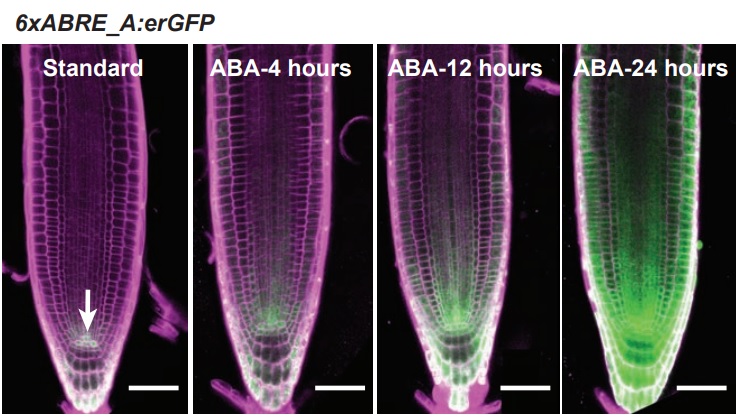
The 6xABRE synthetic promoter enables the spatiotemporal analysis of ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA) is known as stress hormone. Apart from its role in plant growth and development, it is widely studied due to its involvement in biotic and abiotic stresses. Although it had been studied for such a long time, a sensitive spatiotemporal marker for ABA is still elusive. Wu et al. developed…

Nitrate Ahoy! Shoot Cytokinin Signals Integrate Growth Responses with Nitrogen Availability
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefNutrients are rarely distributed homogenously in soil. Consequently, plants have local and long-distance signaling systems in place to monitor and coordinate both demand and supply of essential macronutrients such as nitrogen (N). The “N-demand” long distance signal emanates from a section of the…
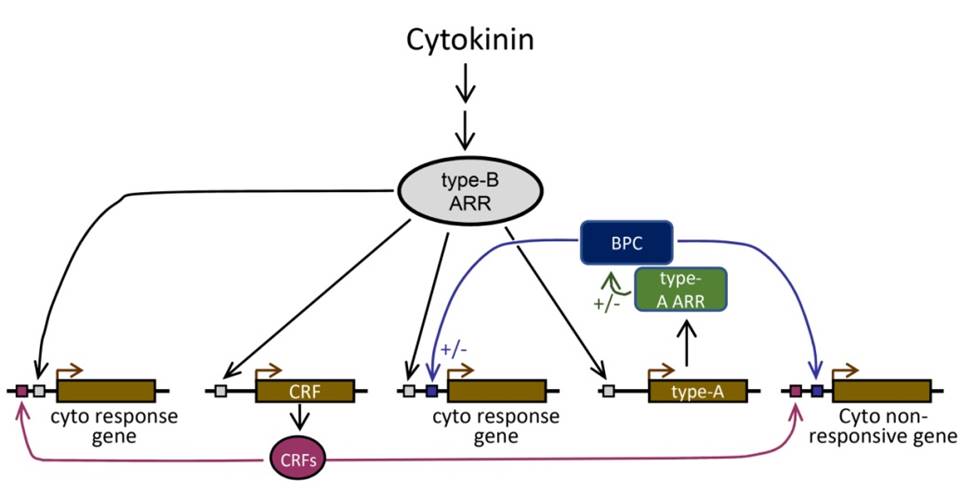
Role of BASIC PENTACYSTEIENE transcription factors in a subset of cytokinin signaling responses (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen cytokinin binds to its receptor AHKs (Arabidopsis Histidine Kinase), the signal is transduced through AHPs (Arabidopsis Histidine-containing Phosphotransfer protein) and eventually to type-B ARRs (Arabidopsis Response Regulators) transcription factors (TFs). Type-B ARR TFs mediate the primary cytokinin…
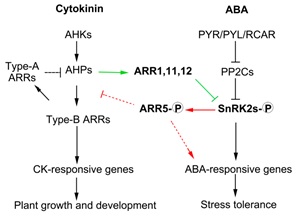
Antagonistic action of ABA and cytokinin signaling mediates drought stress response in Arabidopsis ($) (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDrought stress results in a conglomeration of hormone pathways that interact to coordinate plant growth and stress response. ABA and cytokinin signaling are known to be antagonistic but it is unclear how these two pathways are connected. Huang et al. identified roles for several ARR proteins, negative…

ONE GENE: DIFFERENT mRNAs, DIFFERENT TISSUES, DIFFERENT FUNCTIONS IN DEVELOPMENT
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellNapoli et al. show that mRNA splicing variants have tissue- and developmental stage-specific activity in flower development https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00840.
By Roberta Ghelli and Patrizia Brunetti
Background: Plants that are self-pollinating contain both male (stamen) and female (pistil)…

Mutations in a subfamily of ABA receptor genes promote rice growth and productivity ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLike all plant hormones, ABA controls diverse processes, including stomatal aperture and seed dormancy, and growth rate. Miao et al. have used CRISPR/Cas9 technology in rice to selectively mutant subsets of the 13-member PYL family of ABA receptors. They found notable differences when mutating group…
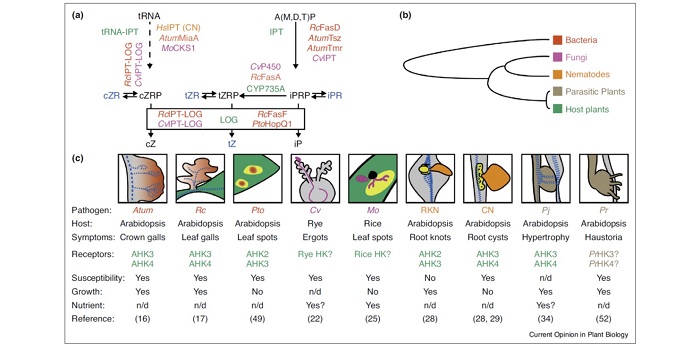
Review: Same tune, different song — cytokinins as virulence factors in plant–pathogen interactions? (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany pathogens produce virulence factors that improve their pathogenicity, including in some cases compounds produced by the host, such as the hormone cytokinin. Spallek et al. review the various plant pathogens — spanning from bacteria to parasitic plants — that use cytokinins as virulence factors;…
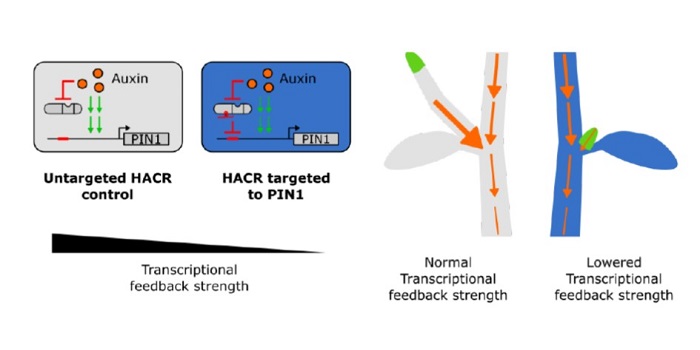
Synthetic hormone-responsive transcription factors can monitor and re-program plant development (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKhakhar et al. have developed a system by which genes can be made exquisitely responsive to specific hormones. They take advantage of the specificity of the guide DNA/Cas9 system, but use a deactivated (dCas9) enzyme that targets but does not cleave the target DNA. By fusing dCAS9 to a hormone-responsive…
Intra-Organ Regulation of Shade Responses
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlants beneath a canopy compete with neighboring plants for light by triggering various physiological responses, collectively known as shade avoidance syndrome. Because of the selective absorption of red (R) light by plants in the upper canopy, plants in the shade are exposed to low R to far-red (FR)…

