
Friend or Foe? How fungi switch between helping and harming plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants coexist and interact with various microorganisms in the soil environment, including fungi. These associated fungi can not only cause diseases but also establish symbiotic interactions that boost plant health. This is the case of the endophyte Colletotrichum tofieldiae, where some strains can improve…
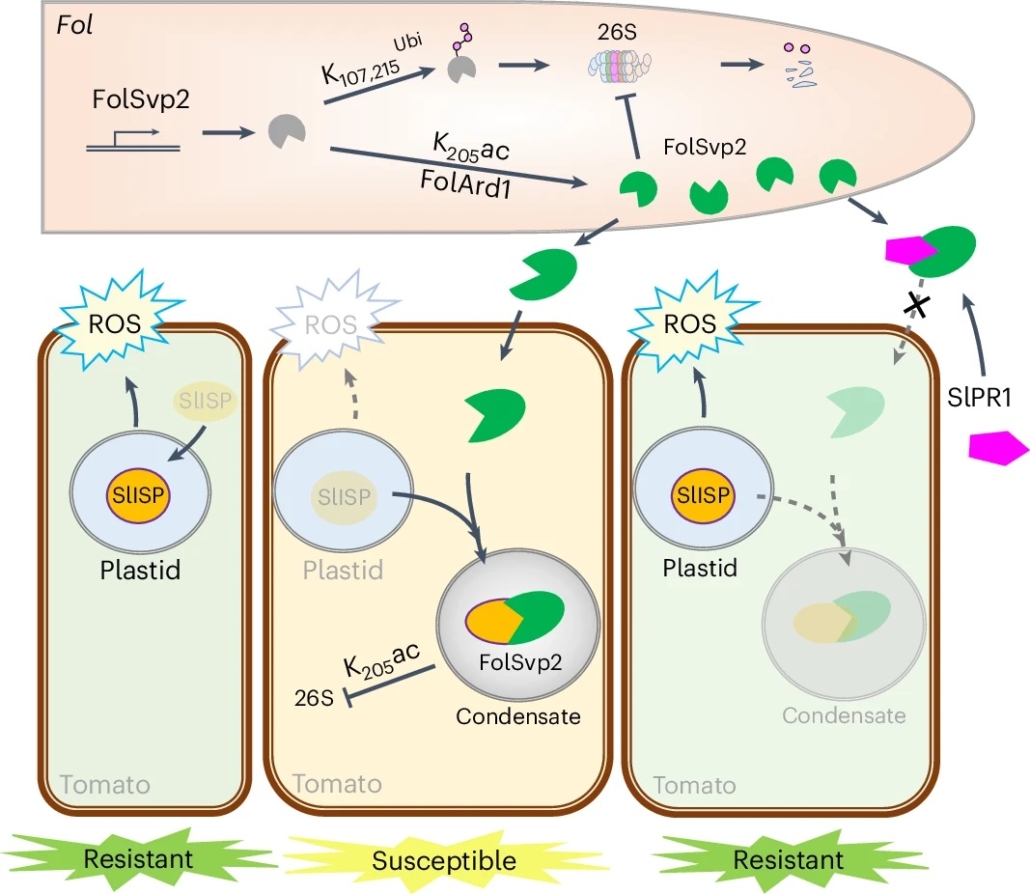
Tomato PR1 protein prevents the fungal effector FolSvp2 from suppressing SlISP-mediated ROS production
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and pathogens are locked in a co-evolutionary arms race. Pathogens secrete effectors into plants, leading to effector-triggered susceptibility. Plants in turn respond through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the expression of defence-related genes to defend themselves, which…
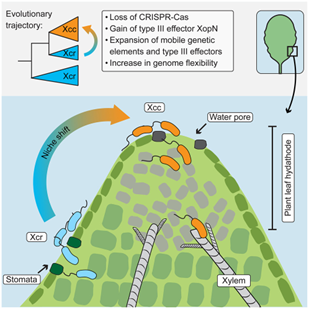
Shaping pathogenicity: How CRISPR-Cas loss fuels Xanthomonas evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved diverse infection strategies governed by virulence factors, often targeting specific host organs or tissues. Genome fluidity plays a crucial role in enabling microbial pathogens to adapt to the dynamic selection pressures imposed by co-evolution with their hosts. In a recent study,…
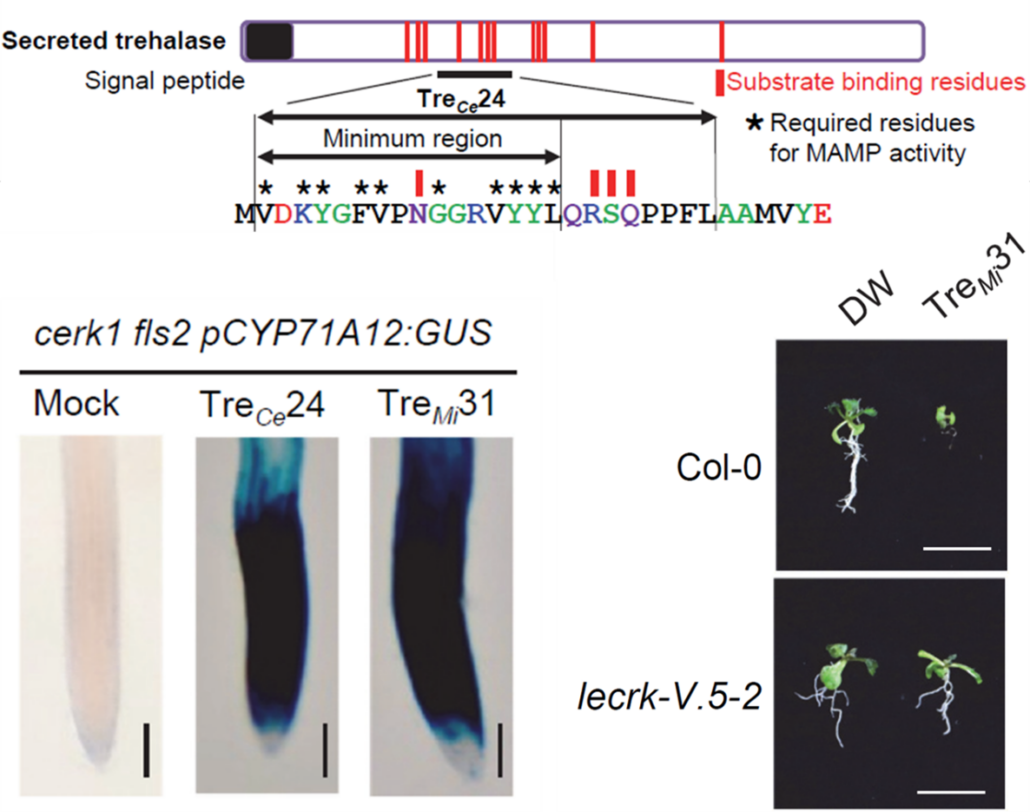
LecRK-V and trehalose-associated immunity: a conserved defense mechanism across kingdoms
Plant Science Research WeeklyMembrane-localized receptor-like kinases (RLKs) are essential for perceiving diverse signaling molecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, hormones, reactive oxygen species, ions, and damage-associated molecular patterns. Among the well-characterized RLKs, FLS2, EFR, and CERK1 are known to recognize…
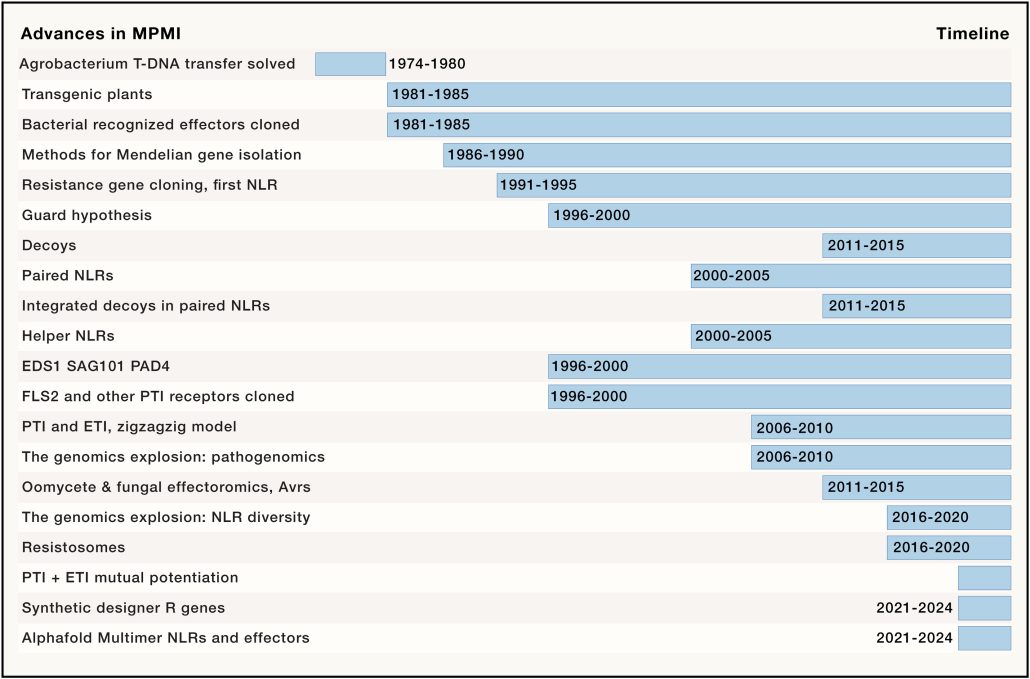
Review: The plant immune system: From discovery to deployment
Plant Science Research WeeklyA review of the past 50 years of plant immunity by Jones, Staskawicz, and Dangl? Yes please! I particularly enjoy historical perspectives of a discipline, as they frame conceptual breakthroughs with the benefit of hindsight. As the article lays out, understanding the plant immune system benefitted greatly…
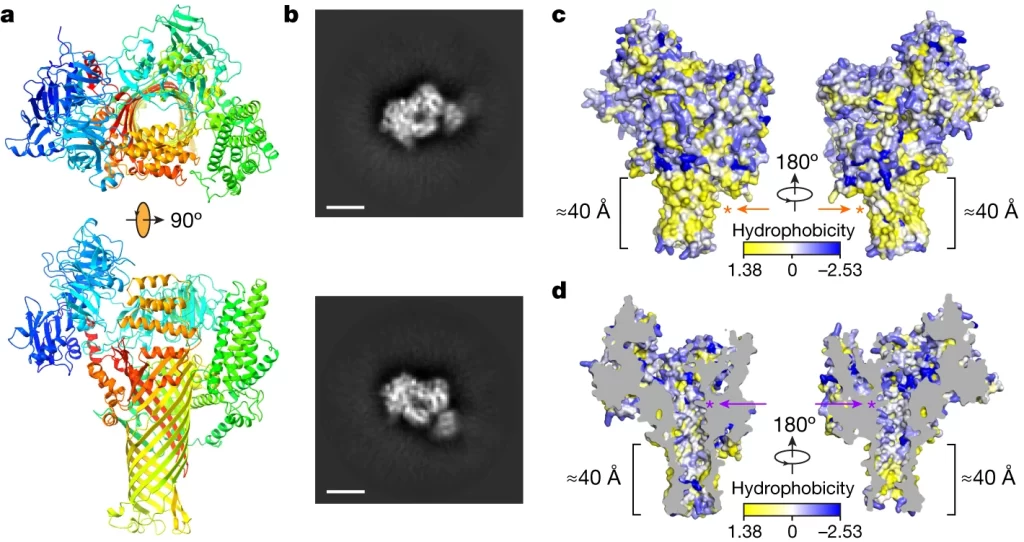
Bacterial pathogens deliver water- and solute-permeable channels to plant cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhat do you do when you’ve identified a gene that you know is important, but you don’t know how it functions? Usually, you can get hints from homology searches, overexpression studies, or the identification of protein domains, but sometimes those approaches don’t work. That’s where the story…
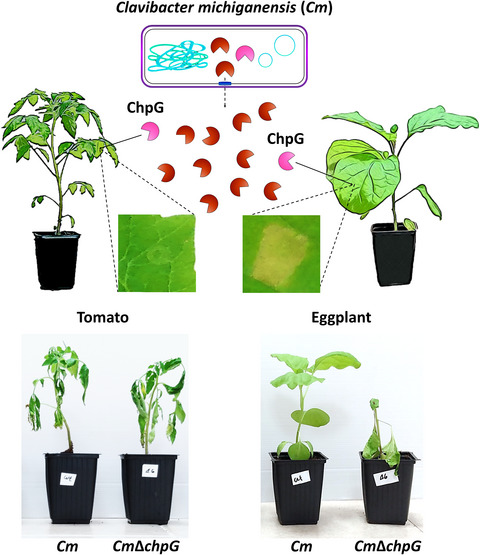
Bacterial avirulence gene encodes for a secreted protease and restricts host range (Mol Plant Path)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant pathogenic bacteria of the genus Clavibacter tend to have a narrow host range, but different species affect many important crops. Clavibacter michiganensis (Cm) causes bacterial wilt and canker in tomato, pepper and a few varieties of eggplant. There are no Cm-resistant tomato varieties but many…
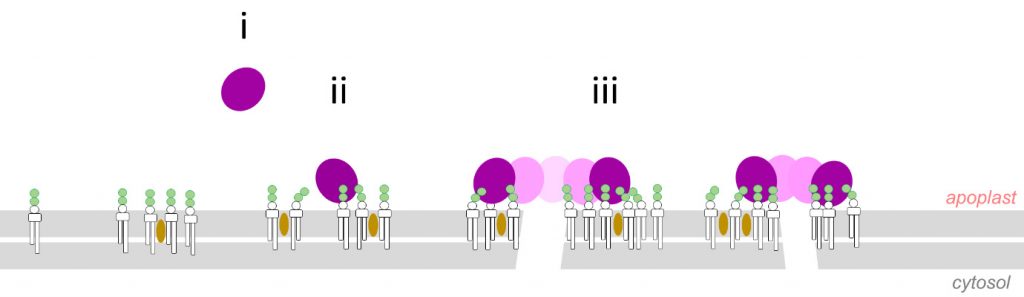
An oomycete peptide cytolysin forms transient small pores in lipid membranes (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNLPs (Necrosis and ethylene-inducing peptide 1–like proteins) are small peptides produced by a variety of plant pathogens. Some NLPs are cytolysins meaning that they trigger lysis of their target cells. Here, Pirc et al. use an assortment of tools including molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, neutron…
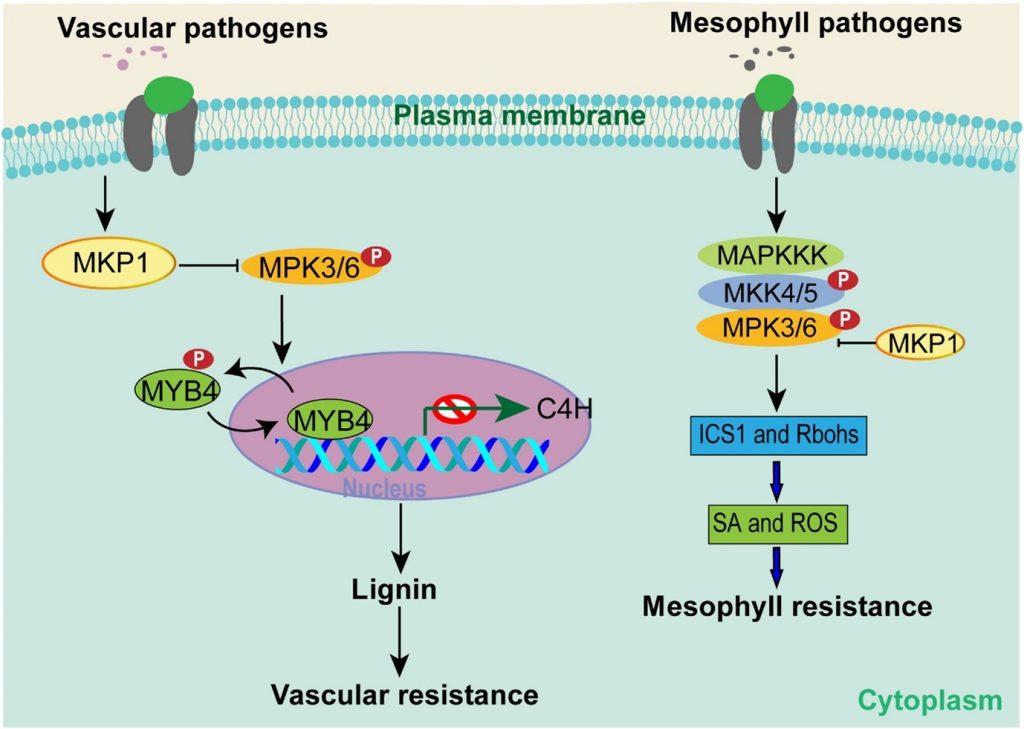
MAP kinase cascade acts as a hub to decide the ways to fight infection (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of plant immunity comes from studies of pathogens that infect mesophyll tissues, (e.g., Pseudomonas syringae). However, there are many pathogens that specifically invade vascular tissues (e.g., Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; Xoo), which causes rice bacterial blight. In a recent…

