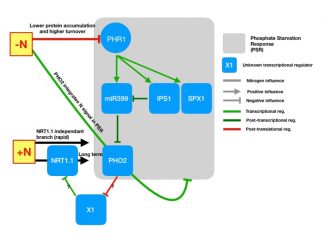
Nitrogen actively controls phosphate starvation response in plants (Plant Cell) ($)
Phosphate and nitrogen are two essential macronutrients for growth of plants. The homeostasis and sensing pathways for these two macronutrients have been investigated extensively, but independently. Recently, -omics approaches have enabled finding interlinks and cross talks between two or more macronutrients.…
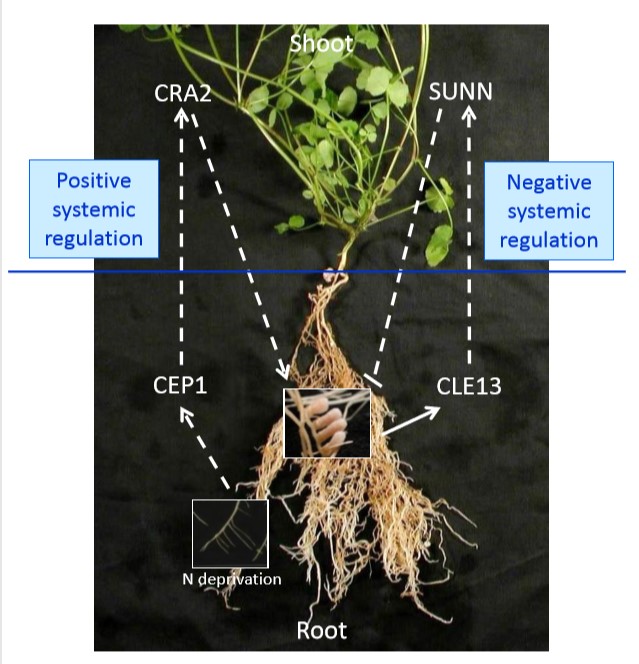
Independent regulation of symbiotic nodulation by the SUNN negative and CRA2 positive systemic pathways (Plant Physiol) ($)
Autoregulation of nodule development (AON) is a process by which leguminous plants control nodule development. SUNN, a LRR-RLK, and a systemic CLE peptide play a negative role in nodulation through systemic signaling. In this paper Laffont et al. showed the another systemic regulation of nodulation in…
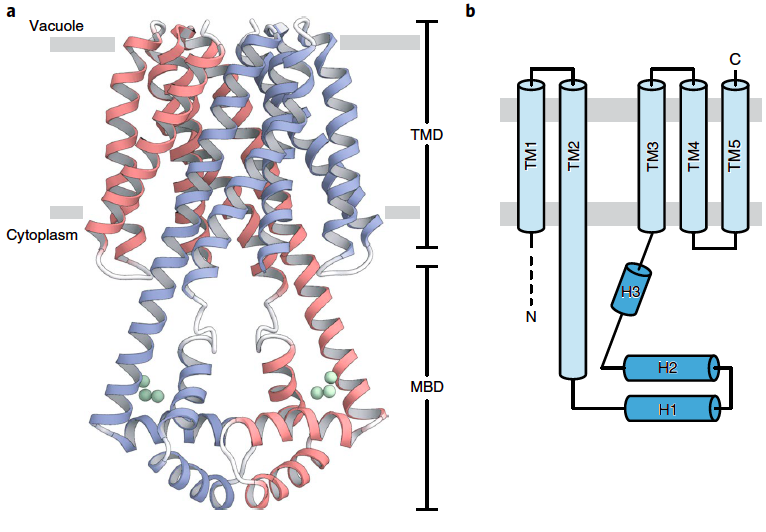
Crystal structure of plant vacuolar transporter VIT1 (Nature Plants) ($)
Iron is an essential nutrient for plants that participates in cellular processes such as DNA replication, photosynthesis, and respiration. Excess iron accumulation is harmful to plants due to its participation in the generation of reactive oxygen species, which can damage cellular machinery. One of the…
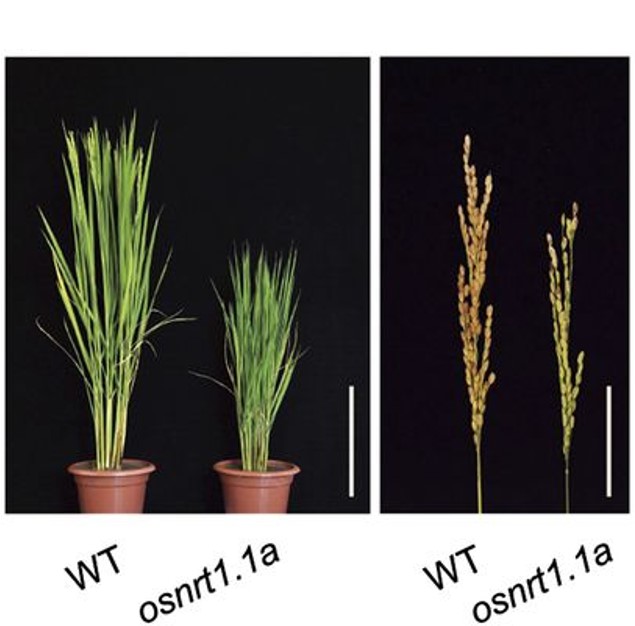

Nitrate transporter gene OsNRT1.1A/ OsNPF6.3 confers high yield in rice (Plant Cell)
In many ecosystems, nitrogen (N) is a limiting factor for plant growth. In agro-ecosystems, the application of synthetic N fertiliser has solved that issue. However, N fertiliser application is costly both to the farmers and the environment (in terms of N leaching and atmospheric release of greenhouse…
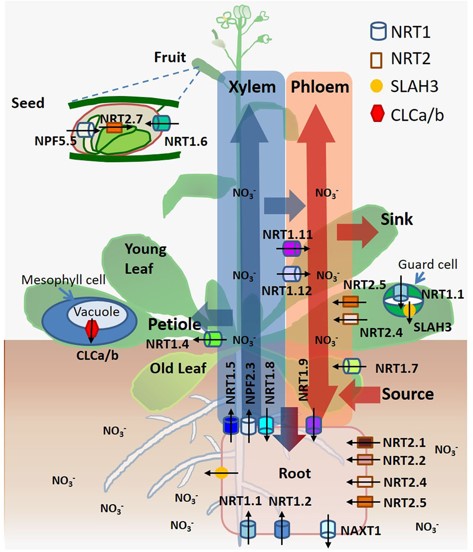
Dancing with hormones: A current perspective of nitrate signaling and regulation in Arabidopsis (Frontiers in Plant Science)
Nitrogen (N) is a main constituent of amino acids and nucleotides and therefore plays a central role in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plants are able to take up nitrogen from the soil in two forms, nitrate and ammonium. Nitrate is the predominant form of nitrogen found in most crop…
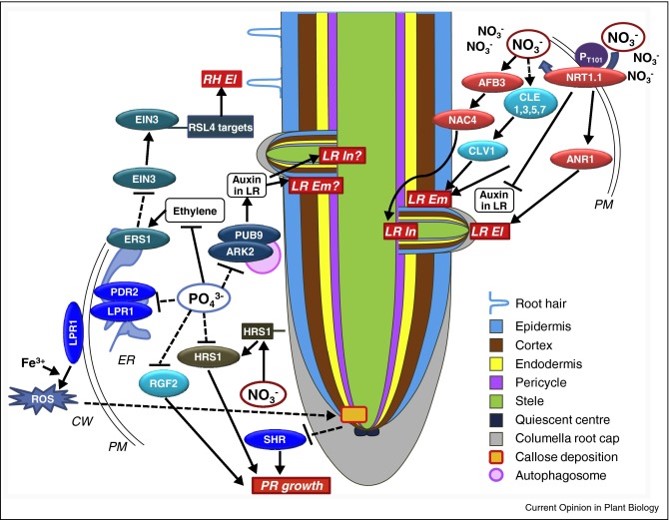
Food for thought: How nutrients regulate root system architecture (Current Opinion in Plant Biology)
The arrangement of a plant’s root system in the soil (root system architecture, RSA) changes in response to nutrients through different signaling pathways. It is assumed that RSA adapts to optimize the uptake of nutrients from the environment, but strong evidence is still lacking. This review by Shahzad…
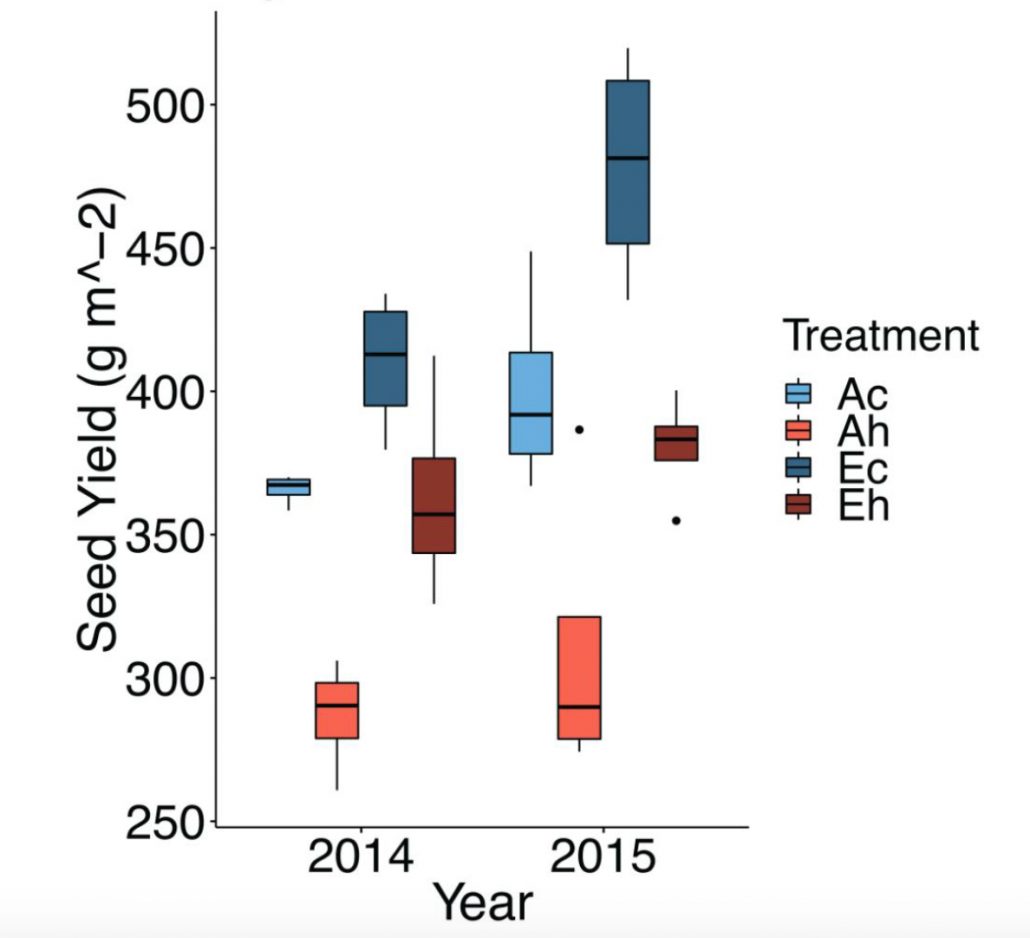
Increased temperatures may safeguard the nutritional quality of crops under future elevated CO2 concentrations (Plant J)
Increases in atmospheric CO2 have been shown to confer enhanced photosynthetic rates, boosting plant growth and yield. Unfortunately, there is evidence that the content of minerals important for human health are reduced in both the foliar and edible tissues when plants are grown under elevated CO2…
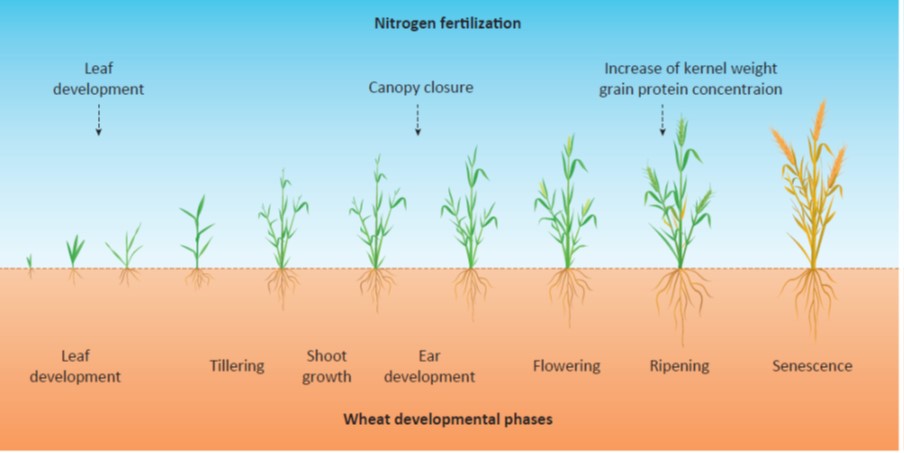
Review: Perspective on wheat yield and quality with reduced N supply (TIPS)
Wheat production demands huge inputs of nitrogen as fertilizer, with accompanying financial and environmental costs. Zorb et al. discuss several strategies by which to maintain wheat yields and wheat quality while decreasing N use and wastage. Some of these are agronomic, such as ensuring that the N…
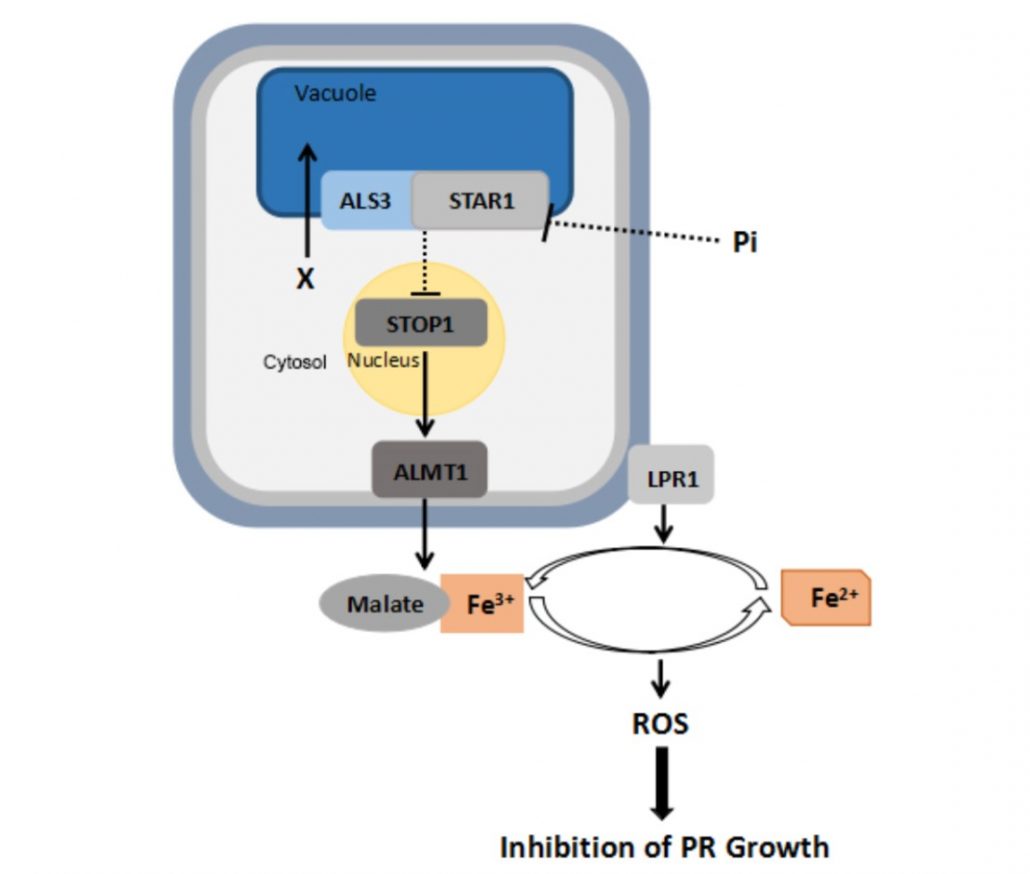
Genetic dissection of Fe-dependent signaling in root developmental responses to phosphate deficiency ($)
Phosphate deficiency leads to arrest of primary root elongation. Previous work has shown that this arrest depends upon Fe, raising the possibility that Fe accumulation in the root apex is the cause of growth arrest. Several genes involved in low Pi response have been identified, including genes encoding…

