Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
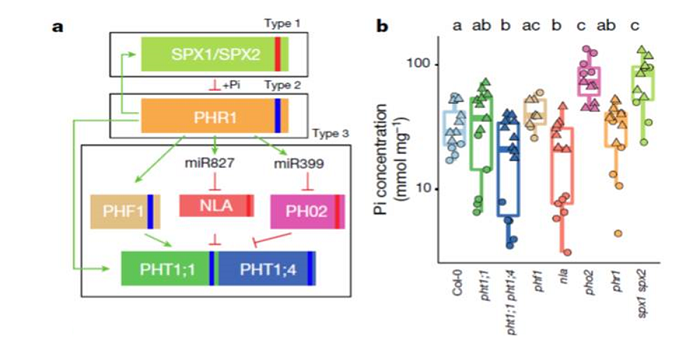
Many of the genes involved in the phosphate-stress response (PSR) have been identified from plants growing on sterile medium. Castrillo et al. examined how the root microbiota affectthe phosphate stress response, and how phosphate affects the association between roots and microbes. Plants deficient…
Role of LOTR1 in Nutrient Transport ($)
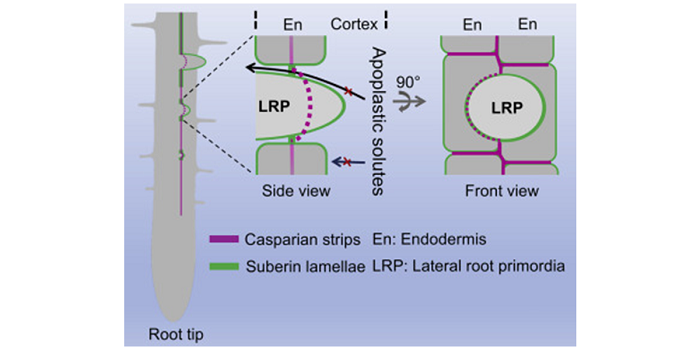
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCasparian strips, named after the German botanist Robert Caspary who discovered them, are a cellular feature found in the roots of all higher plants. They are ring-like lignin polymers deposited in the middle of anticlinal cell walls (parallel to the root radius) between endodermal cells. Along with…
Coordination of auxin-triggered leaf initiation by tomato LEAFLESS ($)
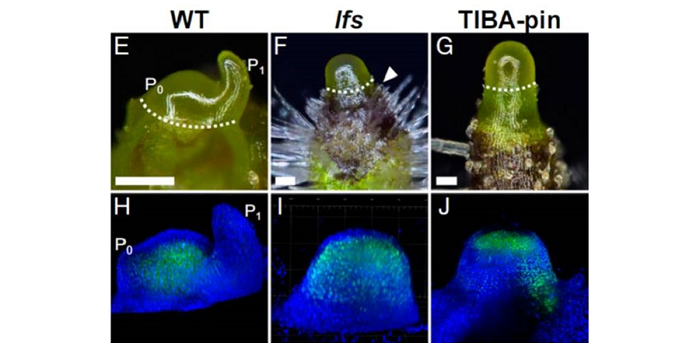
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCapua and Eshed explored the link between auxin and leaf initiation at the shoot apical meristem, using the tomato mutant leafless (lfs), which is an ortholog of the Arabidopsis DORNRONSCHEN (DRN) and DRN-like (DRNL) genes that encode AP2-type transcription factors. The lfs mutant and the drn/drnl double…
Update: Transitory starch metabolism in guard cells: unique features for a unique function
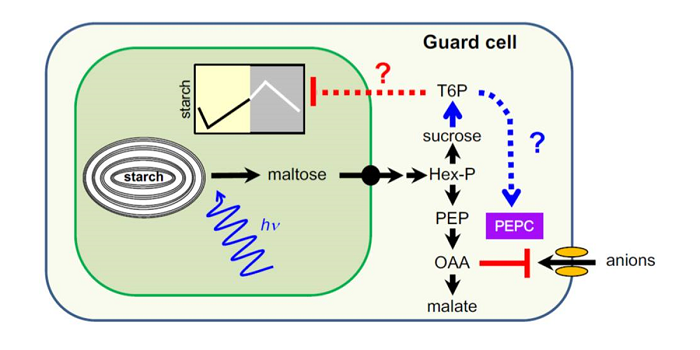
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn leaf mesophyll cells, some of the sugars produced by photosynthesis are stored as transitory starch, which is then broken down to provide the cells with energy during the night. Recent advances in imaging and staining and the use of mutants have enabled the pattern of accumulation of transitory starch…
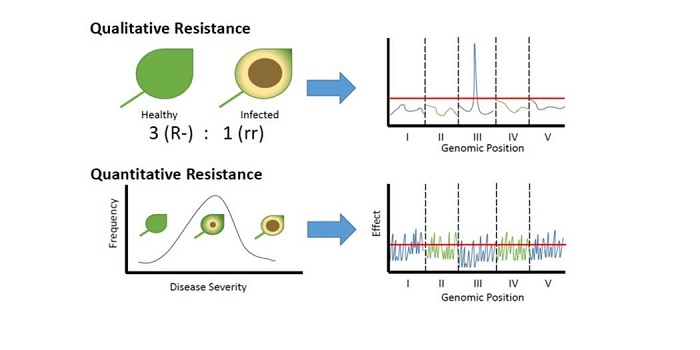
Review: Quantitative resistance: More than just perception of a pathogen
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSome forms of pathogen resistance function like an on/off switch: if a plant has an appropriate receptor it recognizes a pathogen and shows resistance. Corwin and Kliebenstein review the other kind of resistance, quantitative resistance, in which many genes make small contributions to the plant’s resistance.…
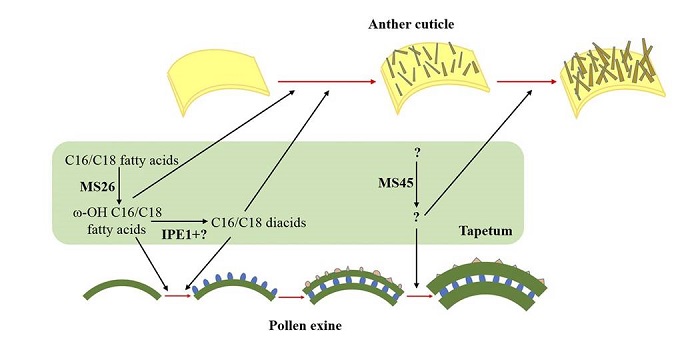
IRREGULAR POLLEN EXINE1 Is a novel factor in anther cuticle and pollen exine formation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchChen et al. identified a novel male-sterile Zea mays mutant, named ipe1. Mutant pollen grains show defective development of the tapetum and pollen exine (outer surface), causing microspore abortion. In addition, ipe1 anthers are smooth instead of reticulate, suggesting defects in anther cuticle formation. …
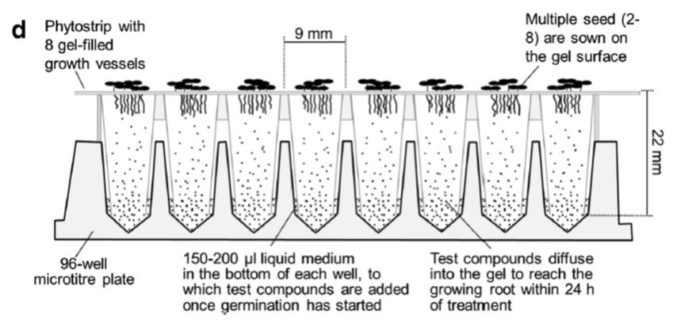
Method: Microphenotron, a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHigh-throughput screening greatly extends the number of individuals that can be screened, so is particularly crucial for genetic or chemical genetic approaches. Burrell et al. report on a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform, “Microphenotron” designed for chemical genetic screening. Seeds…

Review: Progeny responses to maternal vs progeny environmental cues
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe range of responses an individual could display is a contribution of the inheritance of gene variants that determine such responses and the environments experienced by the individual itself and prior generations (nongenetic inheritance). In this review, we discuss recent empirical data to help us…

Update: Understanding and Manipulating Meiotic Recombination in Plants
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, ResearchAbstract
Meiosis is a specialized cell division, essential in most reproducing organisms to halve the number of chromosomes, thereby enabling the restoration of ploidy levels during fertilization. A key step of meiosis is homologous recombination, which promotes homologous pairing and generates crossovers…

