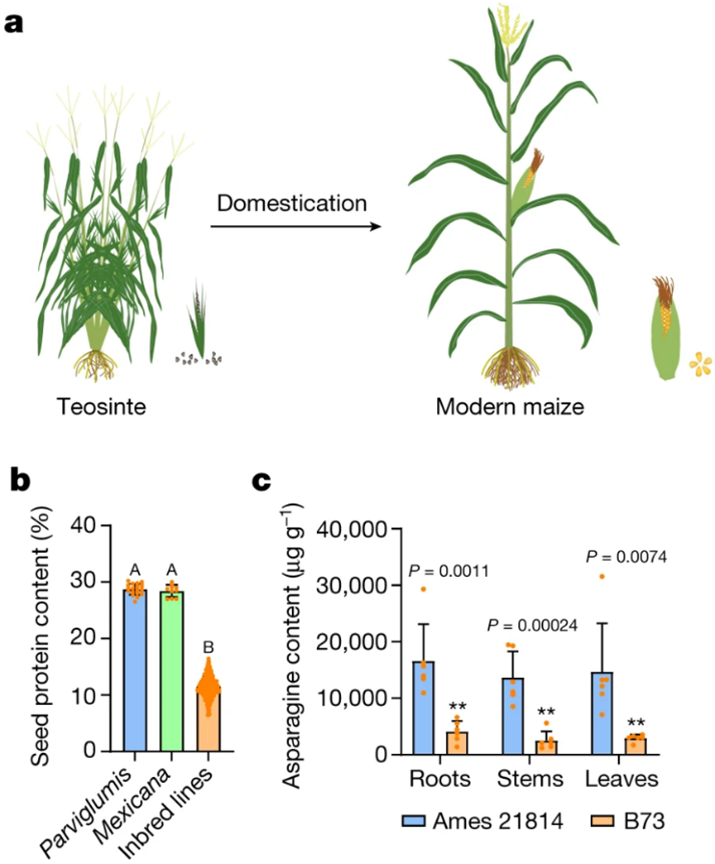
A teosinte gene enhances seed protein content in maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyIncreasing nitrogen-use efficiency (NUE) and seed protein content are important for maize breeding. Modern maize hybrids have 6.5-16.5% seed protein content, while the wild ancestor of maize, called teosinte, has ~30% seed protein content. In addition, teosinte (accession Ames 21814) contains notably…

Productivity and agronomic potential of perennial rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyModern rice is descended from a perennial grass, which through millennia of selection evolved into an annual “one-sow, one-harvest” crop. However, it has become apparent that perennial grains have the potential to decrease soil erosion and competition, as well as lower the labor required to produce…

Drought resistance or yield? In search of gold, we lost the diamond (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArtificial selection has significantly increased crop yield. However, this has come at the cost of compromising abiotic stress tolerance. Stomatal aperture has an important role in abiotic stress tolerance. Abiotic stress induces stomatal closure and involves the intracellular production of reactive…
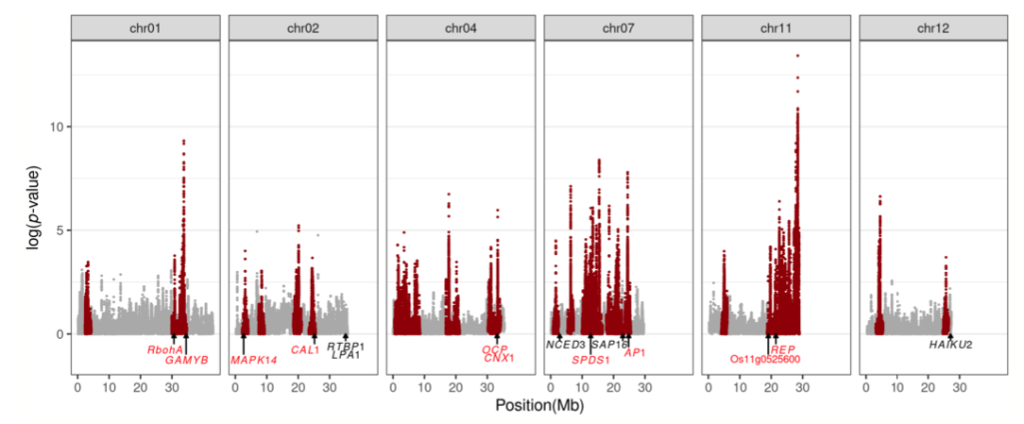
Hybrid-derived weedy rice maintains adaptive combinations of alleles associated with seed dormancy (Mol. Ecol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cross between genetically distant parents is an essential source of genetic variation. This process, known as hybridization, might result in the loss of adaptive gene combinations due to the introduction of non-adaptive alleles. However, Imaizumi and colleagues show this is not the case with weedy…

Teff breeding potentials from data-driven, participatory characterization of farmer varieties (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere is a clear need to synergize advances from cutting-edge genomic approaches with the needs and knowledge of growers, particularly small-holder growers who have access to much of a crop’s genetic diversity. Here, Woldeyohannes, Iohannes et al. took a transdisciplinary approach to explore the breeding…
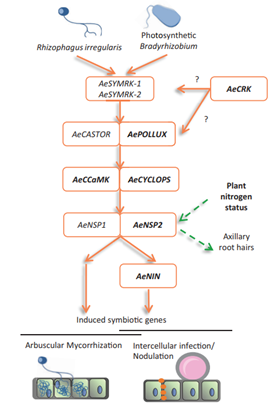
Modus operandi of Nod-independent symbiosis in Aeschynomene evenia (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbioses and nodule organogenesis processes that occur independently of Nod-factors are relatively unexplored. Quilbe et al. investigated the semi-aquatic legume Aeschynomene evenia, which has recently been shown to establish symbioses with Bradyrhizobium sp. that do not produce Nod factors. The authors…
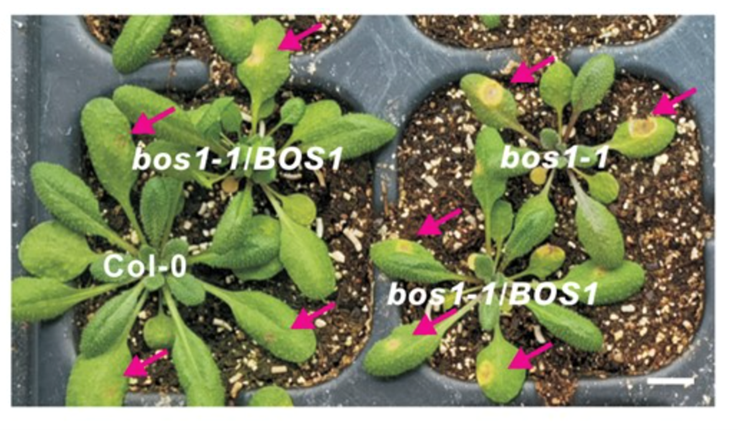

Ectopic expression of BOTRYTIS SUSCEPTIBLE1 reveals its function as a positive regulator of wound-induced cell death and plant susceptibility to Botrytis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProgrammed cell death (PCD) is a ubiquitous eukaryotic process in which specific cells are eliminated during development or in response to stress. Here, Fuqiang Cui and colleagues confirm for the first time the exact role of the BOS1 gene in the regulation of PCD in Arabidopsis thaliana. Originally identified…
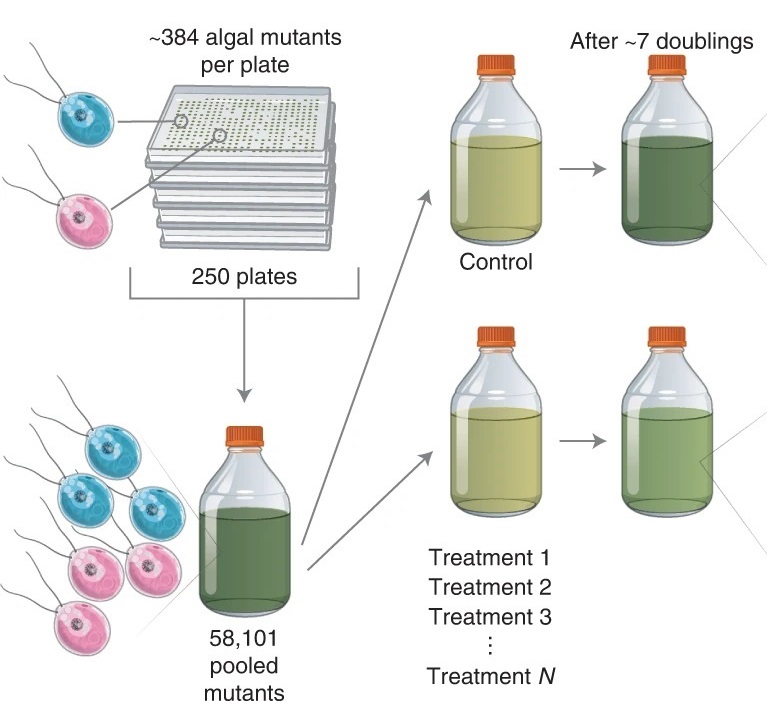
Systematic characterization of gene function in the photosynthetic alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is a useful model system to study photosynthetic organisms, as this single-celled species allows for more high-throughput methods than in multicellular plants, and many conserved pathways of interest can be identified. Here, Fauser et al. demonstrate the value…

URM Plant Scientist Highlights - Taylor Beaulieu (she/her)
BlogTaylor Beaulieu (she/her) is currently a third year graduate student at UC-Riverside (UCR). She received her BS in Plant Biology from UCR and also received a minor in Education. She originally spent her undergraduate education training to become a K-12 science teacher which gave her training experience…

