
Diterpenoid Defense in Host- and Non-host Disease Resistance in Rice
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLu et al. show that diterpenoids contribute to disease resistance in rice. Plant Cell. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00205
Background: Rice (Oryza sativa) is an important food crop. Diseases caused by the fungal blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae and bacterial leaf blight pathogen Xanthomonas…

Paint the tobacco red: Anthocyanin production in tobacco cells lines
Plant Science Research WeeklyAnthocyanins are common plant pigments that provide dietary benefits, causing an increase in their use as a food coloring agents. However, purifying anthocyanins from current plant sources (such as waste grape skins, red cabbage and berries) is expensive and creates a variable product. Modifying biosynthetic…
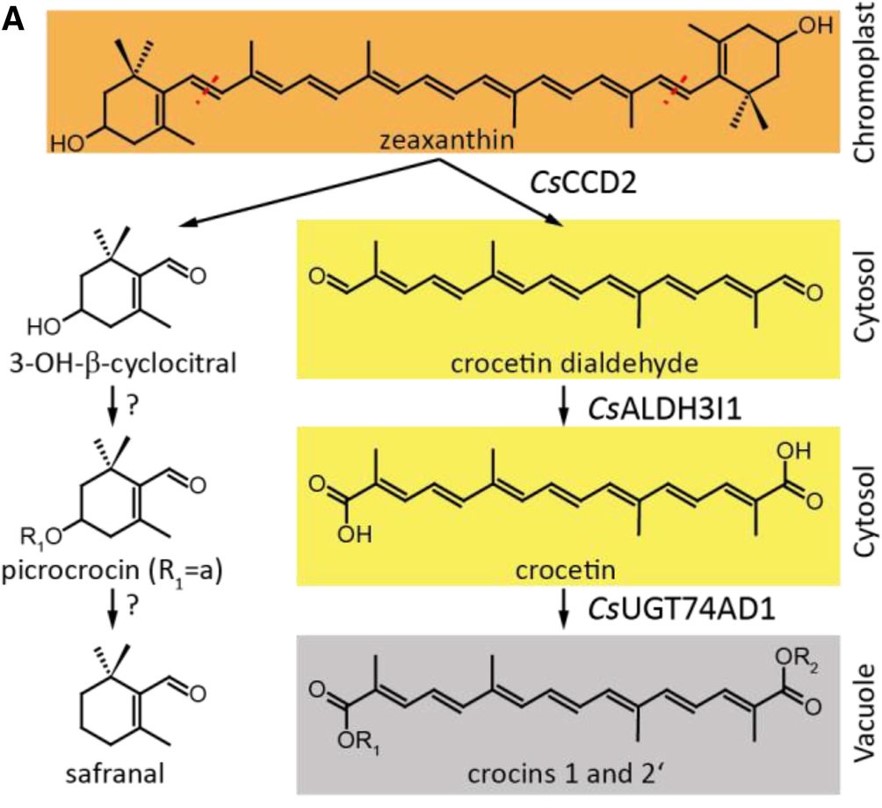
Subcellular Spice Trade Routes: Crocin Biosynthesis in the Saffron Crocus (Crocus sativus)
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsCommentary by Trevor H. Yeats and Raimund Nagel
Saffron is produced from the stigmas and styles of Crocus sativus flowers and is one of the most expensive spices. In C. sativus, both stigma and style are intensely crimson red in color due to the presence of three major classes of apocarotenoids: crocins,…
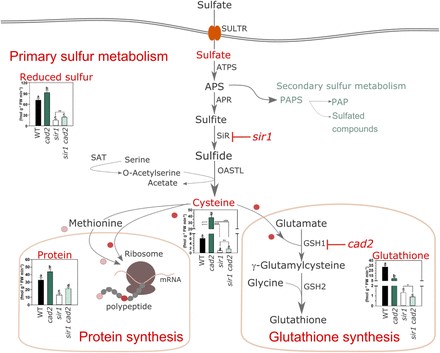
Managing Competing Interests: Partitioning S between Glutathione and Protein Synthesis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsSulfur (S) is an essential element for cell function and responses to the environment. The primary S source is sulfate, which, following uptake by specific transporters, is reduced and incorporated into the amino acids Cysteine (Cys) and Methionine, and thereafter into proteins and peptides, including…
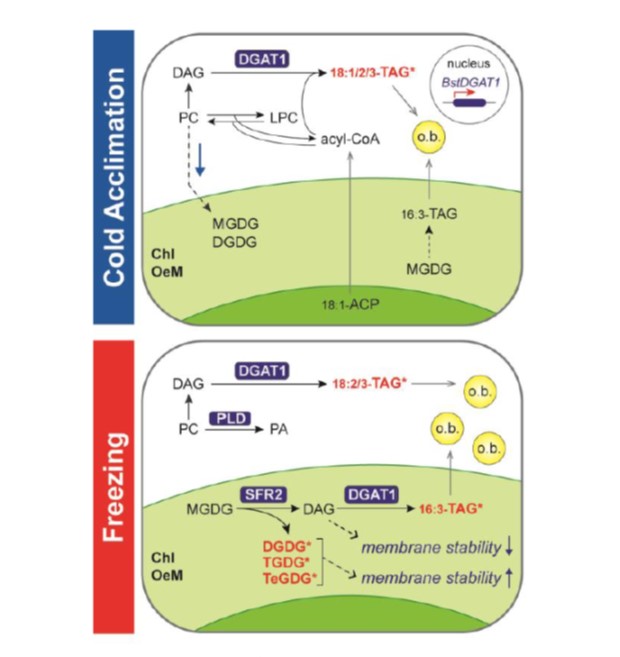
A Lipid Synthesis Enzyme Confers Freezing Tolerance
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDespite major advances in understanding cold signaling, cold acclimation, and freezing protection in model and crop species, and extensive studies of natural variation in freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis accessions, the question of which genes and mechanisms underlie freezing tolerance of wild species…
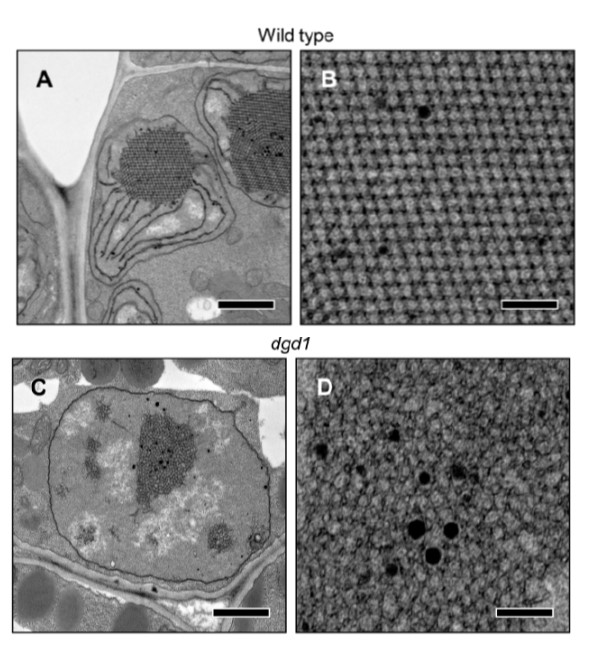
Etioplasts: The Role of Digalactosyldiacylglycerol
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn dark-grown plants, the plastids of cotyledon cells develop as etioplasts. Etioplasts contain unique internal lattice membrane structures called prolamellar bodies (PLBs) and lamellar prothylakoids (PTs). PLBs accumulate protochlorophyllide (Pchlide), a chlorophyll intermediate, in a complex with NADPH…

Summer fun: how plants beat the heat
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News
By Adam Phillips. Reprinted from It Ain't Magic, The RIKEN Global Communications Team https://itaintmagic.riken.jp/hot-off-the-press/plants-beat-heat
It seems like I’ve been writing a lot about plants recently. The truth is that I hardly have enough time to write about all the cool plant…
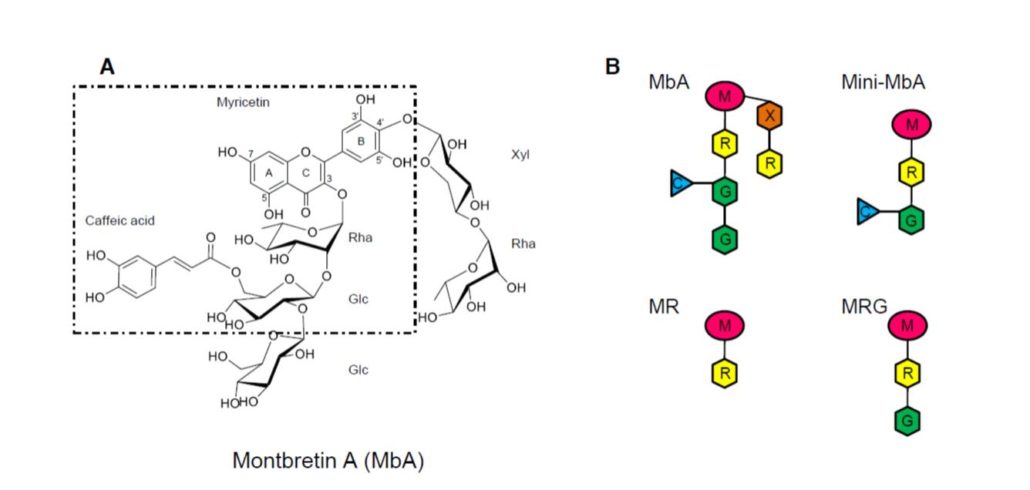
A pretty plant of summer produces a promising anti-diabetes compound
Blog, The Plant CellDiscovery of the biosynthetic pathway of a plant metabolite lays the groundwork for its use as an anti-diabetes drug
Roughly half of the western medicines used today were derived from naturally occurring plant metabolites. Plants produce over 200,000 of these specialized metabolites, but identifying…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Inês Carqueijeiro
Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesInês Carqueijeiro, featured first author of Two tabersonine 6,7-epoxidases start synthesis of lochnericine-type alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus
Current Position: Postdoctoral Researcher, University of Tours
Education: PhD in Plant Biochemistry at the University of Porto (2013), MS in Plant Biology…

