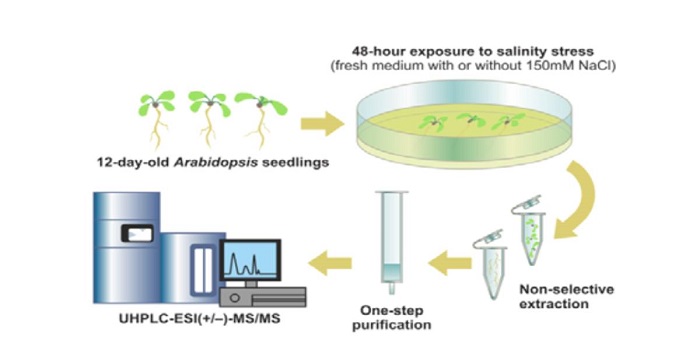
Multiple Phytohormone Screening Method
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePhytohormones are naturally occurring signaling molecules that play key roles in the regulation of plant physiology, development, and adaptation to environmental stimuli. Generally, their concentrations in plant tissues are extremely low (fmol-pmol/g fresh weight, FW). Although certain phytohormones…
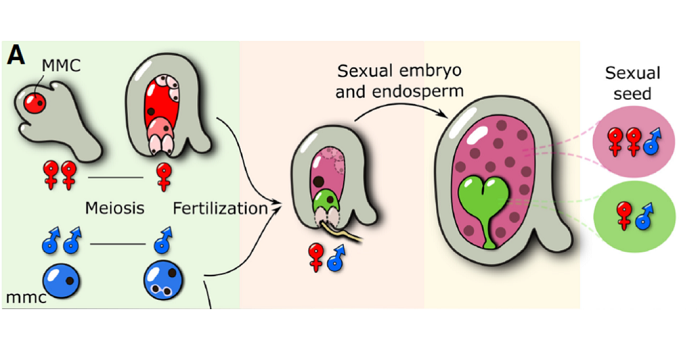
Review: Auxin: a molecular trigger of seed development (Genes Devel.) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeeds are hugely important, providing the opportunity for reproductive dormancy in seed-bearing plants and as a nutrient-dense food source for animals. Seed development involves the formation of three genetically distinct tissues, the embryo, seed coat and endosperm. Although normally dependent on fertilization…
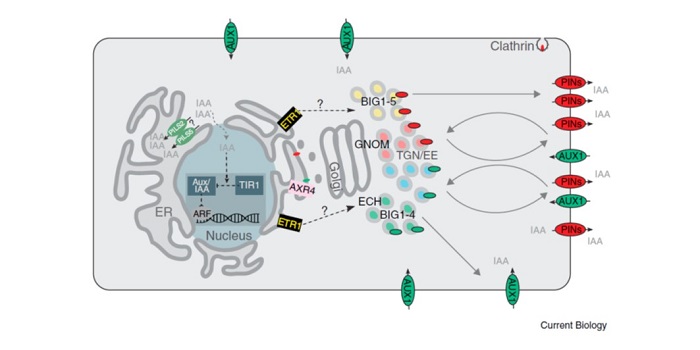
Review: The road to auxin-dependent growth repression and promotion in apical hooks (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe often hear that auxin controls plant growth. In a special issue of Current Biology focused on membranes, Béziat and Kleine-Vehn observe that due to its role in controlling the distribution of auxin transporters (and therefore auxin), it is also reasonable to say that vesicle trafficking controls…
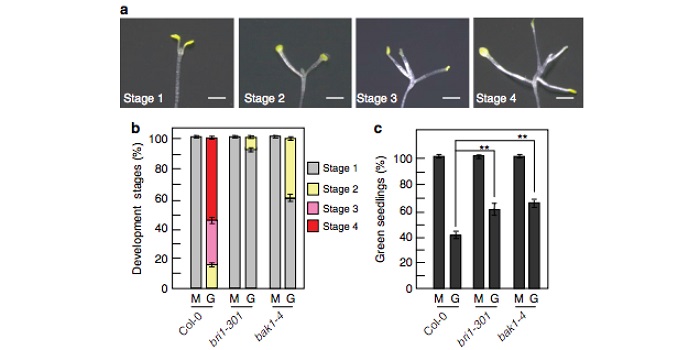
BRI1 and BAK1 interact with G proteins and regulate sugar-responsive growth and development (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySensing sugar is important, especially if you are a plant, as it helps you to decide whether to invest it in new tissues, or rather store it for later. Low levels of glucose promote seedling growth, while high concentrations repress the development. Peng et al. discovered that brassinosteroid signaling…
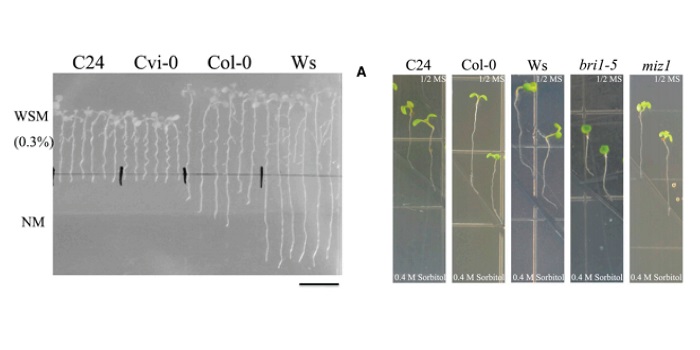
Comparative analysis of Arabidopsis ecotypes reveals a role for brassinosteroids in root hydrotropism (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlastic plant growth serves them well, as it ensures efficient exploration of the environment. A plant can direct the growth of its roots towards the water, but the mechanisms behind hydrotropism are still to be fully understood. Miao et al. performed a screen of 30 Arabidopsis accessions for altered…

RH8-PP2CA interaction in ABA signaling ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research BlogIt is well understood that abscisic acid (ABA) inhibits PPC2A phosphatase activity, which subsequently relieves phosphate-induced inhibition of a kinase interacting partner. This pathway composes the ‘core’ ABA signaling pathway, activating process involved in the ABA response such as stomatal closure…
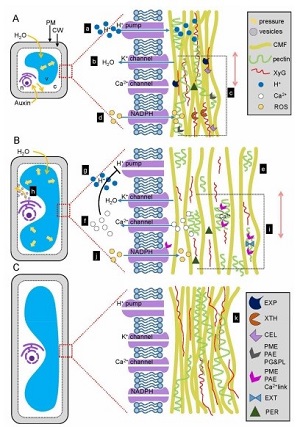
Review: The role of auxin in cell wall expansion (OA)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research BlogCell wall is the outermost boundary for a cell. For the protection of cell, it maintains its rigidity. At the same time, for providing the shape of cells, it is capable of becoming flexible. This means that the cell wall has the capacity to maintain both rigidity and flexibility based on the requirement.…
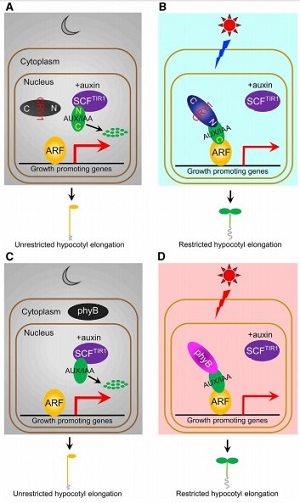
Photoactivated CRY1 and phyB interact directly with AUX/IAA proteins to inhibit auxin signaling in Arabidopsis (OA)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research BlogSo far we know that light inhibits hypocotyl cell elongation and that the master regulatory plant hormone auxin induces hypocotyl elongation. Light signal depends on cryptochrome (CRY1) and phytochrome (PhyB). Auxin signal follows the traditional TIR1/AFB receptor-mediated degradation of AUX/IAA repressor.…
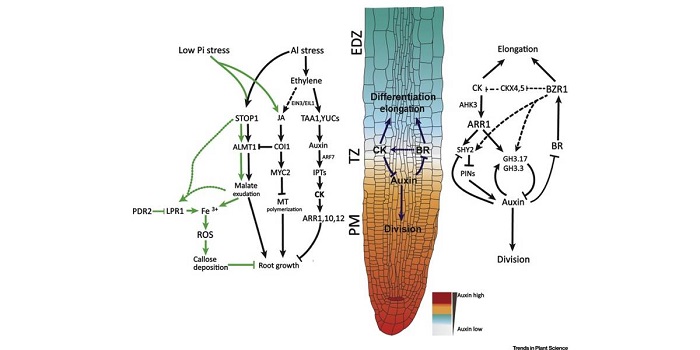
Review: The root transition zone: A hot spot for signal crosstalk (TIPS) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots are an excellent system to study the interactions between endogenous (phytohormones) and exogenous (abiotic stresses) stimuli. The root can be considered as three sections: the meristematic zone (where active cell division occurs), the transition zone (acting as a boundary between meristem…

