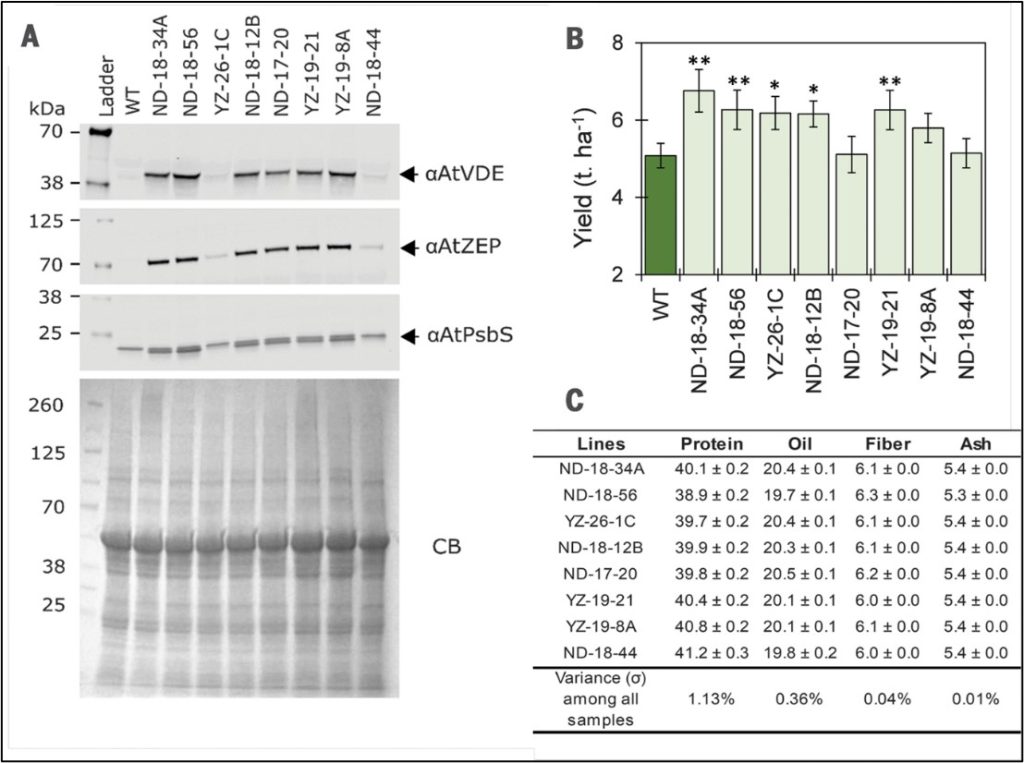
Improved soybean photosynthesis and yield by accelerating recovery from photoprotection
Plant Science Research WeeklyEnhancing crop yield for future food supplies involves increasing photosynthetic efficiency, which can be achieved by improving photoprotection through non-photochemical quenching (NPQ). NPQ enables leaves to dissipate excess absorbed light energy as heat, minimizing the negative effects of photodamage.…
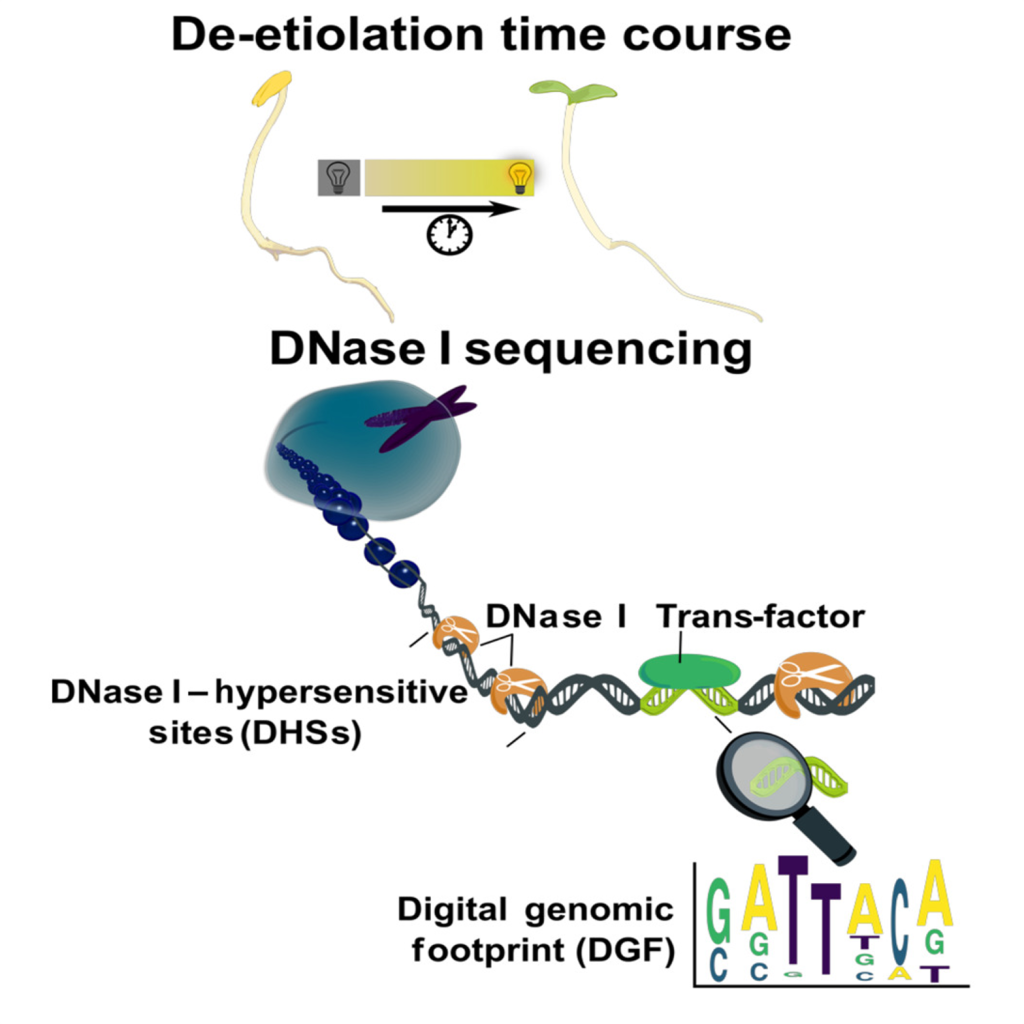
Gaining cis-elements contributed to enhanced expression of C4 genes
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 photosynthesis is derived from C3 photosynthesis. When related genes are compared, those involved in C4 photosynthesis tend to be more highly expressed. To understand this phenomenon, Singh et al. undertook a very impressive approach to look at transcriptional regulation of essentially all the photosynthetic…

Roots are the ‘kitchen’ for leafless epiphytic orchids
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is the major process which supports plant survival. It’s the kitchen serving food (sugars) to the plant by converting the light energy. Leaves are the major site of photosynthesis for most plants. However, certain plants evolved unconventional ways of performing photosynthesis. In a…

Recruiting the ATP-generating nanomotor in chloroplasts
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellReiter et al. investigate the molecular basis for coupling factor CF1 recruitment in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell (2022).
By Thilo Rühle
Background: Thylakoid ATP synthases are impressive molecular engines that harness the light-driven proton gradient to generate ATP during photosynthesis.…
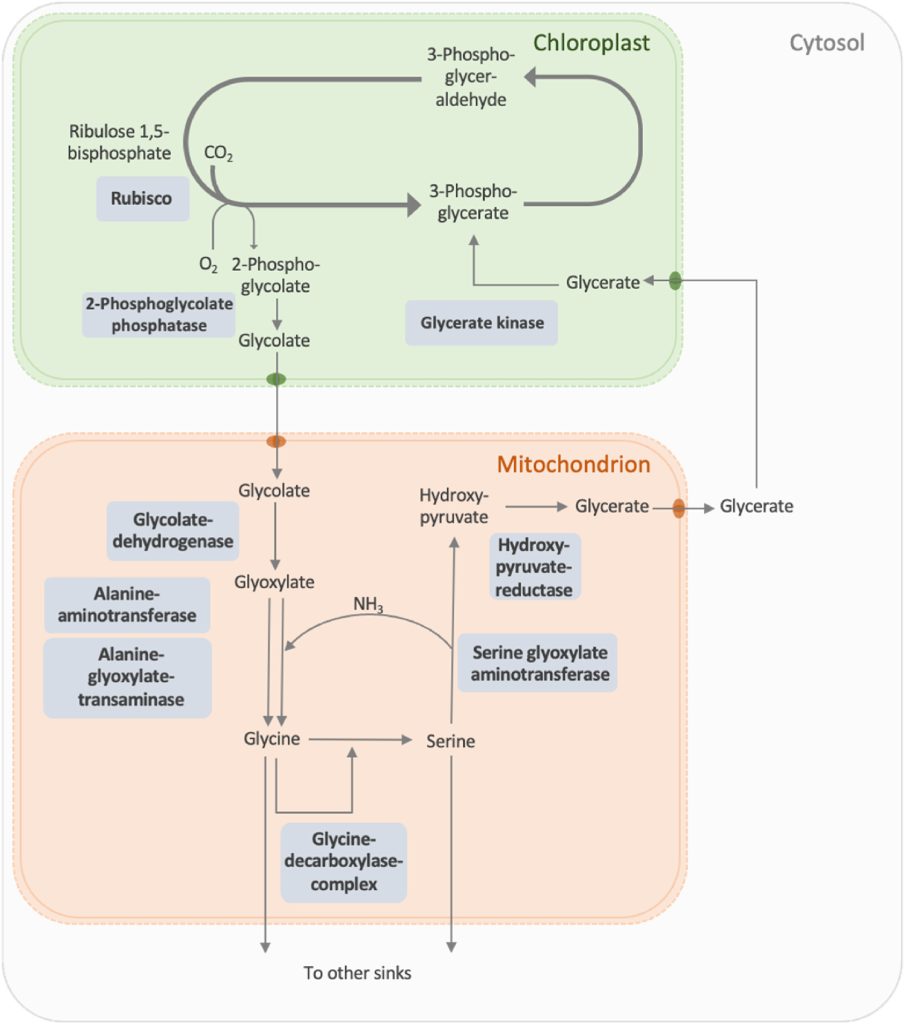
Review: Photorespiration is the solution, not the problem
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is one of a kind, simultaneously recognized as one of the most abundant and important enzymes, and also widely characterized as flawed because it uses both O2 and CO2 as substrates, leading to both carboxylation and oxygenation of ribulose bisphosphate.…
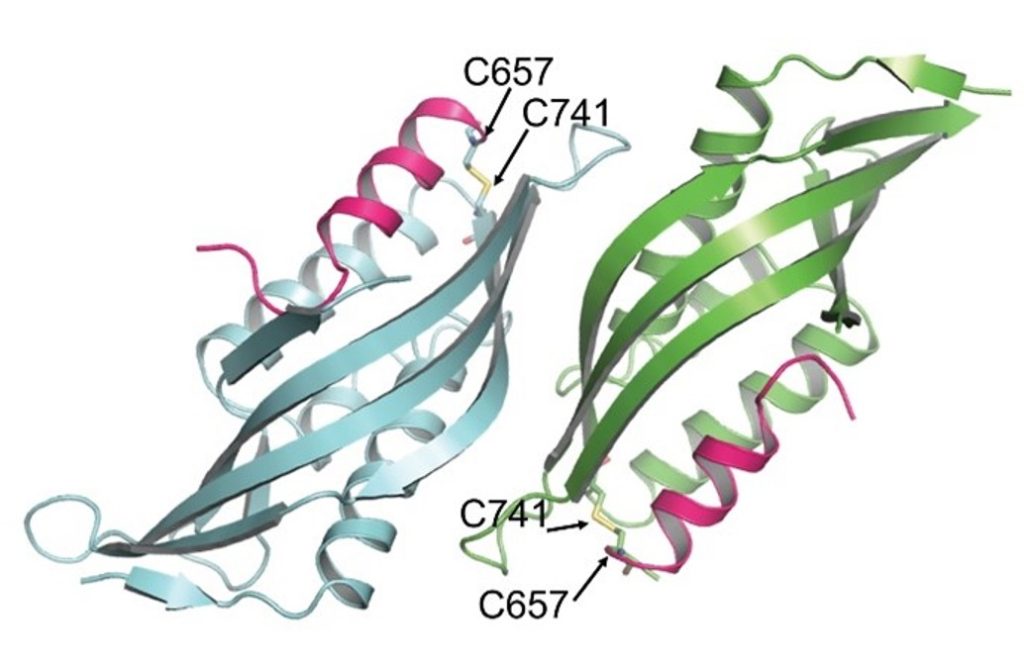
Insights into the chloroplast division site regulators and light
Plant Science Research WeeklyChloroplasts divide by binary fission driven by a protein ring, the position of which is regulated by the Min system (derived from the system in bacteria). The inner envelope membrane protein PARC6 (PARALOG OF ARC6) is a key component. Here Sun et al. generated crystal structures showing that PARC6 interacts…
Special issue: Rubisco and its regulation
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyzes the fixation of atmospheric carbon from CO2 to molecules used for biosynthesis and energy production. Several studies have focused on understanding the nature, complexity, activity, and regulation of Rubisco due to its key role in the production…
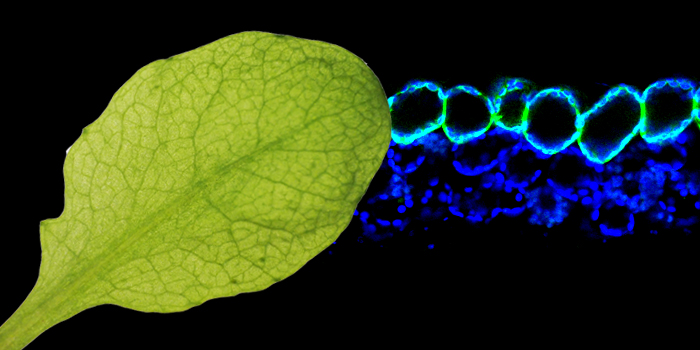
Similar yet different: A leaf photosynthetic cell type reveals its unique molecular blueprint
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellProcko et al. investigate the molecular identities of specialized photosynthetic cell types in leaves.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac167
By Carl Procko and Travis Lee.
Salk Institute for Biological Studies, CA
Background: Photosynthesis is arguably the most important biochemical process…
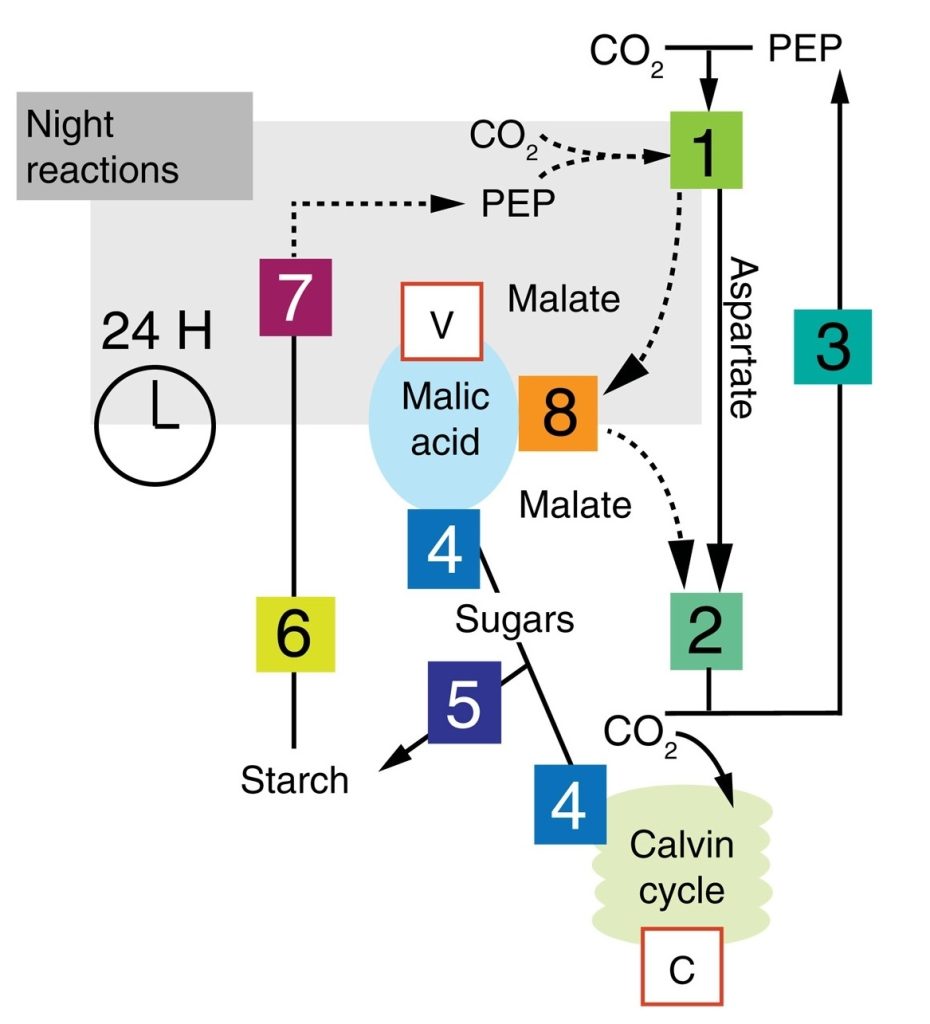
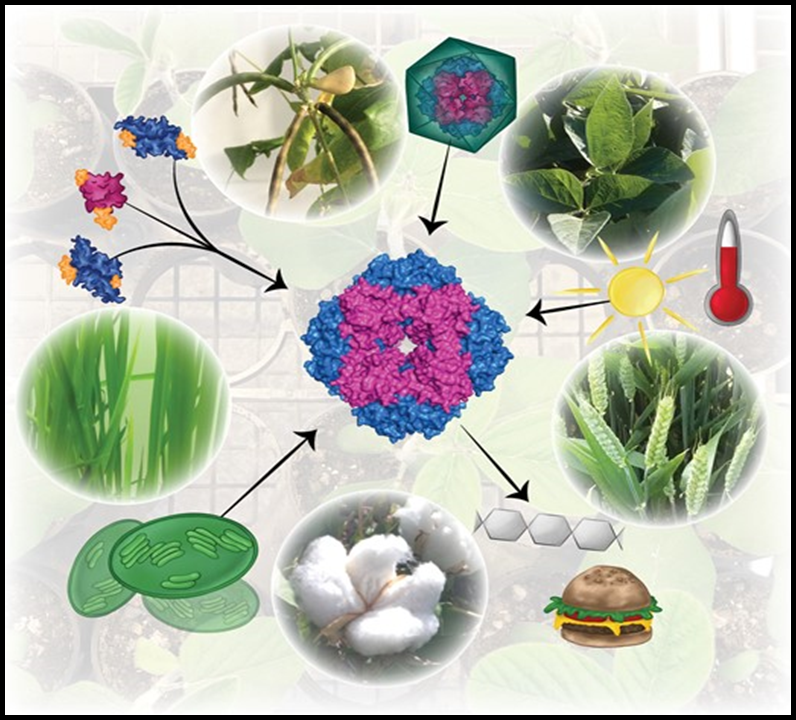
Spatial resolution of an integrated C4+CAM photosynthetic metabolism (Sci. Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 and CAM are both photosynthetic strategies that concentrate CO2 upstream of RuBisCO, somewhat uncoupling photosynthetic carbon fixation from transpirational water loss. Both strategies use the enzyme PEP-carboxylase to produce an organic acid, which can then be decarboxylated to provide CO2 to RuBisCO.…

