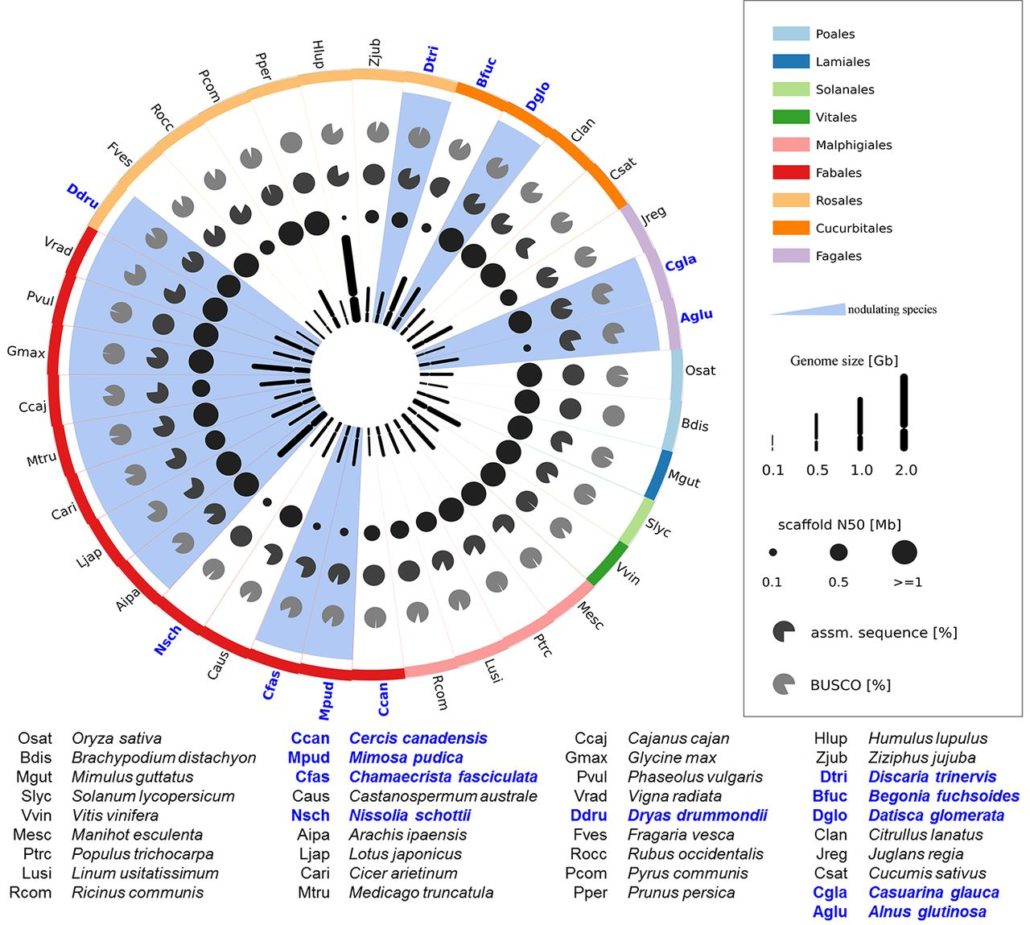
Phylogenomics reveals multiple losses of nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to participate in nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis shows an interesting phylogenetic pattern, with some families showing a large number of nodulating species interspersed with non-nodulating ones, and some families showing only a few nodulating species. A current model suggests that…
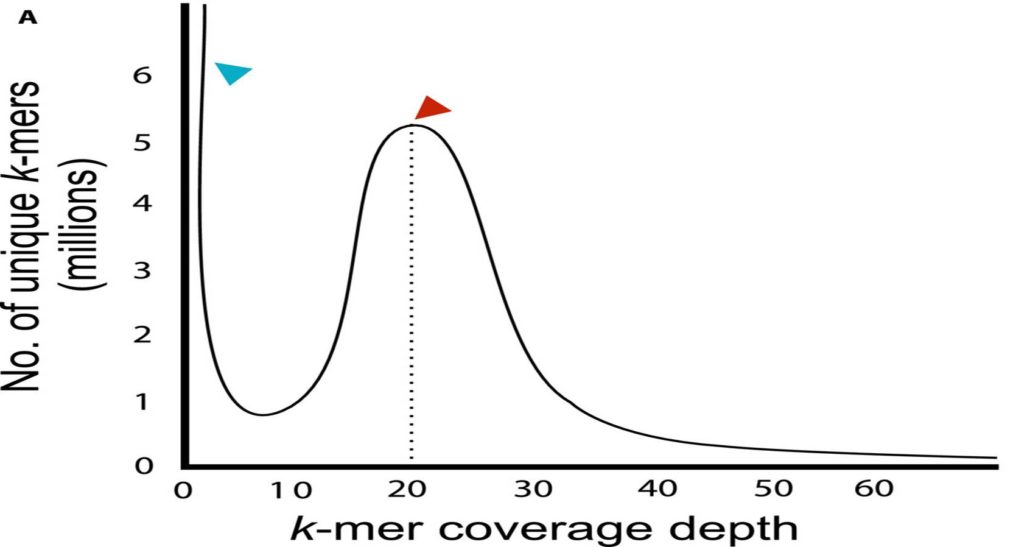
Review: A guide to sequence your favorite plant genomes (App. Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEvery year, genome assembly gets faster and cheaper. Li and Harkness provide a practical guide to today’s methods, with caveats and precautions that need to be considered at each step, even questions to ask before embarking on a sequencing project. Topics include how to estimate genome size and complexity,…
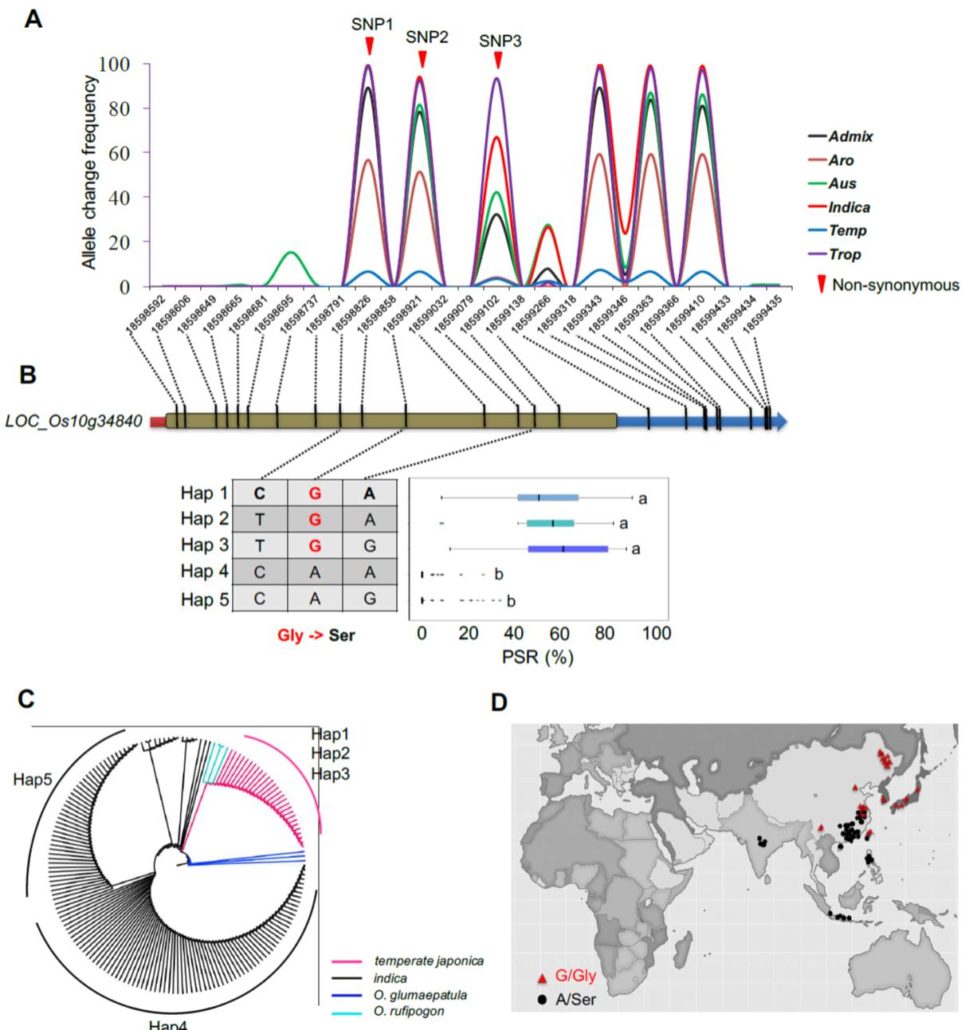
Identification of cold tolerance genes and a functional allele that confers cold tolerance ($) (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyXiao et al. used 1,033 rice accessions for GWAS to identify QTLs associated with cold tolerance. In general, japonica-type varieties showed greater cold tolerance than indica types. The authors identified many QTLs for cold tolerance at the seedling and booting (initiation of panicles) stages. They…
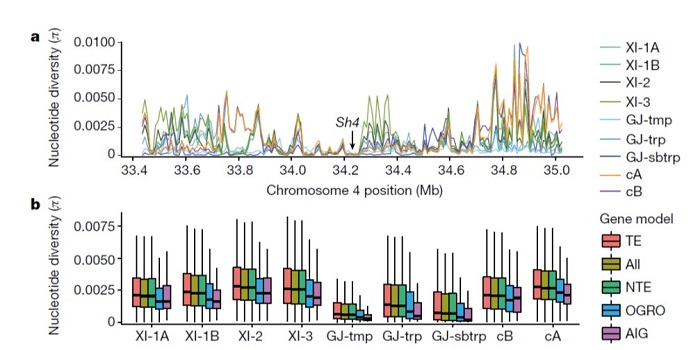
Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWang et al. analyse data from the 3000 rice (Oryza sativa) genome (3K-RG) project, identifying “29 million single nucleotide polymorphisms, 2.4 million small indels and over 90,000 structural variations”. The data of course strongly support the two major rice types (Indica and Japonica), but also…
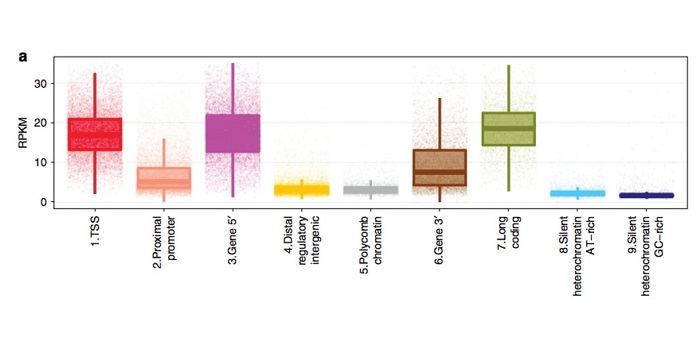
Genome-wide excision repair in Arabidopsis is coupled to transcription and reflects circadian gene expression patterns (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyExposure to ultraviolet radiation and numerous other factors can cause mispairing of the nucleotides in the DNA, compromising genome integrity. Luckily, plants employ excision repair systems to recognize and repair such DNA damage. Oztas et al. examined the dynamics of such a repair system by using excision…

Recognizing featured Plant Cell first authors: André N. Müller
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Author ProfilesAndré N. Müller, featured first author of The Biotrophic Development of Ustilago maydis Studied by RNA-Seq Analysis
Current Position: Project Manager, GSK Vaccines GmbH, Marburg
Education: PhD in Molecular Phytopathology, Department of Organismic Interactions, Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial…
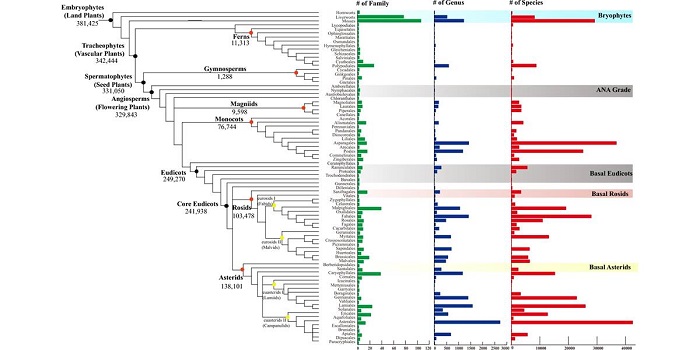
Commentary. 10KP: A phylodiverse genome sequencing plan (GigaScience)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNobody doubts the great insights we have gained about plant diversity and evolution from genome sequencing, but the patchy nature of available genomes within the plant phylogeny remains a problem. Cheng et al. describe the 10KP (10,000 Plants) Genome Sequencing Project, which aims to sequence genomes…
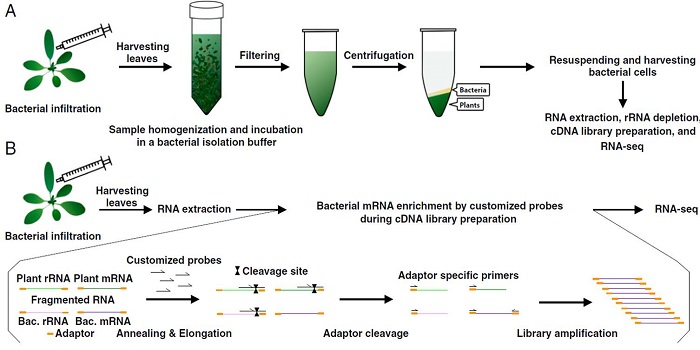
Transcriptome landscape of a bacterial pathogen under plant immunity (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany studies have examined how plants respond transcriptionally to pathogen attack. This study investigates how a bacterial pathogen [Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pto)] alters its transcriptome very early in the infection process. To accomplish this, Nobori et al. developed two methods to…
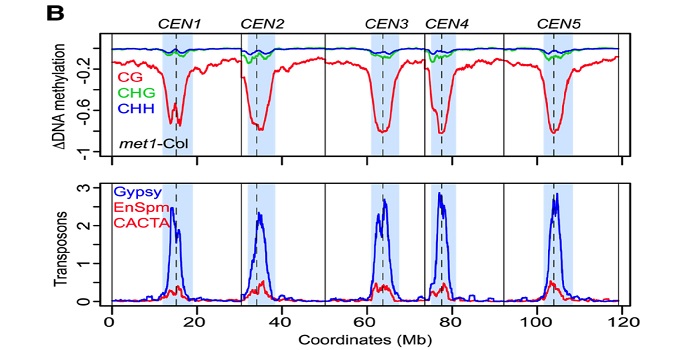
Initiation of meiotic recombination is regulated by epigenetic marks and chromatin structure (Genome Res.)
BlogMeiotic recombination is an important source of genetic diversity by allowing the reshuffling of parental alleles during meiosis. It requires the generation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) initiated by the activity of the SPO11 protein complex. In plants, the impact of chromatin structure and DNA…

