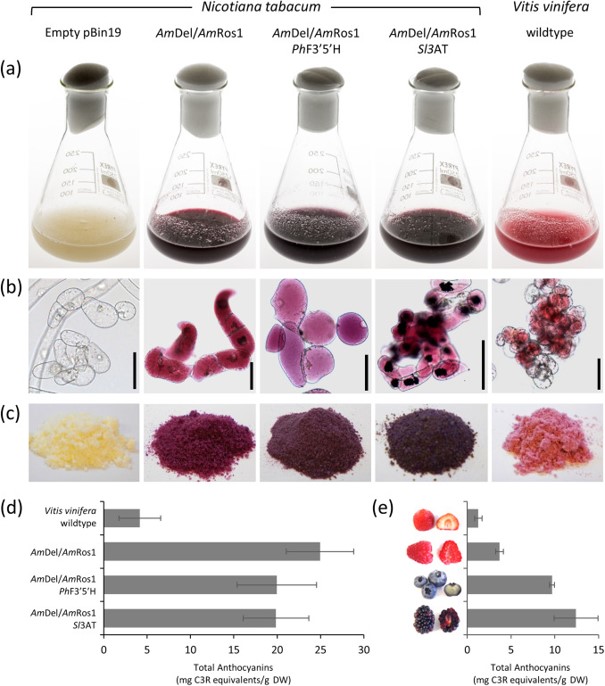

Colour bio-factories: Towards scale-up production of anthocyanins in plant cell cultures (Metabolic Engineering)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAnthocyanins are common plant pigments that provide dietary benefits, leading to an increase in their use as food coloring agents. However, purifying anthocyanins from current plant sources (such as waste grape skins, red cabbage, and berries) is expensive and creates a variable product. Modifying biosynthetic…
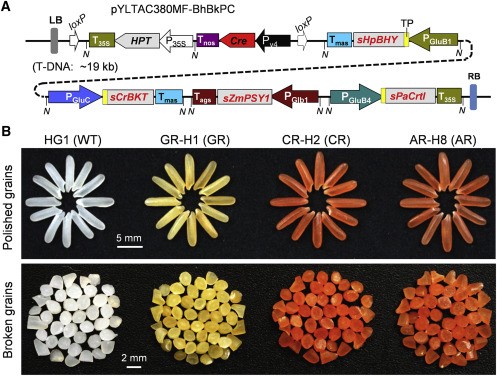
From Golden Rice to aSTARice: Bioengineering astaxanthin biosynthesis in rice endosperm (Molecular Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyZu et al., have successfully harnessed the power of synthetic biology to increase the nutritional content of rice by overexpressing only four synthetic genes in rice endosperm. Here, the authors have created a colorful gradient of carotenoid-enriched rice by expressing two, three, and then four genes…
Hydrogen Cyanide Regulation by S-Cyanylation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDespite its toxicity, cyanide has been proposed to act as a regulator of several biological processes such as seed dormancy and germination, resistance to fungal and viral infection. Arabidopsis null mutants of the mitochondrial enzyme β-CYANOALANINE SYNTHASE (CAS-C1) accumulate cyanide to apparently…
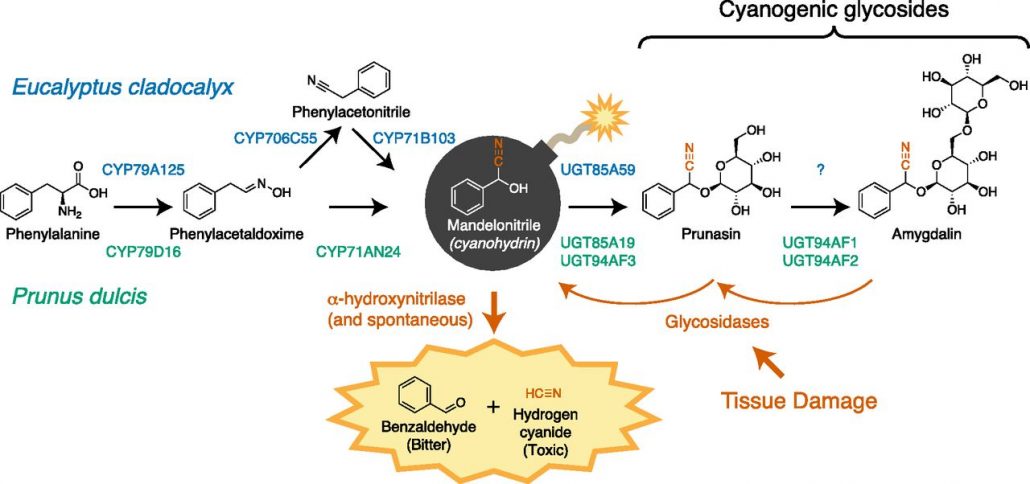
Setting and Diffusing the Cyanide Bomb in Plant Defense
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsHydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase, a conserved component of the respiratory electron transport chain in all aerobic life. Thus, HCN is well suited to serve as a broad-spectrum chemical defense, and indeed it plays such a role in many interactions between plants and…
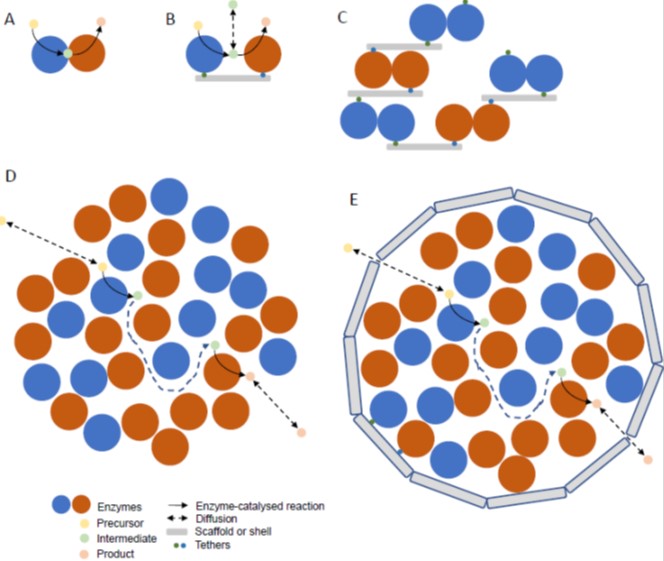
Update: Engineering of metabolic pathways using synthetic enzyme complexes
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Nicholas Smirnoff, University of Exeter. This article is part of the forthcoming Synthetic Biology focus issue.
Plants provide a source of enzymes for metabolic engineering to produce valuable or useful products in micro-organisms or can themselves be engineered (Andre et al., 2016; Vickery et…
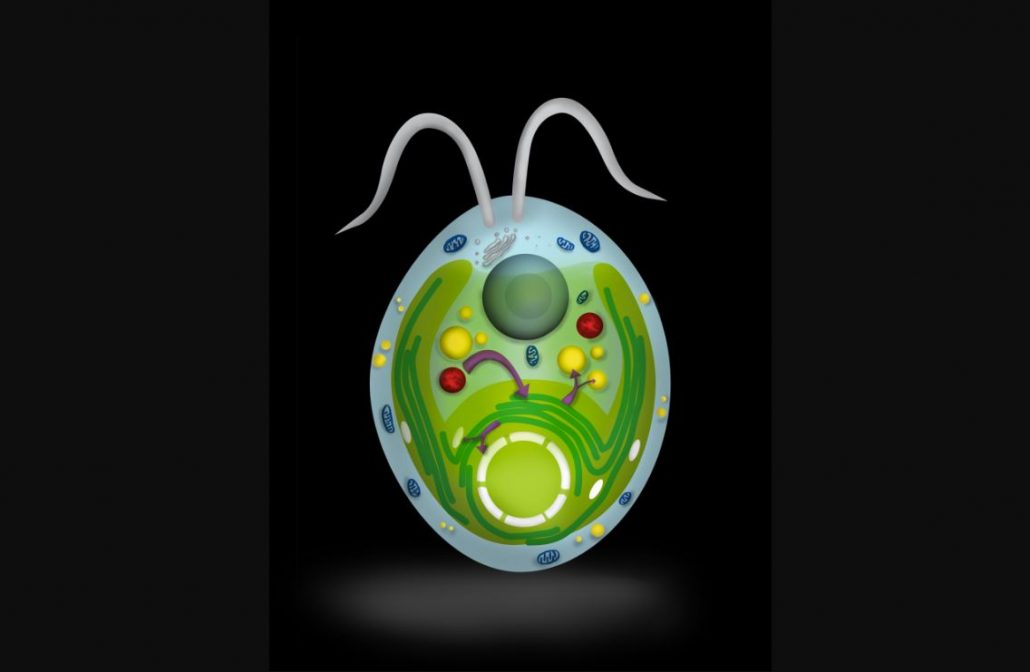
How Peroxisomes Modulate Chloroplast Activity in a Microalga
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBackground: Chloroplasts are the major powerhouse of plant and algal cells, where photosynthesis—the conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds using sunlight energy—occurs. Chloroplasts are also where important cell components (such as membrane lipids and pigments) and energy-rich compounds…
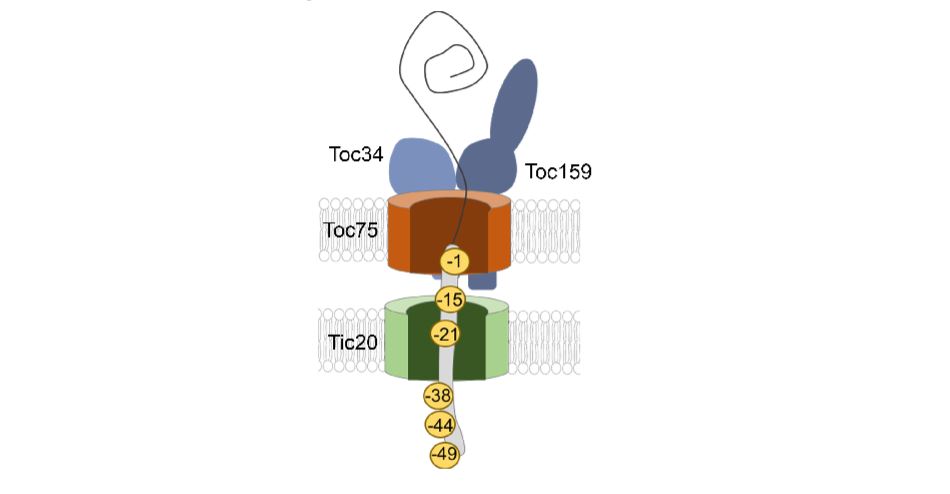
Taking the TOC/TIC path to the chloroplast
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellRichardson et al. explore the molecular topology of the chloroplast transit peptide and its nucleotide-dependent movement within the chloroplast protein import channel. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00172.
By Lynn GL Richardson and Danny J Schnell
Background: Chloroplasts, the site…
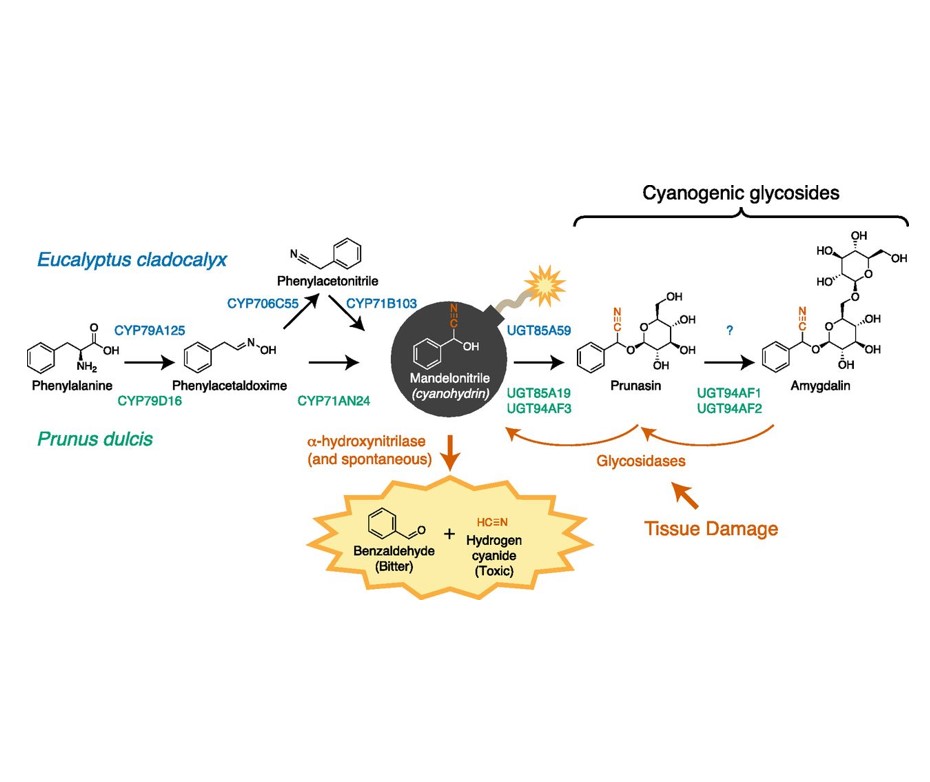
Setting and Diffusing the Cyanide Bomb in Plant Defense
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsHydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase, a conserved component of the respiratory electron transport chain in all aerobic life. Thus, HCN is well suited to serve as a broad-spectrum chemical defense, and indeed it plays such a role in many interactions between plants and…
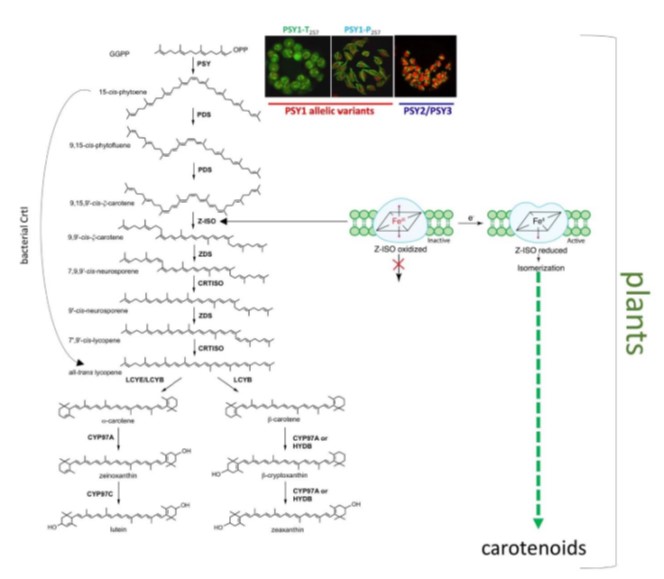
Review: Changing form and function through carotenoids and synthetic biology (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants produce hundreds of carotenoids with functions ranging from photoprotection to signalling, and with important roles in human health as well. Wurtzel describes opportunities arising from applying the tools of synthetic biology to carotenoids. The regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis is complex,…

