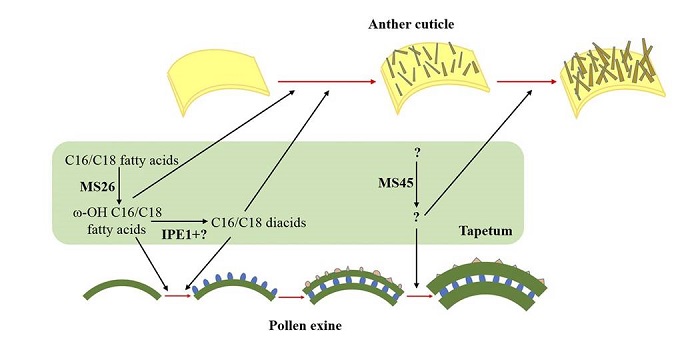
IRREGULAR POLLEN EXINE1 Is a novel factor in anther cuticle and pollen exine formation
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Chen et al. identified a novel male-sterile Zea mays mutant, named ipe1. Mutant pollen grains show defective development of the tapetum and pollen exine (outer surface), causing microspore abortion. In addition, ipe1 anthers are smooth instead of reticulate, suggesting defects in anther cuticle formation. …
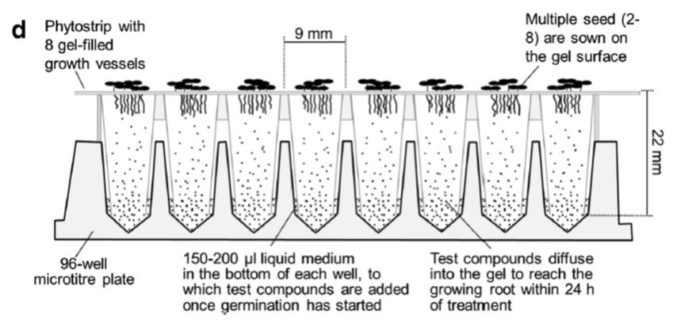
Method: Microphenotron, a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHigh-throughput screening greatly extends the number of individuals that can be screened, so is particularly crucial for genetic or chemical genetic approaches. Burrell et al. report on a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform, “Microphenotron” designed for chemical genetic screening. Seeds…

Review: Progeny responses to maternal vs progeny environmental cues
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe range of responses an individual could display is a contribution of the inheritance of gene variants that determine such responses and the environments experienced by the individual itself and prior generations (nongenetic inheritance). In this review, we discuss recent empirical data to help us…

Update: Understanding and Manipulating Meiotic Recombination in Plants
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, ResearchAbstract
Meiosis is a specialized cell division, essential in most reproducing organisms to halve the number of chromosomes, thereby enabling the restoration of ploidy levels during fertilization. A key step of meiosis is homologous recombination, which promotes homologous pairing and generates crossovers…
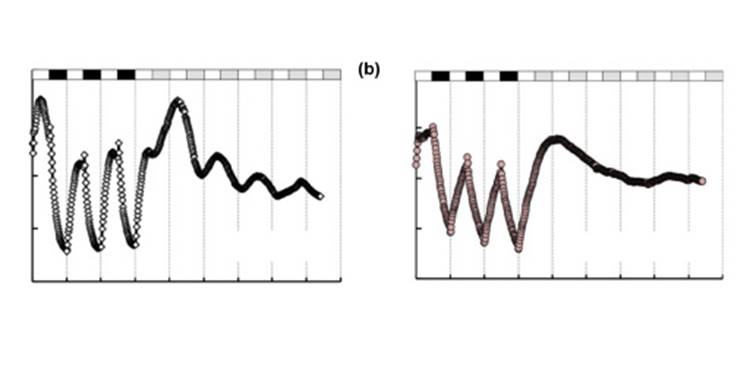
Early evolution of the land plant circadian clock
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchClocks in green algae have been described as simple two-gene loops, while clocks in angiosperms have evolved to complex interlocked loops. This striking jump in complexity led Linde et al. to investigate the clocks in bryophytes and charophytes to shed light on this transition. First, through the sequence…
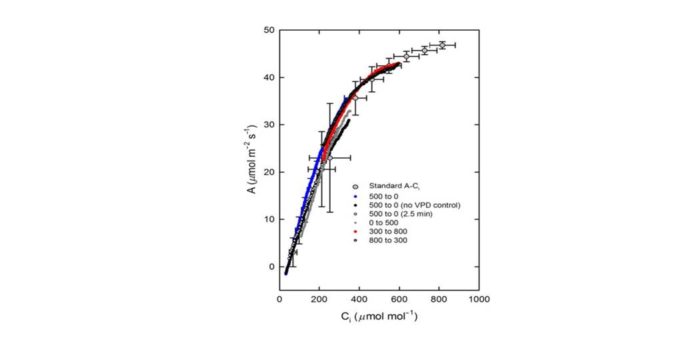
Technical Report: The rapid A–Ci response: photosynthesis in the phenomic era ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchLarge-scale phenotyping efforts depend on large numbers of measurements, so the time taken for any one measurement has a big effect on the number of samples that can be processed. Stinziano et al. describe a breakthrough in the method used to identify the photosynthetic parameters Vc,max (maximum rate…

Review: The genomic basis of adaptation in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEvolution starts with molecular variation and phenotypic diversity, upon which selection acts. Flood and Hancock review the approaches used to detect adaptive evolution. The top down approach starts with the phenotype and works to identify its genomic basis; examples are quantitative trait locus (QTL)…
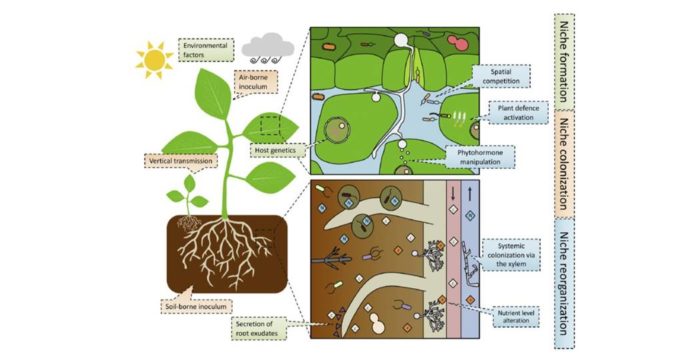
Review: Host-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions for plant breeding ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe idea that the microbes on and within an organism (the microbiota) influence an organism in positive, neutral and negative ways has been a hot topic in popular science, especially the role of the gut microbiota in human health and nutrition. Plants are similarly influenced by their microbiota, as…

Review: Synthetic botany
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAs photosynthetic autotrophs, plants have the potential to convert sunlight into a vast array of useful products: to act as little green metabolic factories. Of course, they already provide us with everything from carbohydrates and vitamins to stimulants and medicinal compounds, but with a few small…

