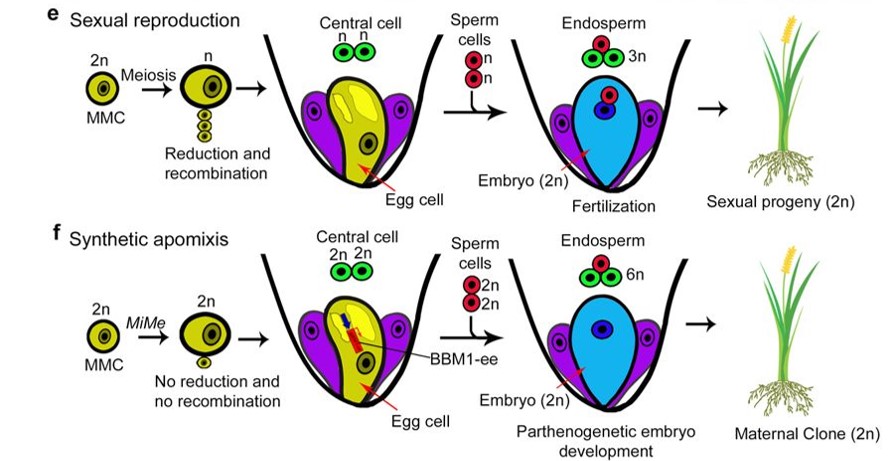
Synthetic apomixis: Asexual propagation through seeds (Nature) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklySexual reproduction mixes up genes and provides genetically diverse progeny, key for survival and fodder for evolution. Sexual reproduction is detrimental to the propagation of hybrid crops though, as mixing up the genes leads to progeny that will be inferior to the hybrid parent. Khanday et al. have…
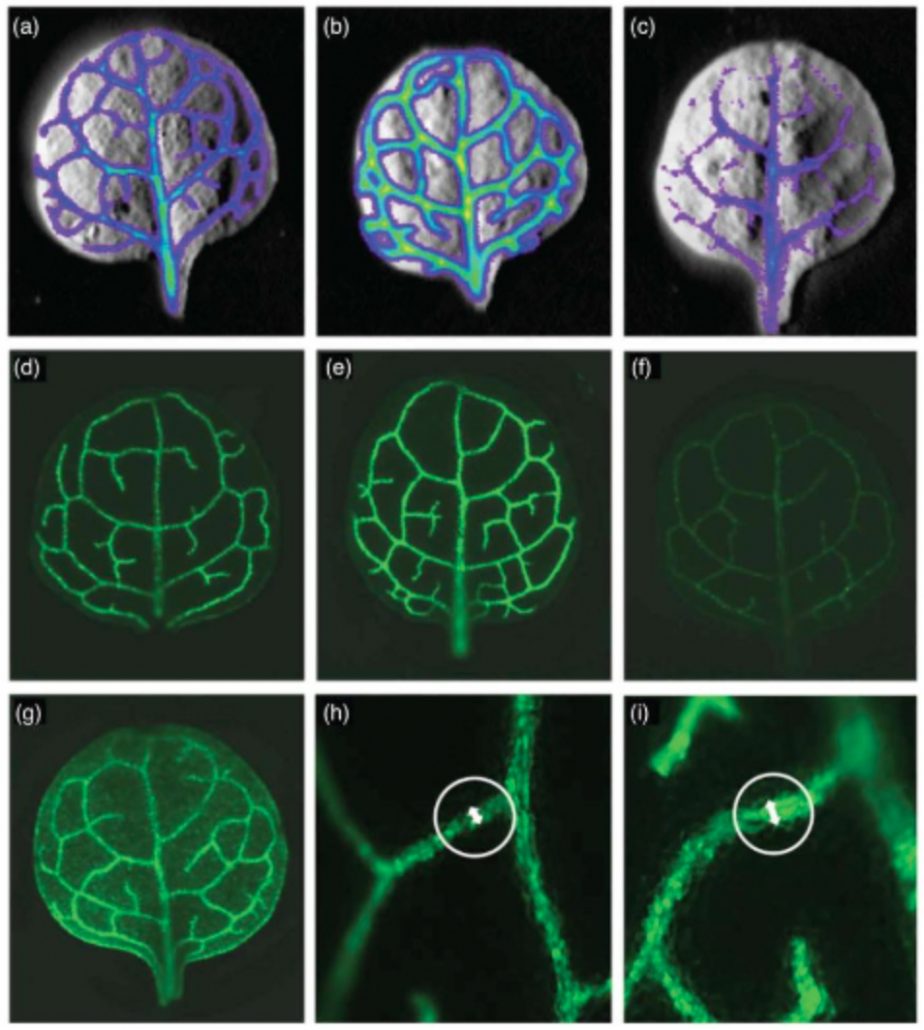
Reporter‐based screen to identify bundle sheath anatomy mutants ($) (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyInstallation of C4 photosynthesis into C3 crops appears a realistic way to boost crop yields. A key aspect of C4 photosynthesis is an enlarged bundle sheath volume and an increase in bundle sheath chloroplast number. To identify the regulators of this phenotype, Döring et al. subjected Arabidopsis…
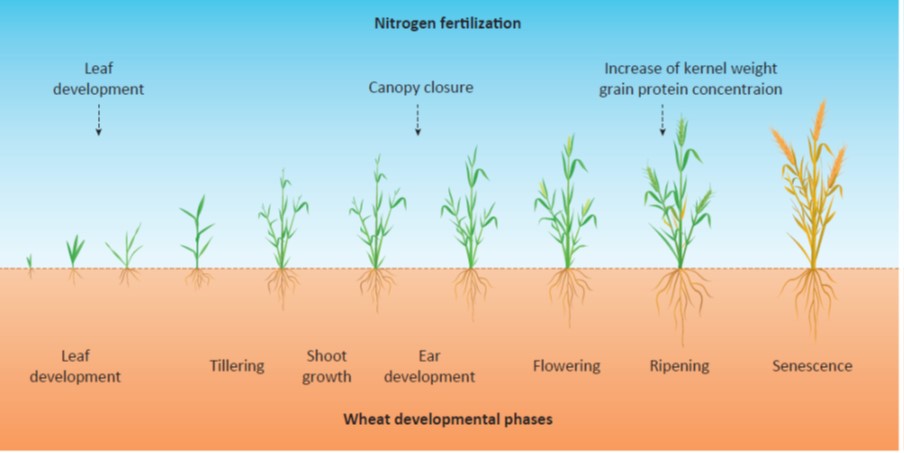
Review: Perspective on wheat yield and quality with reduced N supply (TIPS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWheat production demands huge inputs of nitrogen as fertilizer, with accompanying financial and environmental costs. Zorb et al. discuss several strategies by which to maintain wheat yields and wheat quality while decreasing N use and wastage. Some of these are agronomic, such as ensuring that the N…
Genetic Basis of Natural Variation of Rice Ionomics
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News(Translated from the Chinese original http://news.hzau.edu.cn/2018/1101/52991.shtml)
Nanhu News Network (Correspondent Sheng Ke)
On October 30th, the research group of Professor Tian Xingming from the Rice Science Team of the National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement of our School…
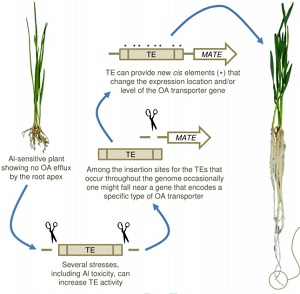
Review: Transposable elements have role in aluminum resistance (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytotoxic aluminum can drastically harm plant roots, leading to decreased nutrient uptake, water absorption and yields. Many plant species efflux organic anions into the rhizosphere to reduce the toxic effects of aluminum. Some of the genes that encode transporter proteins which mediate organic anion…
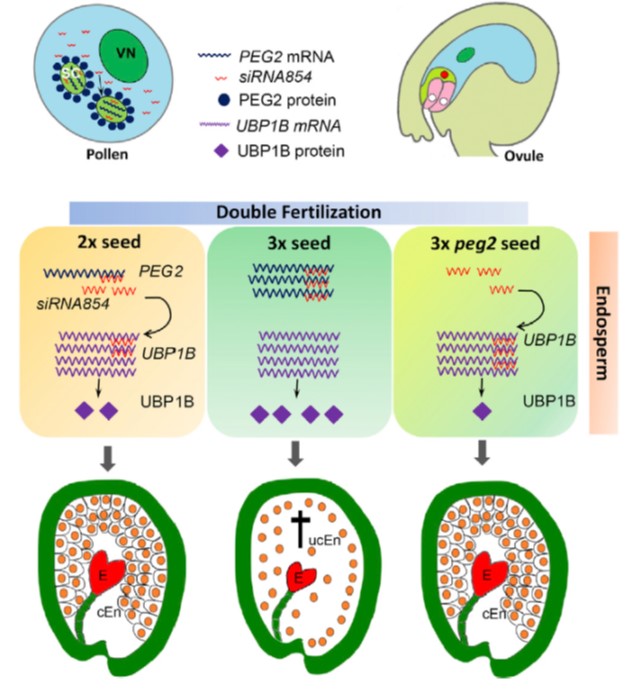
The imprinted gene PEG2 acts as a sponge for the transposon-derived siRNA854, inducing postzygotic reproductive isolation (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClosely related species that have different numbers of chromosomes (e.g., 2n versus 4n) are reproductively isolated, and this can arise as a consequence of an unbalancing in the expression levels of maternally- and paternally-imprinted genes. Wang et al. have identified a fascinating mechanism that explains…
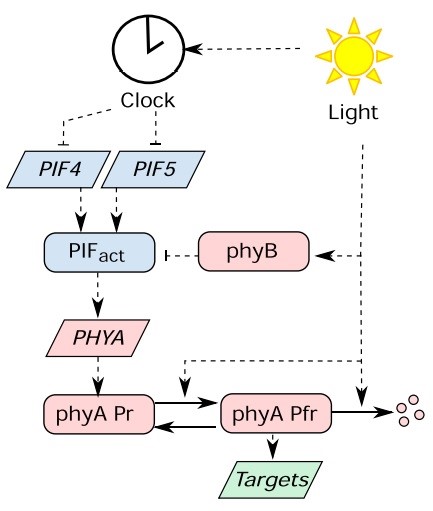
Dawn and photoperiod sensing by phytochrome A ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants perceive the change of seasons based on measuring the duration of daylight. Flowering is a major seasonal response that depends on photoperiod. In this study, Seaton et al. looked at the role of phytochrome A (phyA) in photoperiod sensing. PHYA is the direct target of PIF4 and PIF5 transcription…
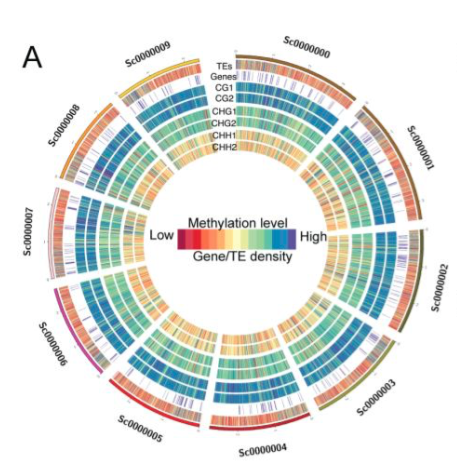
Tea genome expansion linked to TE bursts (Plant Biotechnol. J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyExpansion of plant genomes is thought to be linked to massive bursts of transposable elements activity. This implies consequences on the distribution of epigenetic modifications required for the silencing of the causative transposons. Consequences of transposon bursts have been extensively described…
Stony hard phenotype in peach due to transposon insertion into YUCCA ($) (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFruit softening in melting-flesh peaches is triggered by a major accumulation of ethylene at the late stage of ripening. Existence of stony hard peaches showing inhibition of fruit softening has been correlated with low levels of indole-3-acetic-acid inducing low levels of ethylene, but the underlying…

