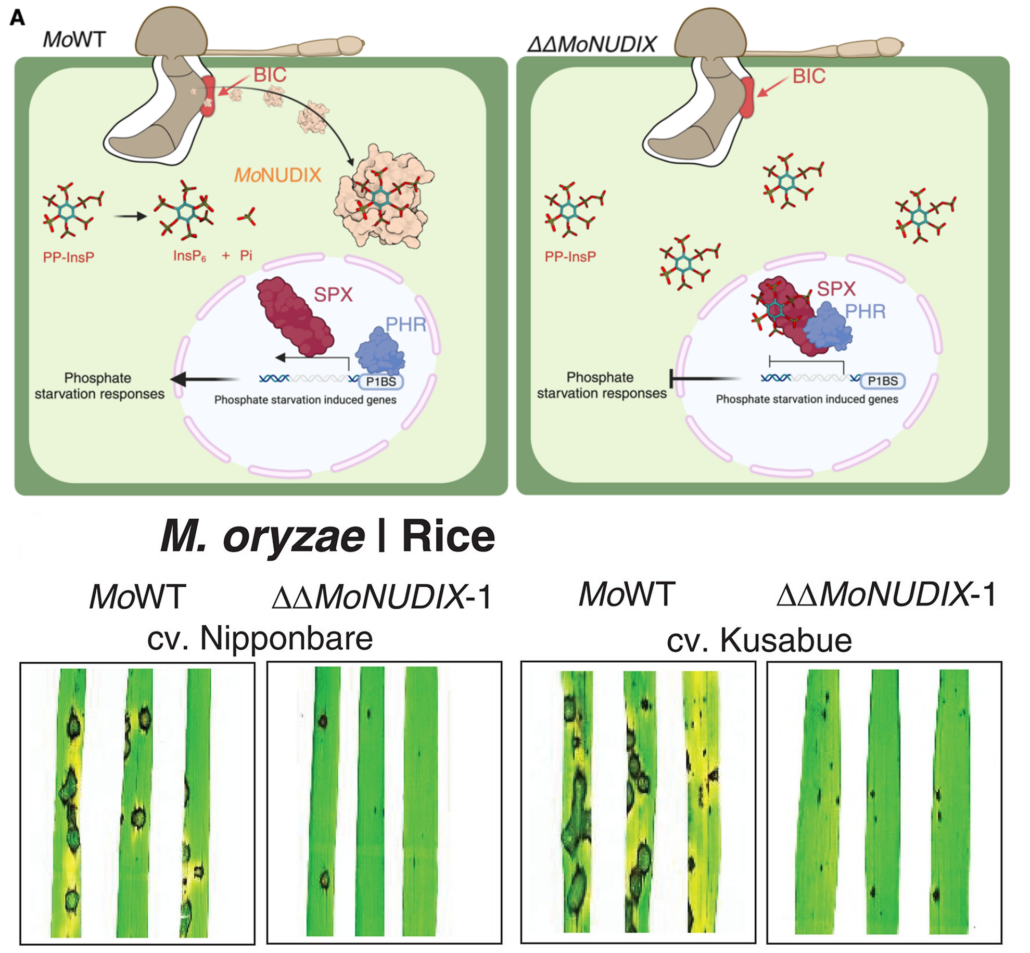
Fungal pathogen hijacks phosphate signaling to promote pathogenicity
Plant Science Research WeeklyWeakening your opponent is an effective way to win a battle. A new paper by McCombe et al. shows that several pathogenic fungi weaken their plant hosts by disrupting their phosphate signaling pathways. Phosphate is indispensable for plant growth, as a component of ATP, nucleotides, phospholipids, and…
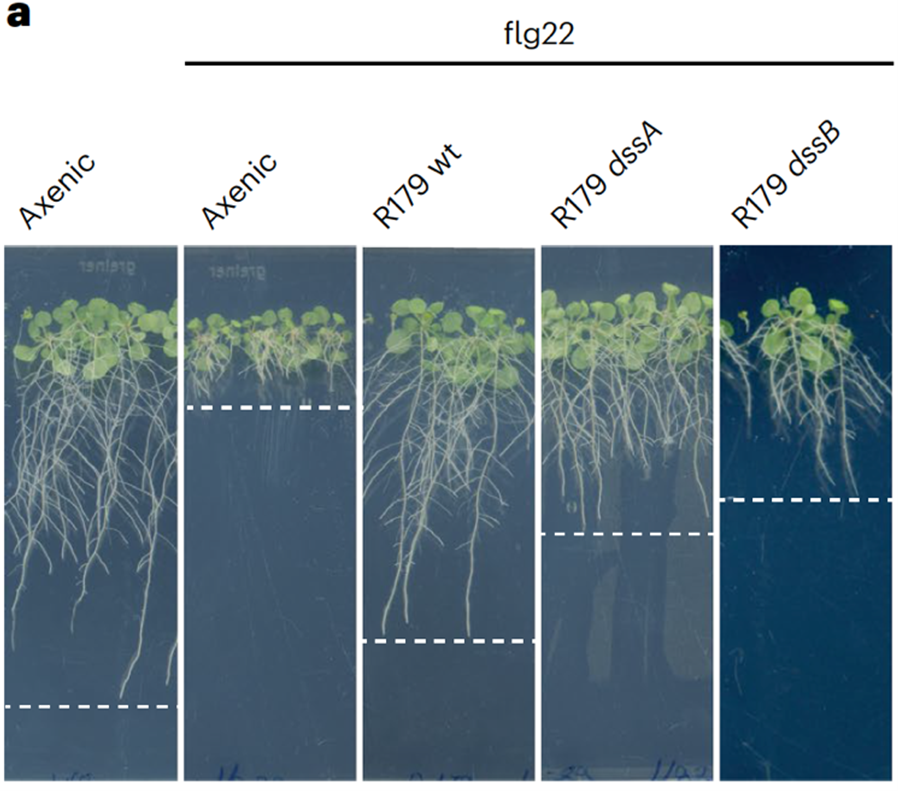
Stealth mode: How Rhodanobacter R179 evades plant immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe soil microbiome harbors a vast diversity of microorganisms that can be pathogenic, beneficial, or commensal to plants. A fundamental question in plant biology is how plants actively detect, differentiate, and optimize their associations with the microbiome to maintain optimal fitness. In a recent…
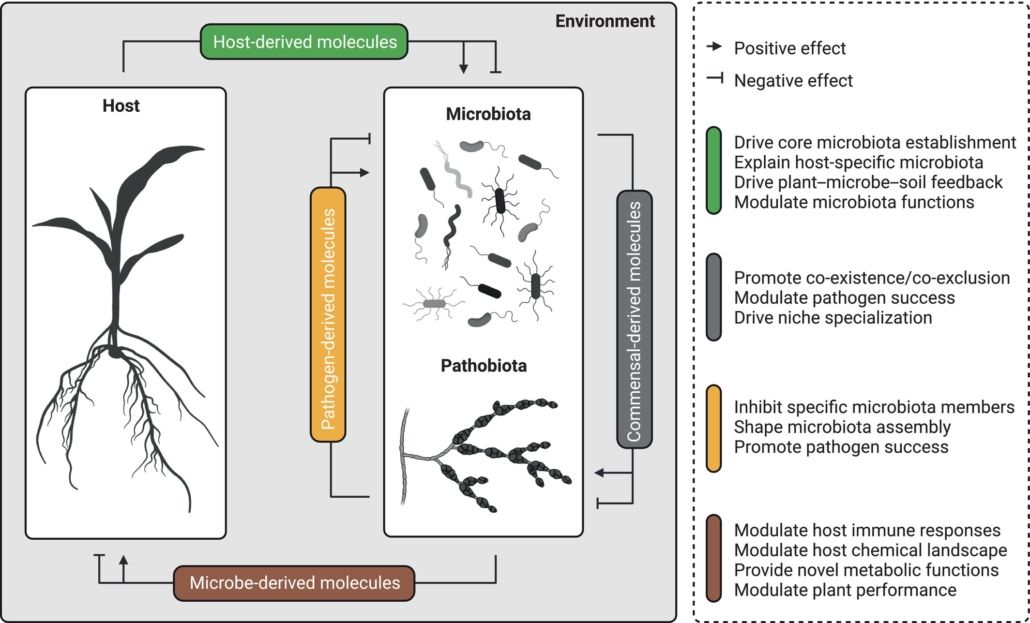
Virtual issue: The chemical language of plant–microbe–microbe associations
Plant Science Research WeeklyDon’t miss this exciting Virtual Issue from New Phytologist on “plant-microbe-microbe” interactions. That’s not a typo – many of the articles address the signals that coordinate such multi-factorial interactions, as there is a growing recognition that interrelations between microbes influence…
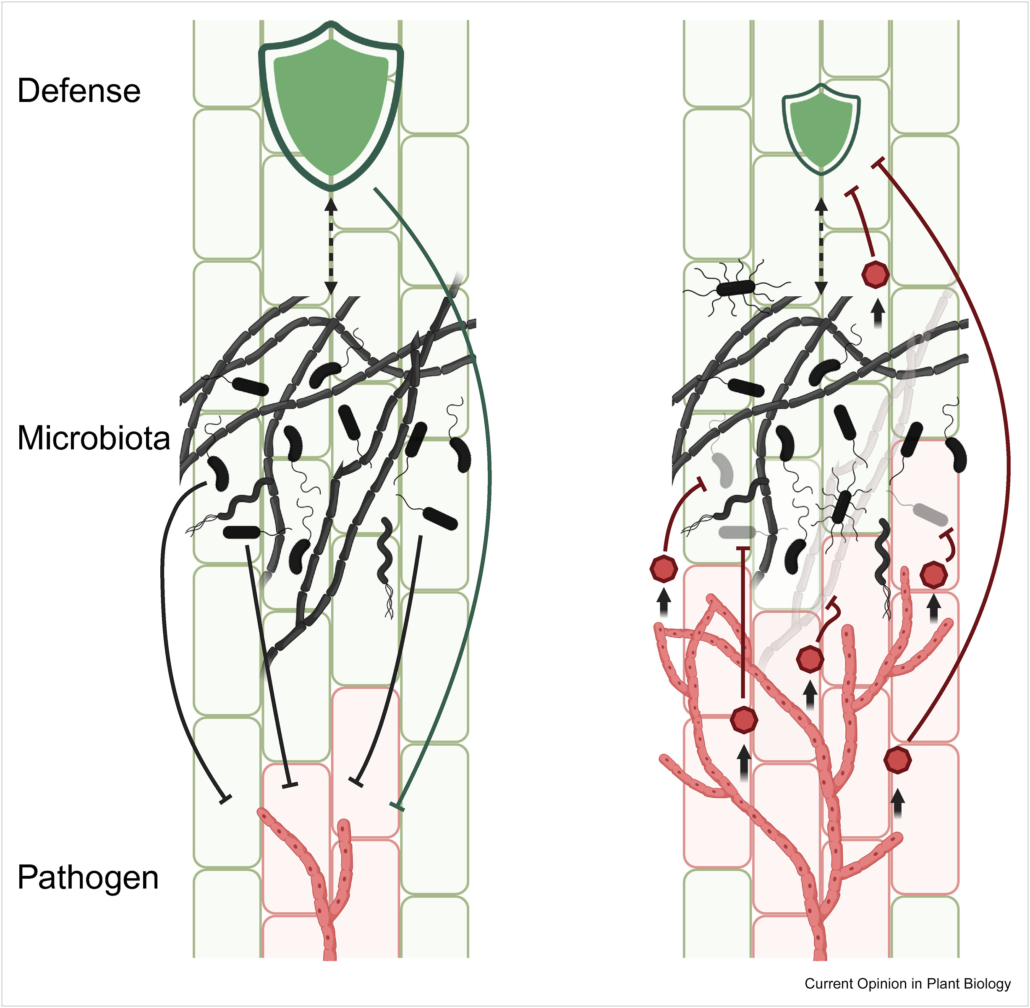
Review. Microbial tug-of-war: How plants and pathogens manipulate microbiomes
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe composition of plant-associated microbes is influenced by plant genetics, immune responses, environmental factors, and interactions between microbes. During disease development, the microbial community at infection sites changes due to tissue damage, altered immune responses, and manipulation via…
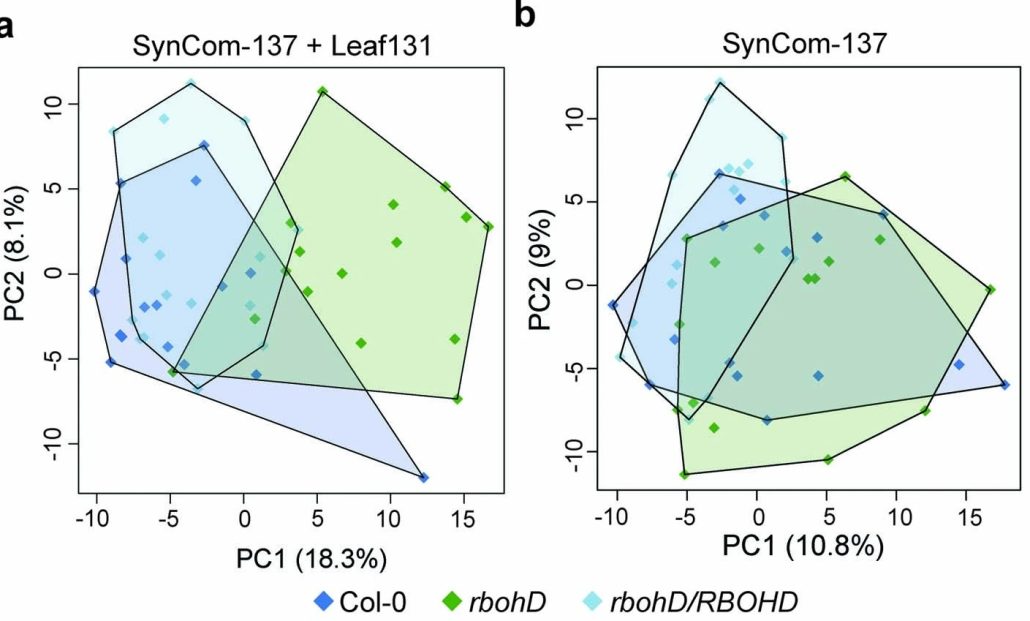
An opportunistic plant pathogen disrupts leaf microbiome through secretion of plant cell wall degrading enzymes
Plant Science Research WeeklyHealthy plants possess a functional immune system, and their leaves harbor a structured microbial community, including opportunistic pathogens. These opportunistic pathogens can trigger plant diseases under conducive conditions, such as when plant immunity is compromised, and the microbial community…

From friend to threat: the mutualist-pathogen transition of plant-fungal interaction is determined by a small gene cluster
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe infection modes of microbes in hosts can be reversible and can range from pathogenic to mutualistic, depending on the environmental conditions. The plant-associated fungus Colletotrichum tofieldiae (Ct) has been shown to promote primary root growth and increase shoot fresh weight of Arabidopsis in…
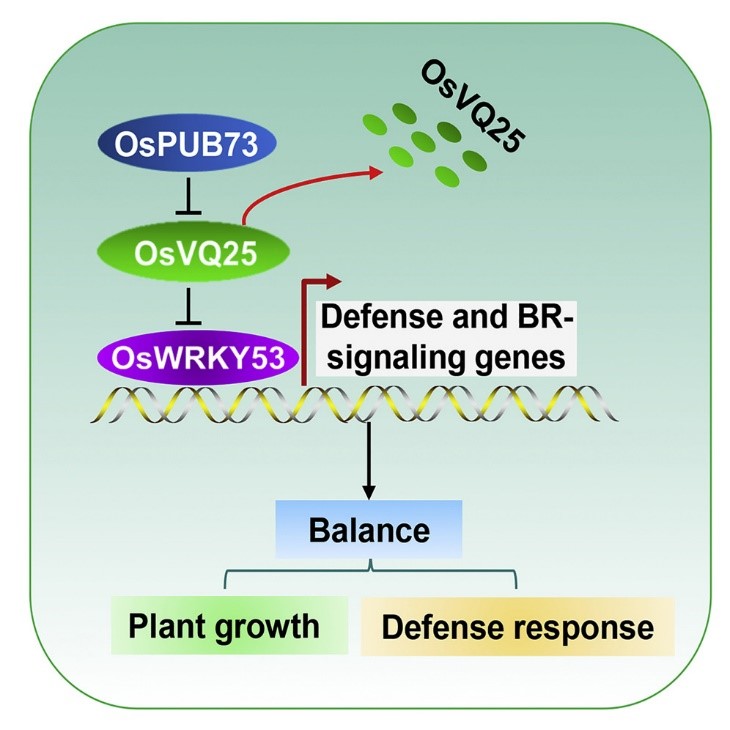
Identification of a cell signaling cascade that regulate s broad-spectrum resistance (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany different pathogens attack plants, and many genes have been identified that confer pathogen-specific resistance. In a recent study, Hao et al. identified a signaling cascade that regulates broad-spectrum disease resistance. This pathway is composed of a rice ubiquitin ligase OsPUB73, a VQ motif-containing…

