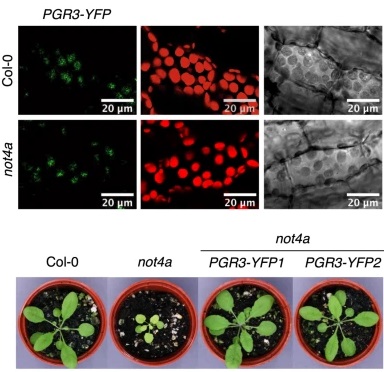
The Arabidopsis NOT4A E3 ligase promotes PGR3 expression and regulates chloroplast translation (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) domain containing proteins are nuclear encoded with functions in the chloroplast, but regulation of PPR gene expression in the nucleus before import to the chloroplast has not been well studied. Bailey et al. identified and characterized the ubiquitin ligase NOT4A and its…

BONZAIs emerge as nodal regulators of osmotic stress responses (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants launch their response to osmotic stress with a sudden spike in cytosolic Ca2+ levels, which subsequently leads to the accumulation of the phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA). This further initiates a chain of events including closure of stomata, large-scale transcriptional changes, retardation of…
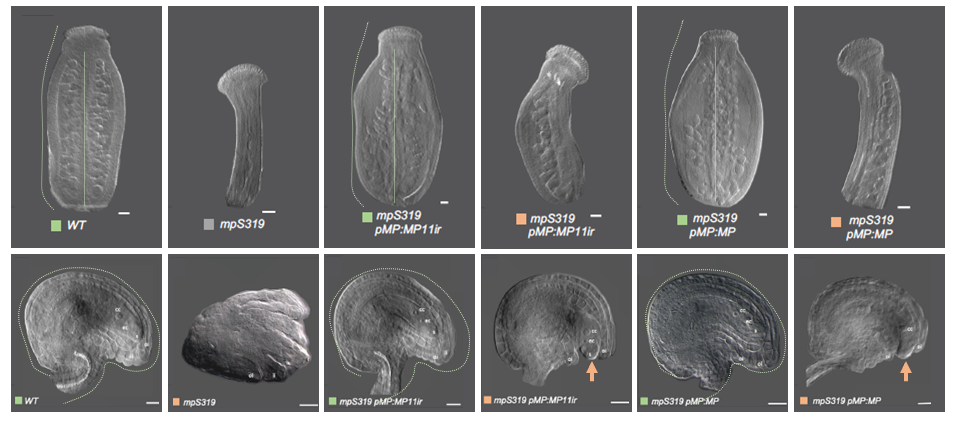
Alternative splicing generates a MONOPTEROS isoform required for ovule development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Auxin shapes the plant body and drives the formation of lateral organs such as roots and ovules. In the current model, AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORs (ARFs) are transcription factors that regulate plant growth by activating signaling in an auxin dose-dependent manner, regulated by Aux/IAA proteins. Here,…
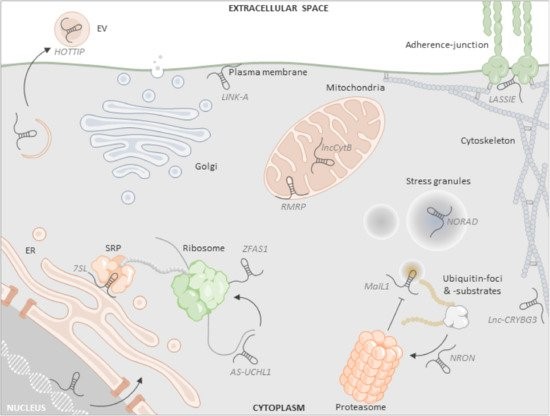
Review: Emerging roles of long noncoding RNAs in the cytoplasmic milieu (non-coding RNA)
Plant Science Research WeeklyReview: Emerging roles of long noncoding RNAs in the cytoplasmic milieu
Note: This article focuses on work in mammalian systems but may be of interest to plant biologists. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) are ³200nt RNAs and represent almost 0.2% of cellular RNA pool. Early work focused on their roles…
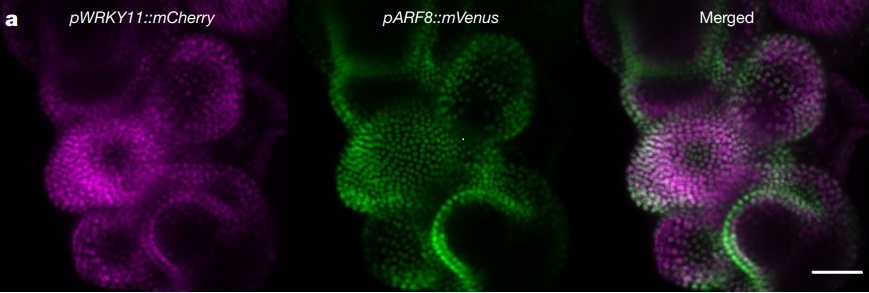
A network of transcriptional repressors modulates auxin responses (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA network of transcriptional repressors modulates auxin responses
Untangling developmental programs and their methods of regulation are key to understanding the lives of all organisms. In plants, auxin is a hormone essential for plant growth and development. The class A AUSIN RESPONSE FACTOR…
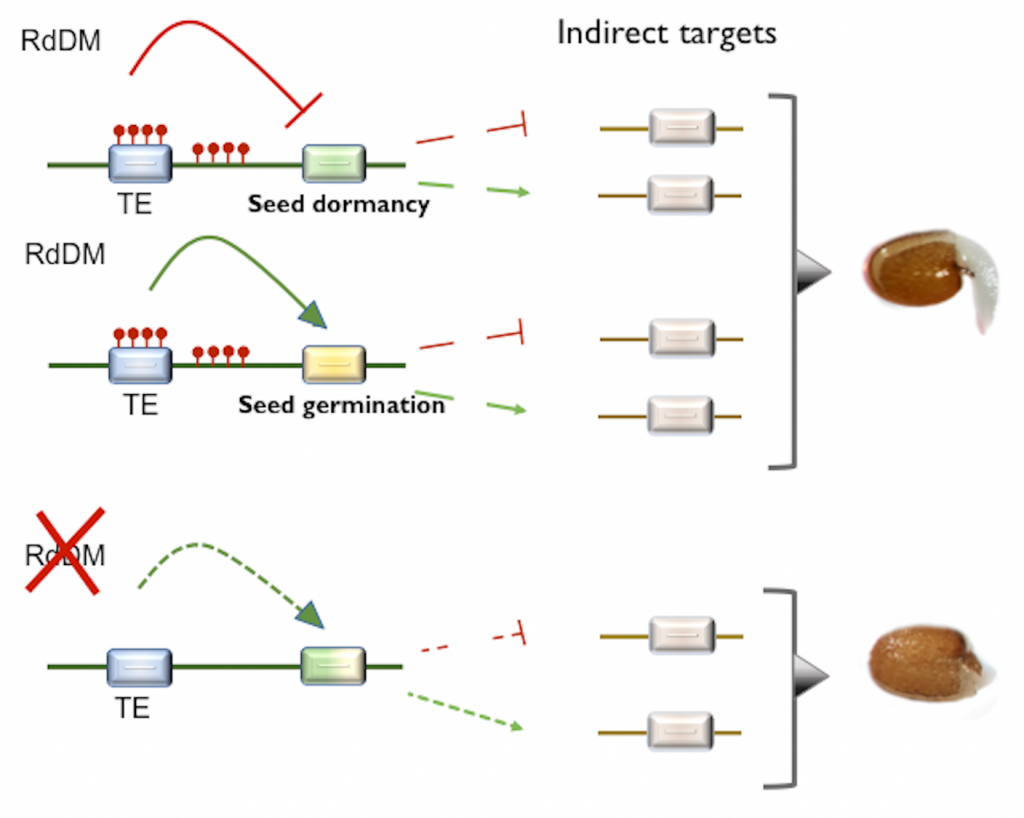
The canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($) (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($)
Epigenetic regulation can ensure that plant developmental programs and stress responses are tightly coordinated so that environmental changes do not compromise plant fitness. One of the mechanisms to achieve…
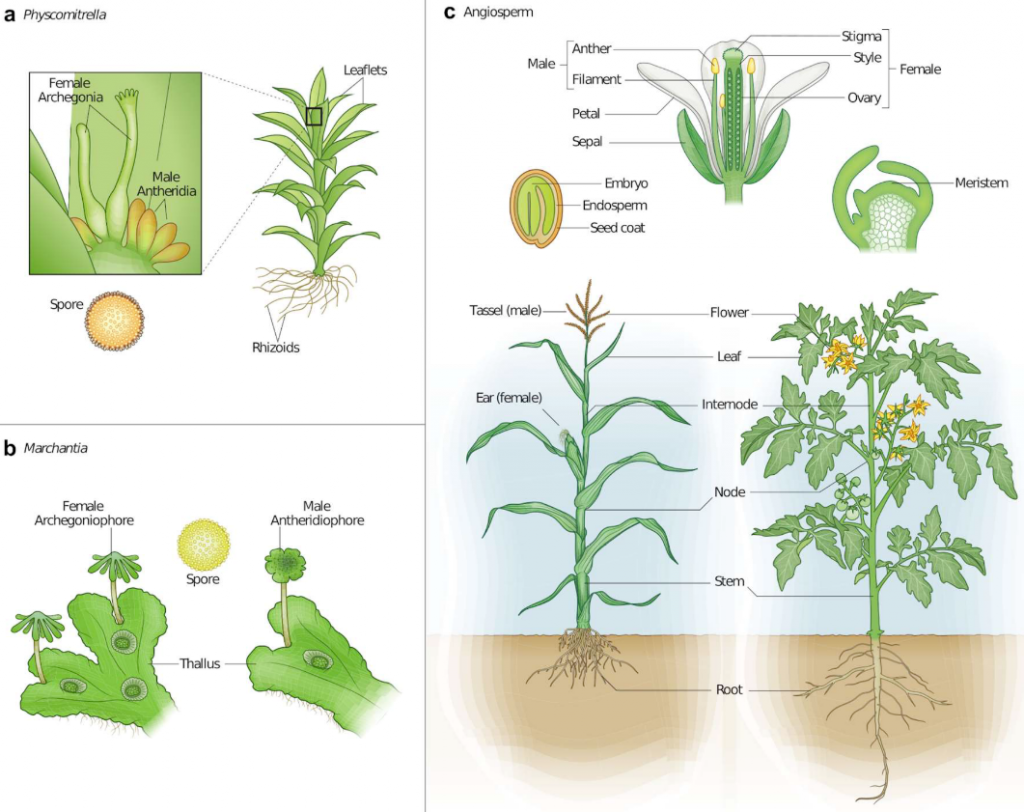
Conserved transcriptional programs underpin organogenesis and reproduction in land plants (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plant evolution accompanied a plethora of evolutionary novelties such as cells that compose complex organs (e.g., stems, leaves, roots) and male/female gametophytes. The identity and conservation of the transcriptional programs underlying organogenesis and reproductive development across land plants…
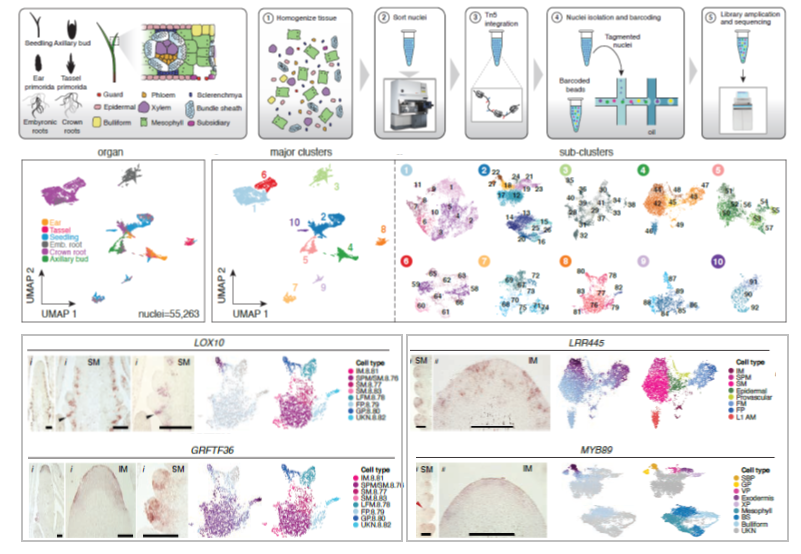
A cis-regulatory atlas in maize at single-cell resolution (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Cis-regulatory elements (CREs) are DNA sequences found near or within genic regions that drive proper gene expression in time and space. Thus, CREs play essential roles in the diversification of spatially distinct cell-types with specialized function in multicellular organisms. To identify CREs underlying…

Transcriptional regulation of PLETHORA1 in the root meristem through an importin and its two antagonistic cargos (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plant root growth is sustained by stem cells in the root meristems, and the stem cell fate is maintained by the quiescent center (QC). PLETHORA (PLT) protein gradients contribute to maintaining the root meristem cell fate, although the transcriptional regulatory mechanism that establishes the PLT…

