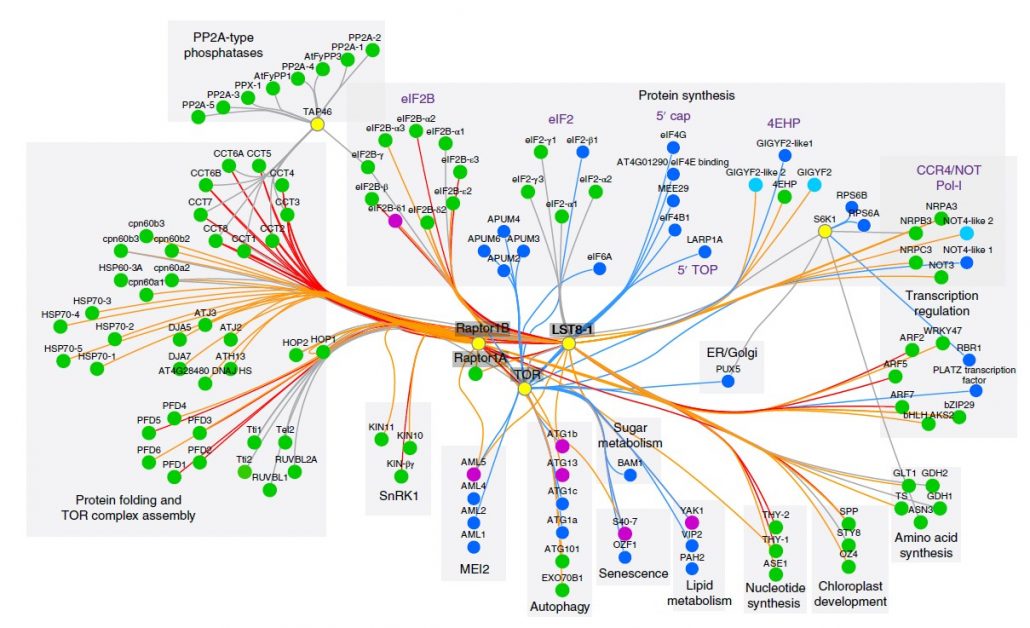
The phosphorylation and protein interaction landscape of the plant TOR kinase (Nature Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe TOR (target of rapamycin) is a conserved regulator of cellular homeostasis and energy status in several clades of life. TOR signaling is well studied in animals while precise regulation and downstream targets of TOR kinase are not very well explored in plants. Some well-studied TOR kinase targets…
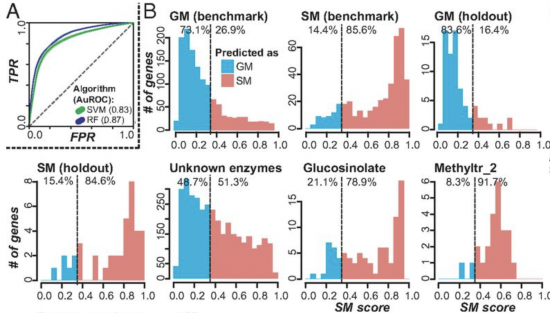
Metabolism gene prediction using diversiform molecular features (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdvances in sequencing technologies enable scientists to obtain molecular features of genes in high-dimensionality. Features of individual gene like expression, methylation, histone modification, evolutionary signals and sequence itself provide high resolution for distinguishing annotated genes. In plant…
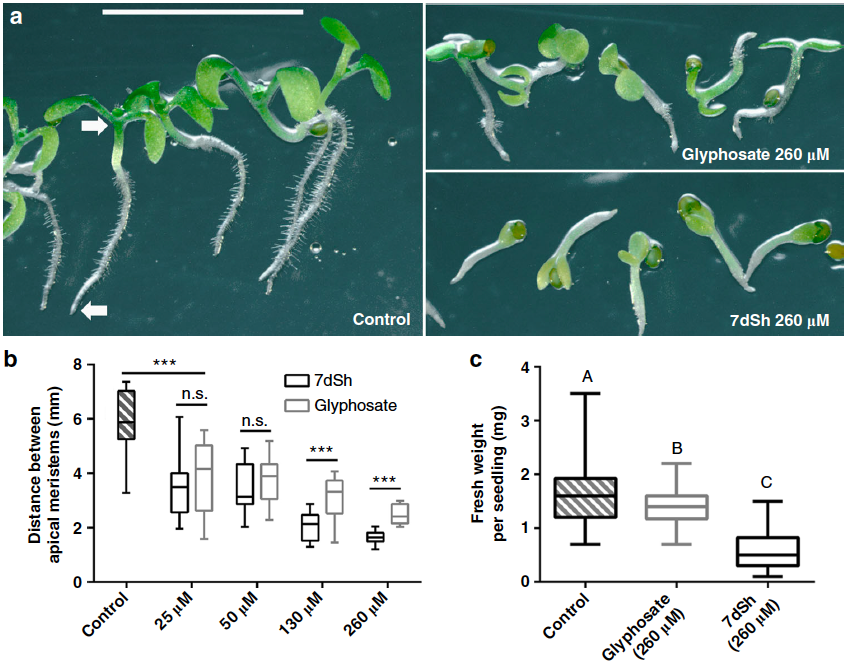
Natural Herbicide: Cyanobacterial antimetabolite inhibits the growth of prototrophic organisms (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe shikimate pathway synthesizes aromatic amino acids in microorganisms and plants, and its absence in animals makes the shikimate pathway a common target for the development of herbicides. Brilisauer et al. 2019 isolated a novel compound from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus—7-deoxy-sedoheptulose…
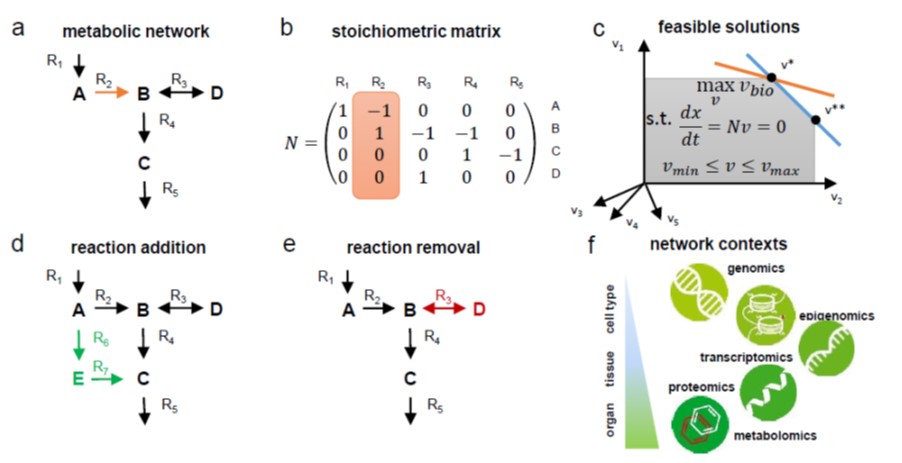
Review: Computational approaches to design and test plant synthetic metabolic pathways (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs photosynthetic organisms, plants are desirable and potentially cost-effective chassis for the production of novel compounds, but they are also inherently metabolically complex. Synthetic metabolic pathways can also improve upon nature by making plants more metabolically efficient. Küken and Nikoloski…

Genome-scale fluxome of Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 using transient 13C-labeling data (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySynechococcus elongates UTEX 2973 (also known as Synechococcus 2973) has the fastest doubling time of known cyanobacteria, completely replicating itself in just over two hours. This fast growth rate makes it an interesting platform for industrial applications. Hendry et al set out to understand what…
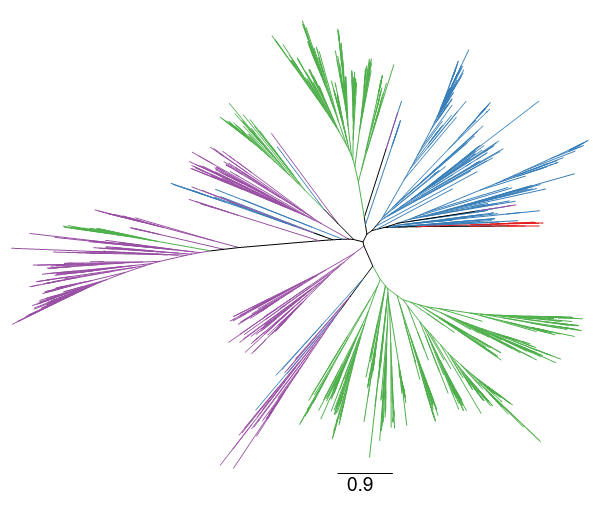
The Terpene Synthases of Red Algae Have a Bacterial Origin
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe red algae (Rhodophyta), encompassing over 8,000 species, are the richest source of marine secondary metabolites. Among red algae, many genera produce terpenes, which constitute the largest class of secondary metabolites. Despite the rich diversity of terpenes in red algae, little is known about how…

Opinion: Capsaicinoids: Pungency beyond Capsicum (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyYou probably saw this article being discussed in your favorite news channel (in the UK, coverage spanned from the Daily Mail to the Guardian). In an Opinion article, Naves et al. discuss the genetics, biochemistry, ecology and health-benefits of capsaicinoids (the “heat” in chili pepper), and consider…
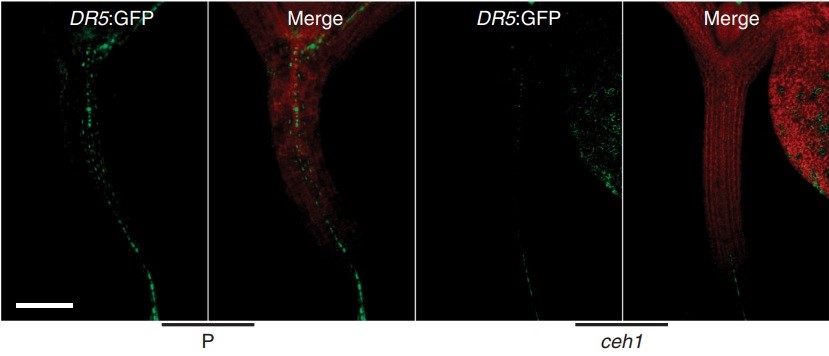
Interplay of auxin and MEcPP regulates adaptive growth (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMEcPP, methylerythritol cyclophosphate, is an essential bifunctional plastidial metabolite that serves as a precursor of isoprenoids and is produced by the plastidial methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. Jiang et al. demonstrated that MEcPP controls adaptive growth by regulating auxin responses…
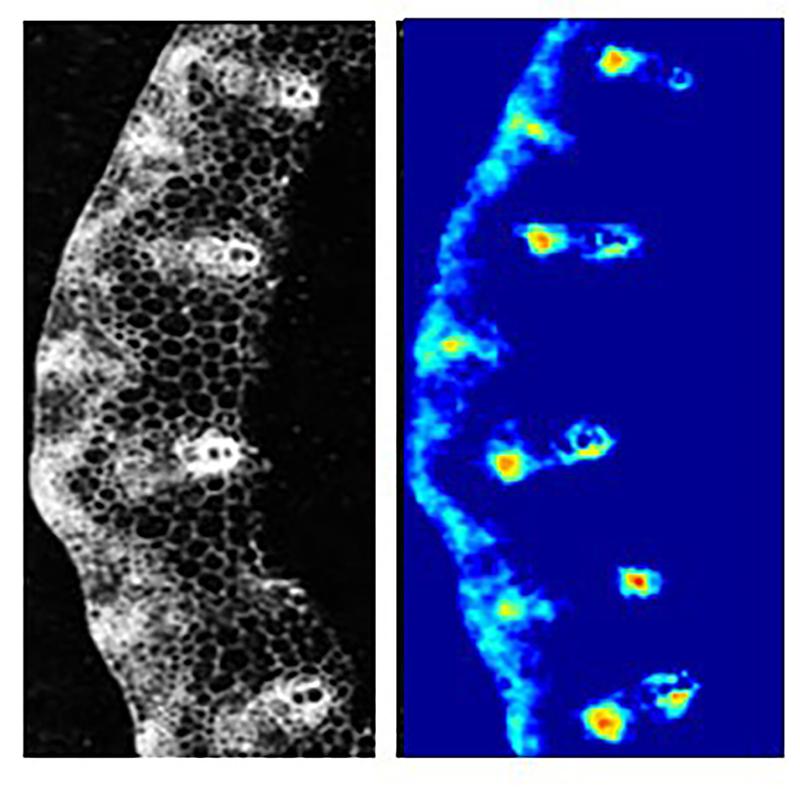
New imaging technique developed for the quantitative visualization of sucrose in plants
Blog, Plant Physiology(Translated from the original)
Regina Devrient Press and Public Relations
Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research
Sucrose is the primary transport form of sugar in plants. It therefore plays an essential role as an energy source, but also as a signal generator under…

