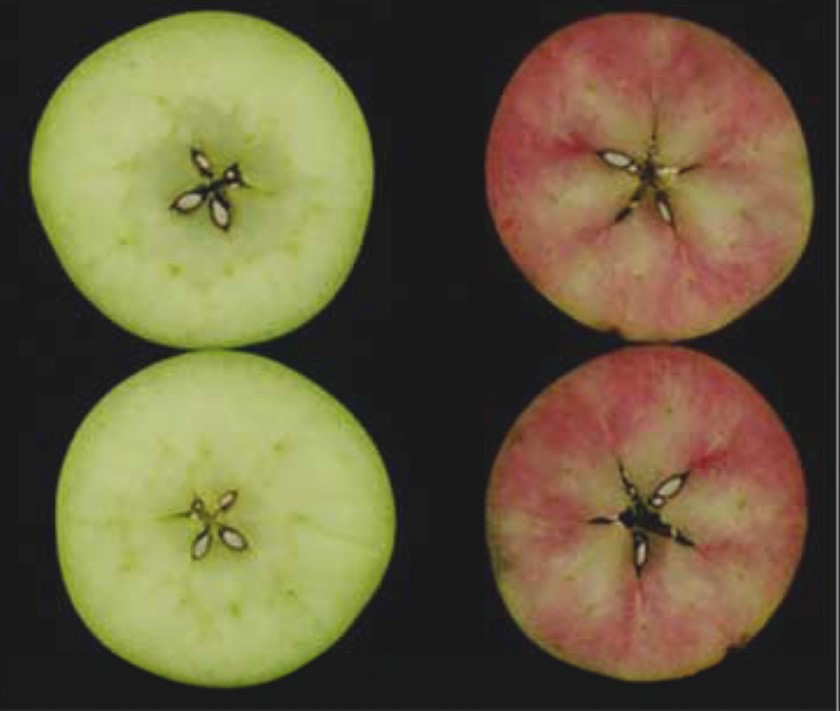

How Ethylene Reddens Apples
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideEthylene is essential for the ripening of climacteric fruits, and a rapid burst of ethylene production and a rise in respiration occur at the transition to ripening. In ripening apple (Malus domestica) fruits, the accumulation of anthocyanins that is responsible for reddening is correlated with ethylene…
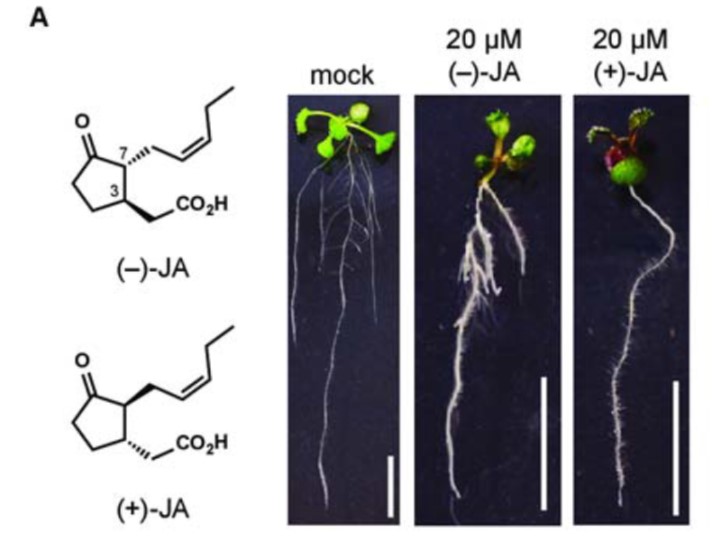
Jasmonic Acid Inhibits Lateral Root Formation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideArchitectural modifications of plant root systems enable plants to survive adverse conditions. Lateral roots, for example, help anchor the plant in the soil, and facilitate the uptake of water and nutrients from the soil. Auxin is a plant hormone essential to root development including the elongation…
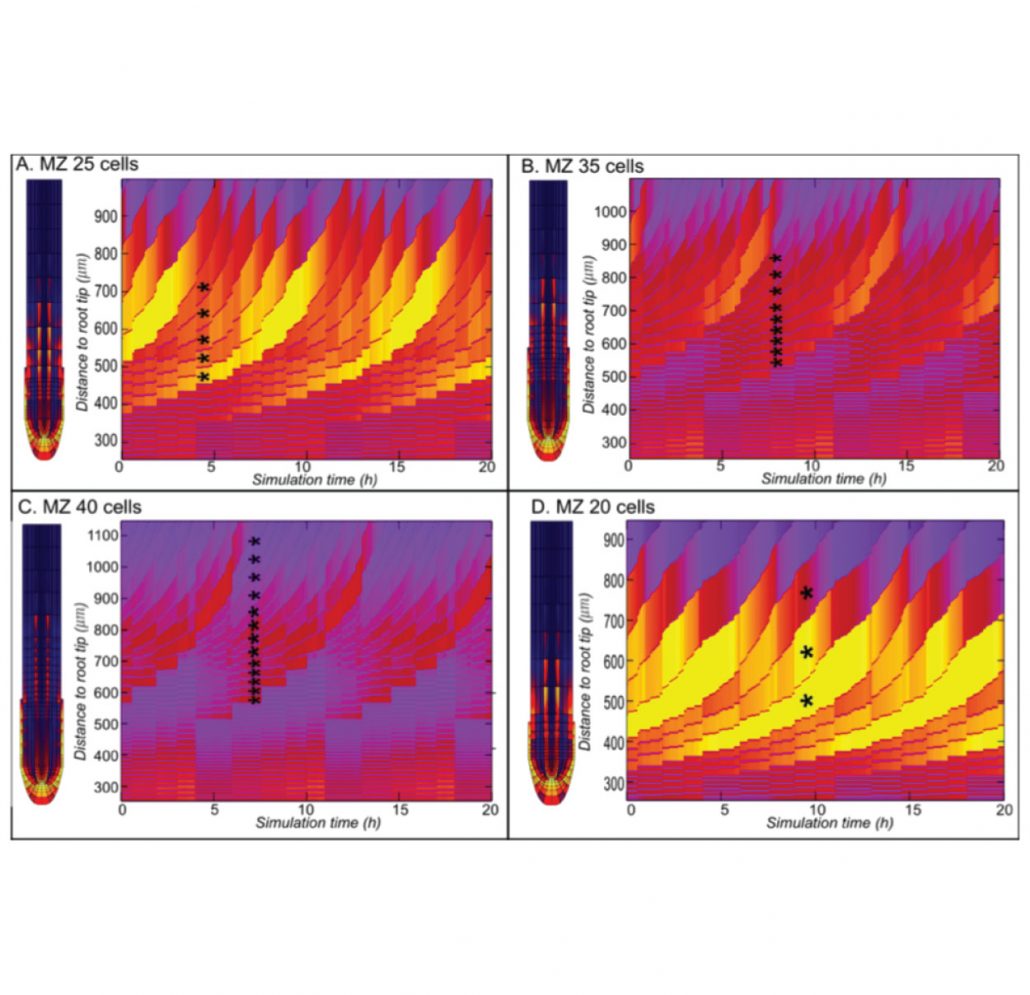
Lateral root priming synergistically arises from root growth and auxin transport dynamics (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot system architecture is primarily determined by branching of the lateral roots. The position of a new lateral root is determined by oscillating auxin concentrations in the main root meristem. To understand the nature of auxin oscillations Van den Berg and ten Tusscher developed a multiscale root…
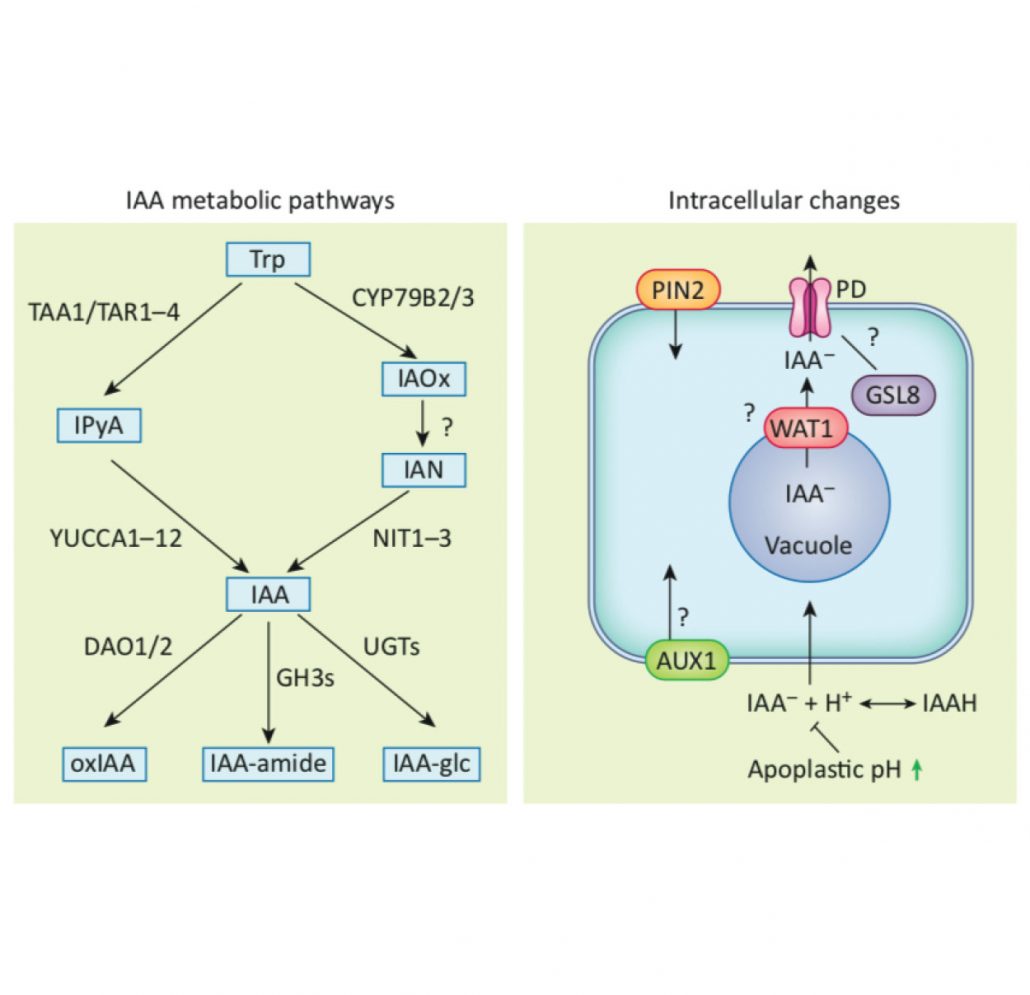
Review. Out of shape during stress: a key role for auxin
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plant hormone auxin is a major player in determining root growth and architecture, but we are just starting to understand how auxin distribution is altered by abiotic stresses. Kover et al. discuss how the “upside-down fountain” of auxin in the root is affected by abiotic stress conditions. Auxin…

The PILNCR1-miR399 regulatory module is important for low-phosphate tolerance in maize (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNearly ten years ago, microRNA 399 (miR399) was recognized as a regulator of phosphate (Pi) homeostasis. miR399 expression is induced upon low Pi conditions, and, in Arabidopsis, rice, soybean and barley, miR399 suppresses PHO2, a negative regulator of Pi uptake. Du, Wang, Zou et al. found that contrary…
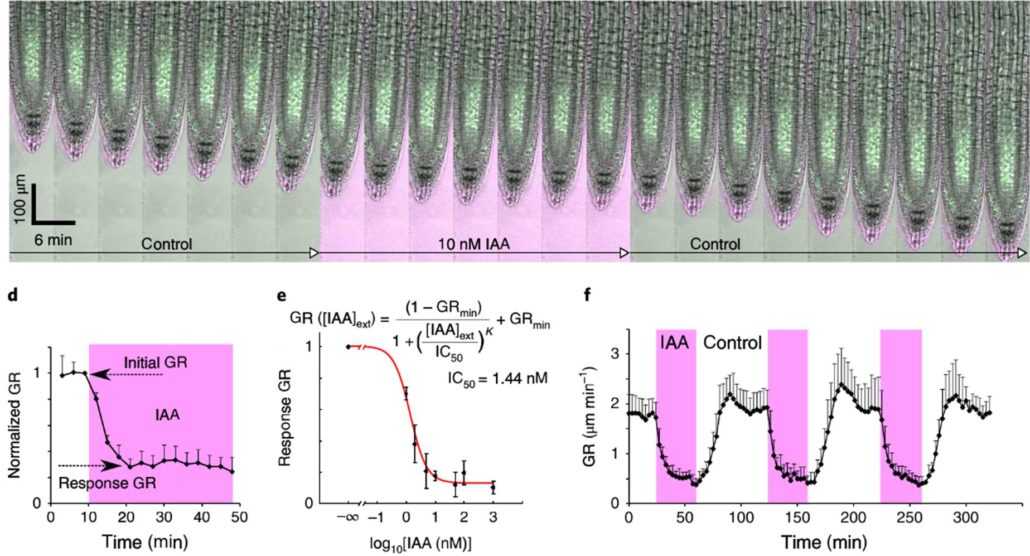
Rapid and reversible root growth inhibition by TIR1 auxin signalling (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin mediates many of its effects through transcriptional changes via the well-known interaction between its co-receptors and transcriptional regulators (TIR1/AFB – Aux/IAA), but some auxin responses happen too quickly to be explained by transcriptional changes. Fendrych et al. demonstrate that root…
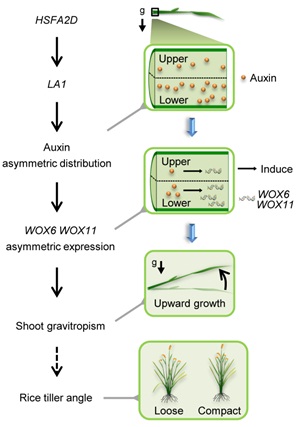
Advances in the analysis of the molecular mechanism of rice tiller angle regulation in genetic development
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: NewsSource: Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Date: 2018-06-22 【 Title : Xiaozhong University 】(Translated from the original Chinese by Google)
The angle of tillering is the angle between the tiller and the main stem of the grass family and is closely related to the crop population.…
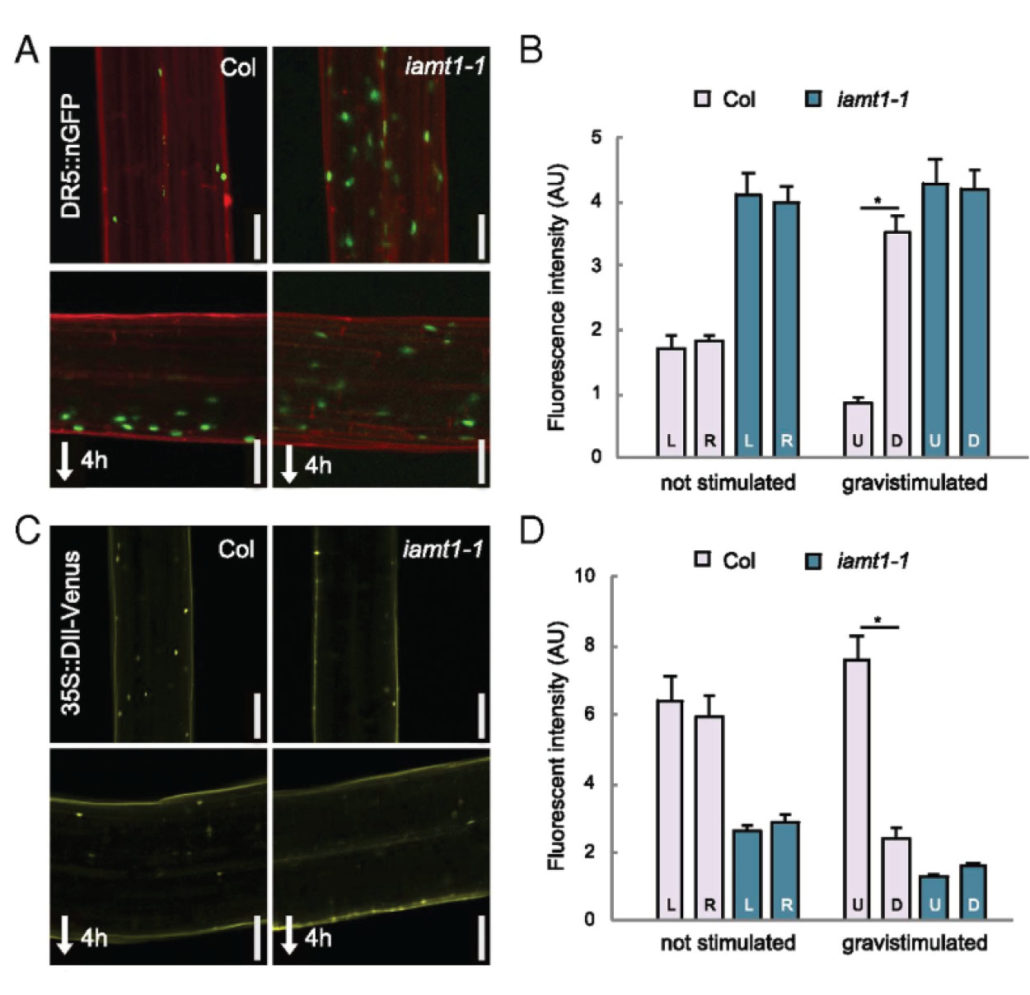
Auxin methylation is required for differential growth in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to navigate and adjust their growth according to the environmental clues, such as light or gravity. Asymmetric distribution of auxin is necessary for organ bending. Abbas and colleagues show that conversion of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) into methyl-IAA (Me-IAA) is important for asymmetric…
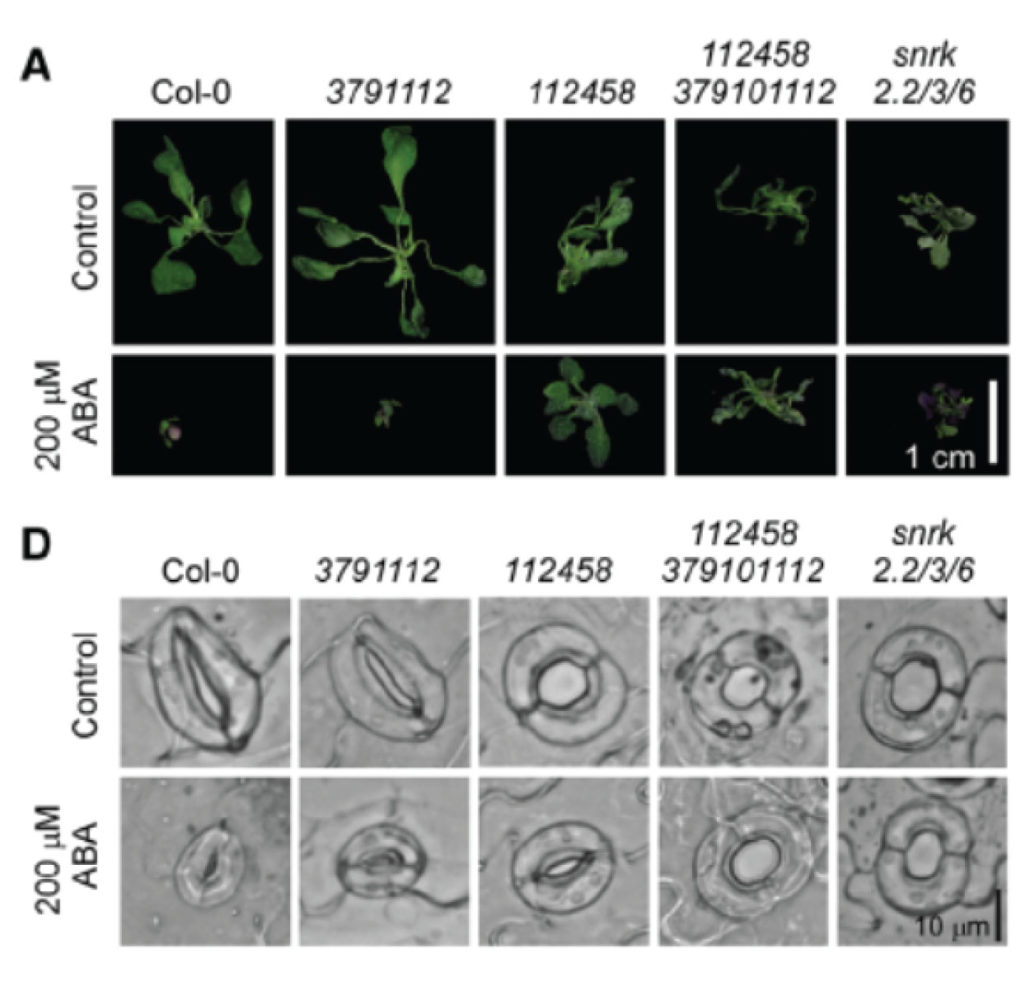
Arabidopsis duodecuple mutant of PYL ABA receptors reveals PYL repression of ABA-independent SnRK2 activity
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone involved in many plant processes – from seed maturation to drought responses. ABA is perceived by intracellular pyrabactin resistance and PYR-like family (PYR/PYL) receptors, counting 14 genes in Arabidopsis, representing the largest family of plant receptors. …

