
Chasing Scattered Genes: Identifying Specialized Metabolite Pathway Genes through Global Co-expression Analysis
Research, The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
Plants produce scores of specialized metabolites (SMs) to attract or repel the organisms around them and to cope with life in a variable environment. For thousands of years, we have been exploiting these compounds to feed, heal, and adorn us. Many more SMs remain to be discovered: the chemical constituents…
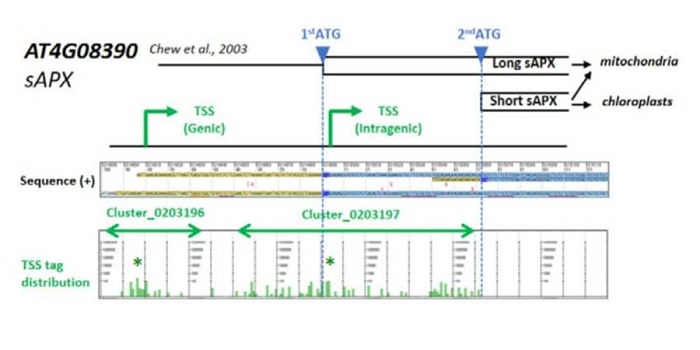
Identification of Arabidopsis genic and non-genic promoters
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA promoter is a region that “determines the position, direction, frequency, and timing of transcription”. A cell can decode the sequence of the promoter to ensure appropriate transcription, but we still can’t. Tokizawa et al. performed a large-scale survey of promoters by sequencing regions upstream…
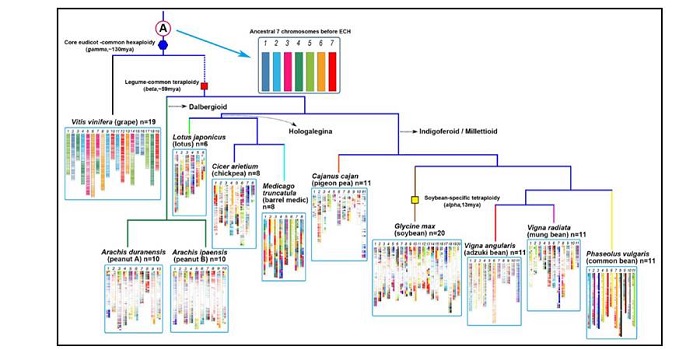
Hierarchically aligning 10 legume genomes establishes a family-level genomics platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMany legumes are important crops, and to date ten legume genomes have been sequenced, including soybean, common bean, mung bean, and two species of wild peanut. Wang et al. used hierarchical comparative genomics analysis of the ten legume genomes, which enabled them to detected gene colinearity between…
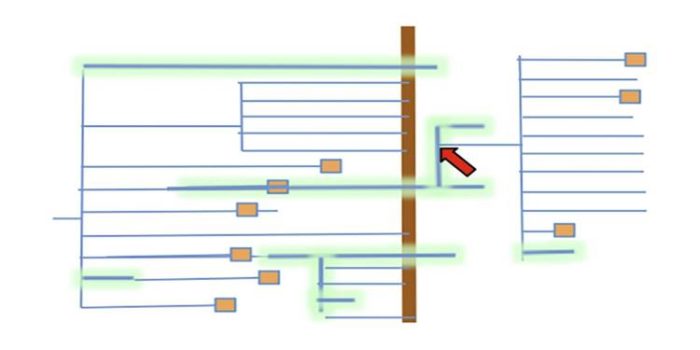
Letter: Picking up the ball at the K/Pg boundary: Ancient polyploidies as a spandrel of asexuality
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRoughly 66 million years ago Earth was hit by a huge asteroid, resulting in climate changes that led to mass extinctions, most famously of the non-avian dinosaurs. This catastrophic event, which marks the boundary between the Cretaceous (K) and Paleogene (Pg) periods, also caused widespread mass extinctions…

Review: Chloroplast function revealed through analysis of GreenCut2 genes
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOf the 3000 or so proteins housed in the chloroplast, we know the functions of only a few hundred. One approach to identify function is to first identify plastid proteins found exclusively in photosynthetic organisms. This subset, GreenCut2, is further subdivided by whether the proteins are found in…
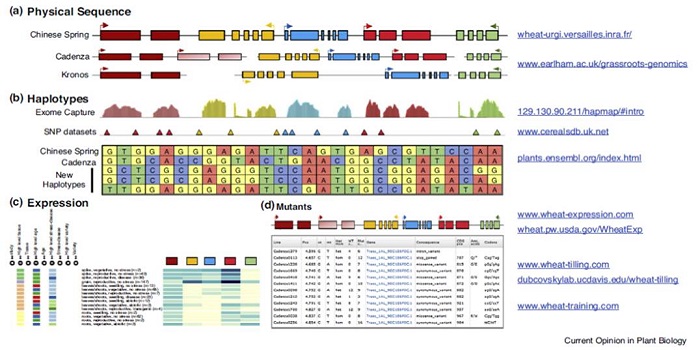
Review: Wheat genomics comes of age
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDue to its highly repetitive, polyploid genome, wheat genomics has lagged behind that of other cereals, but new tools promise to begin closing that gap. Uauy reviews these new tools, which include access to full genomes of several wheat varieties, gene expression data from hundreds of publicly available…
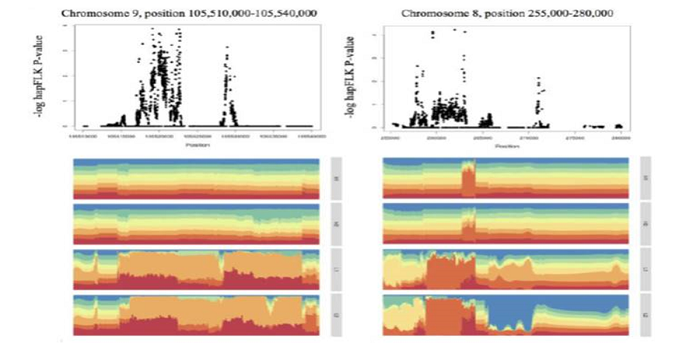
Signatures of local adaptation in lowland and highland teosintes from whole genome sequencing of pooled samples ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTeosinte, the ancestor of maize, grows in a range of environments in México. Teosinte parviglumis (Zea mays ssp parviglumis) is more prevalent in lowland regions while teosinte mexicana (Zea mays ssp mexicana) occupies highland territory (>2000 m above sea level). Admixture between parviglumis and…
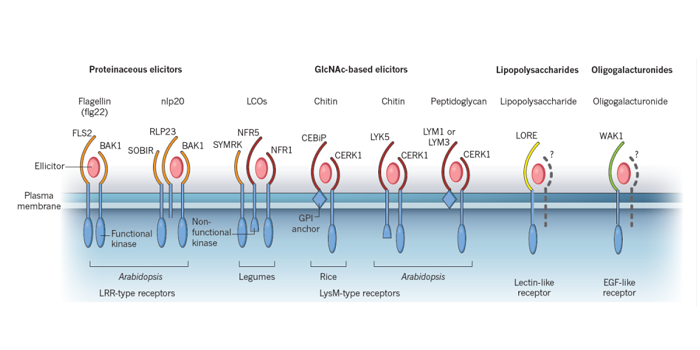
Reviews: Nature Insight: Plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNature journal published a special “Plant Insights” section featuring several excellent reviews. Zipfel and Oldroyd review Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity (10.1038/nature22009), Bevan et al. write about Genomic innovation for crop improvement (10.1038/nature22011), Scheres and van der…

The rice paradox: Multiple origins but single domestication in Asian rice
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRice is the world’s most important food crop and its domestication was a key event in human history. Centuries of propagation across large geographical areas have resulted in five domesticated subpopulations: aus, indica, temperate japonica, tropical japonica, and aromatic rice. Choi et al. analyzed…

