
The Future of Phenomics Enabled Biology: Key Takeaways from Phenome 2018
Blog, Plantae Webinars, Research0 Comments
/
The Future of Phenomics Enabled Biology: Key Takeaways from Phenome 2018
Recorded March 2018
About This Webinar:
In this webinar, Carolyn Lawrence-Dill and Joshua Peschel, members of the Phenome 2018 Organizing Committee, discuss the key takeaways from the February 2018 conference held in Tucson,…
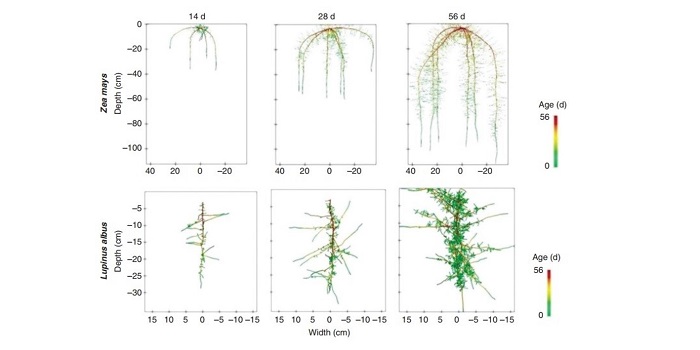
CRootBox: a structural – functional modeling framework for root systems (Ann Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot architecture is important to understand the response of plants during biotic and abiotic stress conditions. Root growth is mostly under soil, which deprives us of the ability to observe its development and growth pattern. In this paper, Schnepf et al. present CRootBox, a framework developed based…
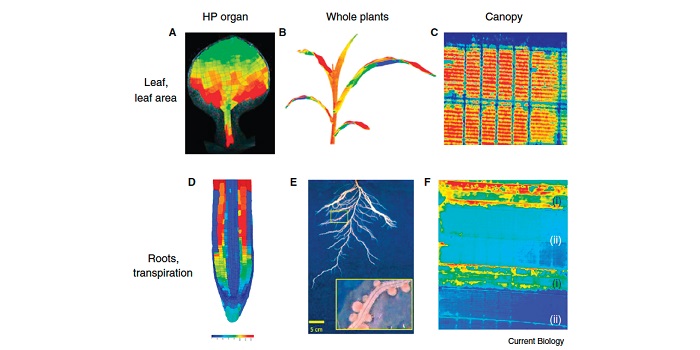
Review: Plant phenomics, from sensors to knowledge ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog
Plants adapt their form, function and metabolism to the surrounding environment. According to Tardieu et al., understanding the plant phenome requires that plant phenotypes to be studied on different spatial and temporal scales. High precision platforms are instrumental for discovery of new physiological…
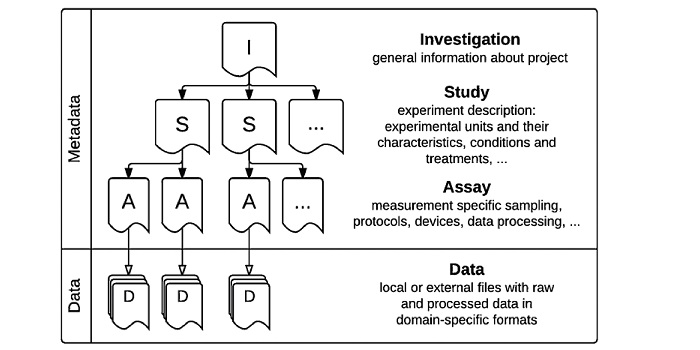
Measures of interoperability of phenotypic data: minimum information requirements and formatting
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog
If you ever tried to compare the results from two different experiments, you probably realized that small variations in the environment have big impact on how the plants grow. There is a lot to be learned from how the variation in the environment affects plant phenotypes, but currently the description…
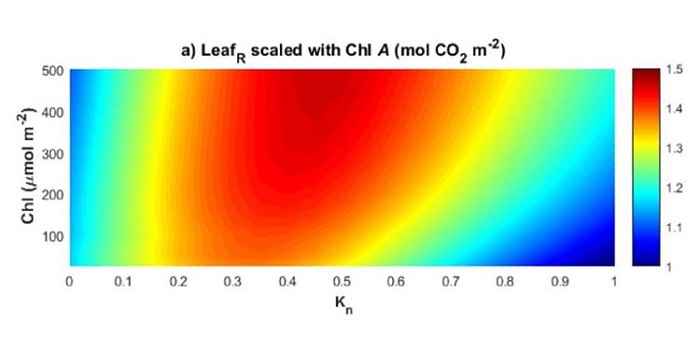
Chlorophyll can be reduced in crop canopies with little penalty to photosynthesis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe effect of reducing leaf chlorophyll content on canopy CO2 assimilation (Acan) is somewhat contentious. Walker et al. obtained data from 67 soybean accessions to parameterise a canopy-root-soil model (MLCan) in order to simulate the effect of altering chlorophyll levels on Acan. There was no increase…

Deep learning for multi-task plant phenotyping
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDespite the significant developments in computational biology and modern plant breeding, crop phenotyping poses challenges for automation. Previous machine learning approaches of plant phenotyping have mainly focused on leaf counting in rosette forms or leaf segmentation, and rely on large datasets not…

New Teaching Tool: Root Phenomics
Blog, Education, Resources, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News, UndergraduateMeet the newest member of the Teaching Tools in Plant Biology family, Phenomics of root system architecture: Measuring and analyzing root phenes -By Larry York and Guillaume Lobet.
This teaching tool discusses the relatively young field of root system architecture quantification. It introduces the concepts…
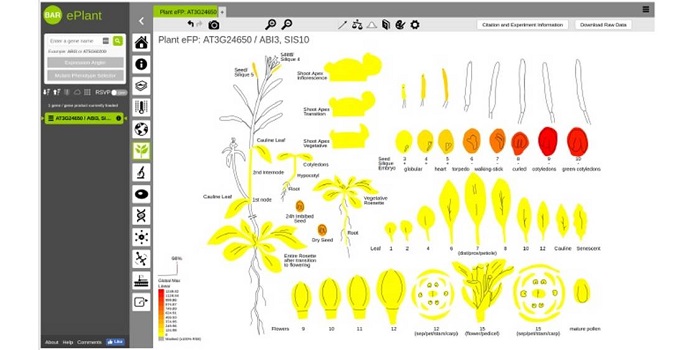
ePlant: Visualizing and exploring multiple levels of data for hypothesis generation ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe application of systems biology is quite phenomenal these days for prediction-based modeling and interactive data visualization. Along with the genome sequencing of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, there has been a parallel increase in systems biology tools. Unfortunately, these tools have been…
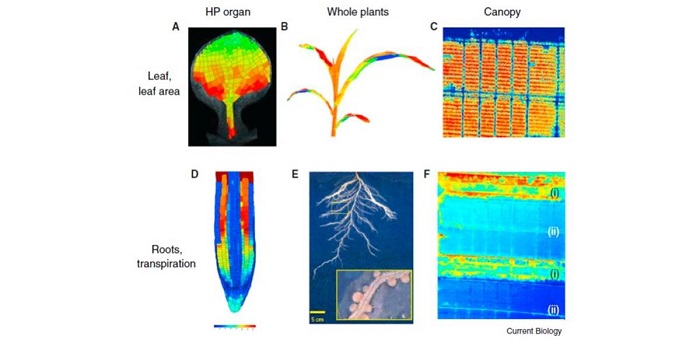
Review: Plant phenomics, from sensors to knowledge
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTardieu et al. have written a comprehensive and very readable overview of the current state and future challenges of plant phenomics, which they define as “the development and application of the suite of tools and methods used for three major goals — (1) capturing information on structure, function…

