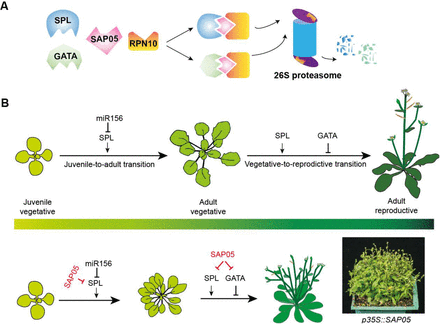
Phytoplasma effector physically interacts with host proteasome to promote bacterial growth
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs a way to circumnavigate the plant innate immune system, phytopathogens evolved effector molecules that protect the pathogen from the plant’s defenses. SAP05, an effector from the insect-vectored phytoplasma Candidatus (a bacterial obligate parasite), is responsible for the plant phenotype observed…
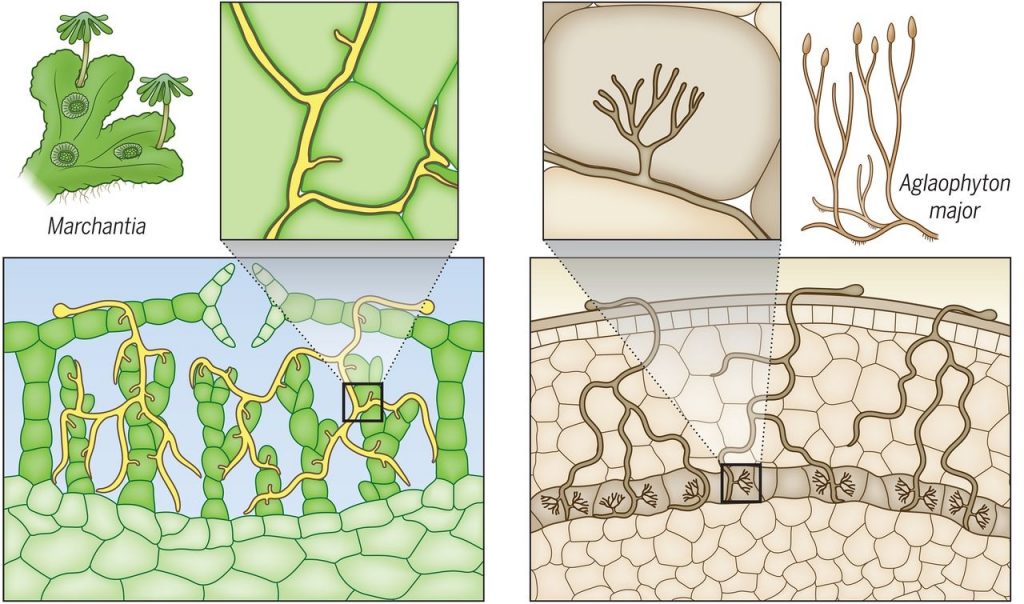
Review: Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the great questions in plant science has been, “How do plants recognize friend from foe?” Like most great questions, this one benefits from a historical perspective. In their new review, Delaux and Schornack look at plant evolution through the lens of plant interactions with symbiotic and…
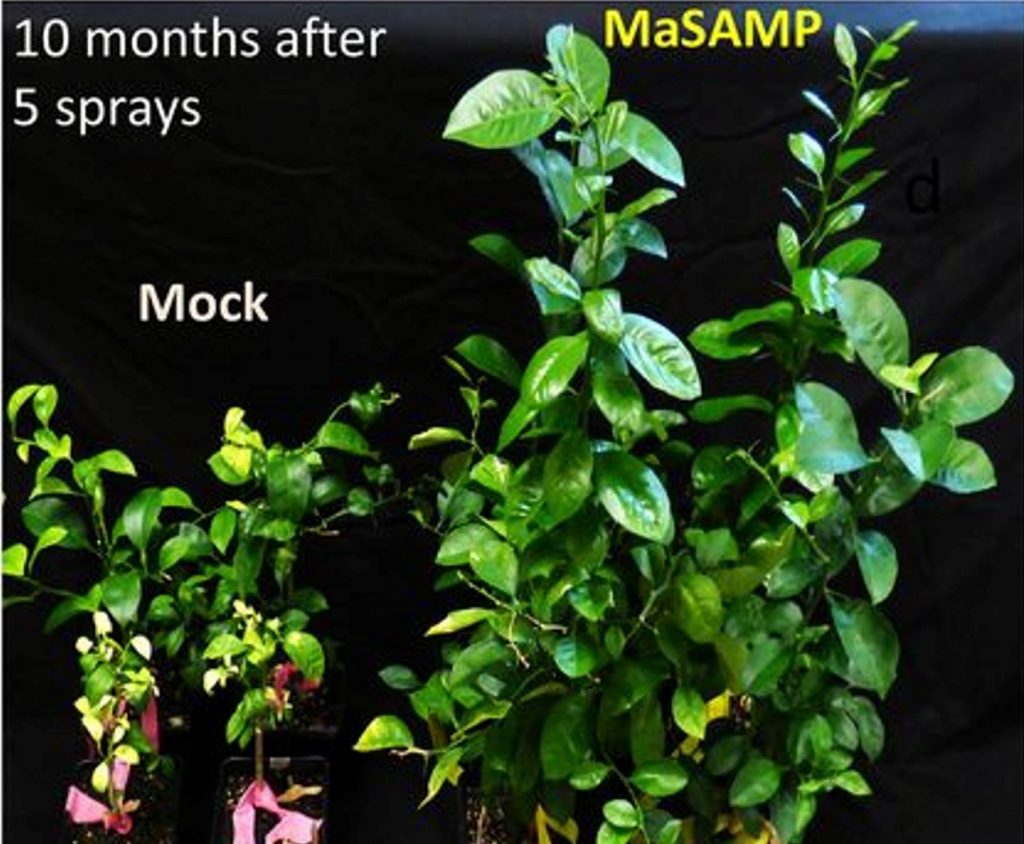

A stable antimicrobial peptide with dual functions of treating and preventing citrus Huanglongbing (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCitrus Huanglongbing (HLB) caused by the bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) is the most destructive disease of citrus and currently has no cure. Current management practices are also not effective. Huang et al. used comparative analysis of small RNAs and mRNAs between HLB-sensitive and…

Plant cell layer-specific responses against pathogenic and beneficial microbes (Cell Host & Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots are composed of concentric cell layers with distinct gene regulatory programs. Cell layer-specific responses are likely critical for plants to cope with microbes with various lifestyles, but little is known about root responses against microbes at cell-layer resolution. Fröschel et al. tackled…
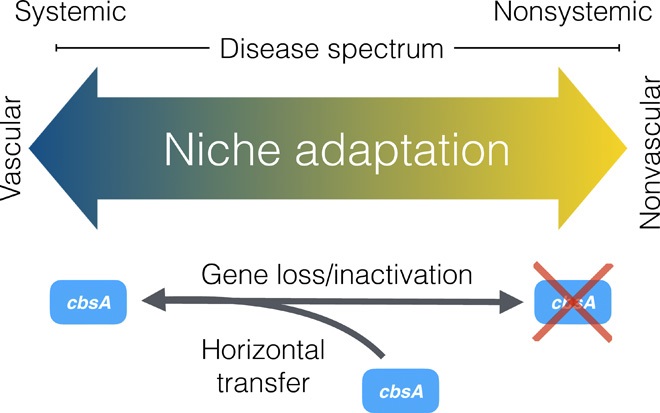
Repeated gain and loss of a single gene modulates the evolution of vascular plant pathogen lifestyles (Science Advances)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Within the bacterial genus Xanthomonas there are many plant pathogens, some of which colonize living cells within leaves, and others of which are vascular pathogens that colonize and spread through vascular tissues. Gluck-Thaler et al. looked at genomes from sets of closely related bacteria that…
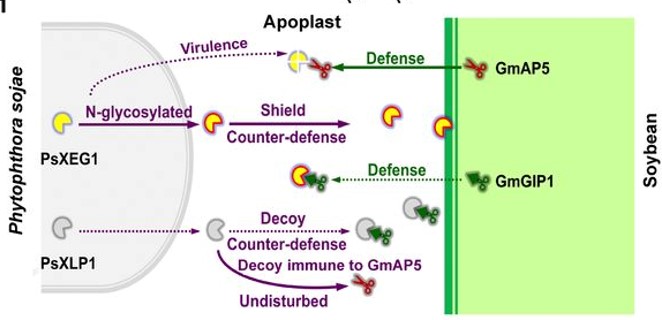
N-glycosylation shields Phytophthora sojae apoplastic effector PsXEG1 from a specific host aspartic protease (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Physicists say “for every reaction there is an equal and opposite reaction,” an expression that applies to the interactions between plants and pathogens as well. Here, Xia et al. have uncovered another layer in the “arms race” between soybeans and the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora sojae.…
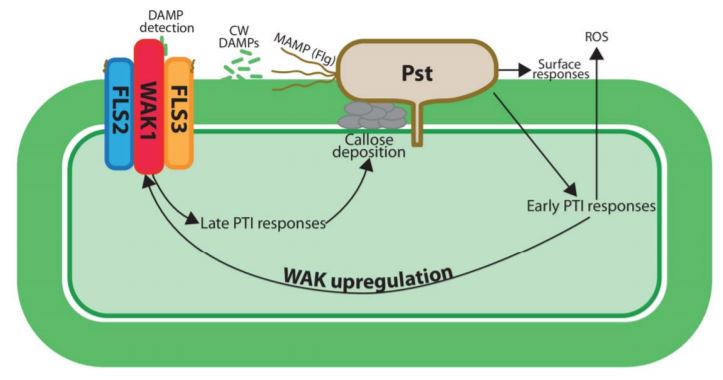
Sensing Attack: The Role of Wall-associated Kinases in Plant Pathogen Responses
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchSam Amsbury
Department of Animal and Plant Sciences, Sheffield, UK
ORCiD: 0000-0002-2767-9768
[email protected]
The physical and chemical barrier provided by the cell wall is one of the first lines of defence for plants against pathogen attack. Plant cell walls provide physical protection…

