
Vascular transcription factors guide plant epidermal responses to limiting phosphate conditions (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants produce more root hairs (epidermal projections) in response to low soil phosphate and the detailed mechanism of this developmental response remains elusive. TARGET OF MONOPTEROS 5 (TMO5) and LONESOME HIGHWAY (LHW) are vascular specific bHLH proteins that work as a heterodimer to activate the rate…
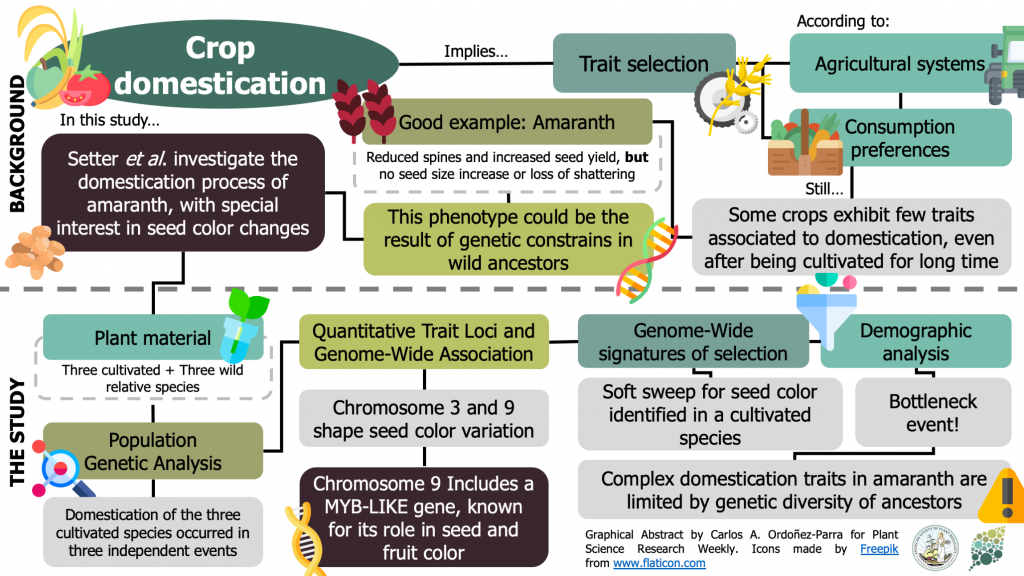
Parallel Seed Color Adaptation during Multiple Domestication Attempts of an Ancient New World Grain ($) (Mol. Biol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmaranth has been cultivated in Central and South America since Pre-Columbian times. Still, it exhibits features that are unexpected in domesticated plants, such as seed shattering and reduced seed size. Here, Setter et al. dissected the genetic signature of this crop’s domestication process, with…
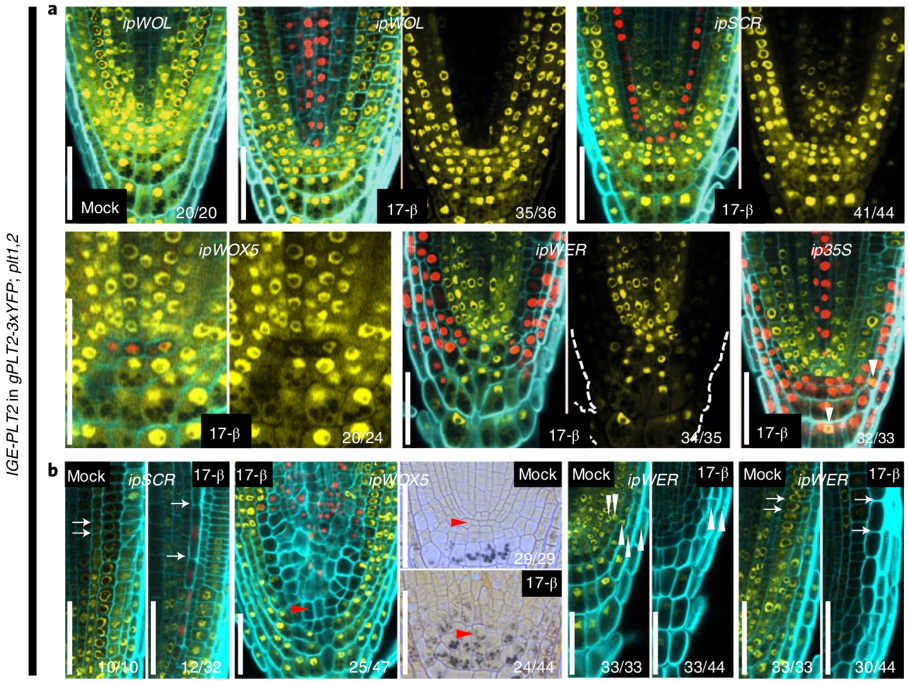
An inducible genome editing system for plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo understand gene function, it is necessary to study loss-of-function phenotypes. However, knockouts of some genes are lethal, which makes it impossible to study their loss-of-function phenotype. Although here are inducible overexpression systems and inducible knockdown systems, as yet there has been…
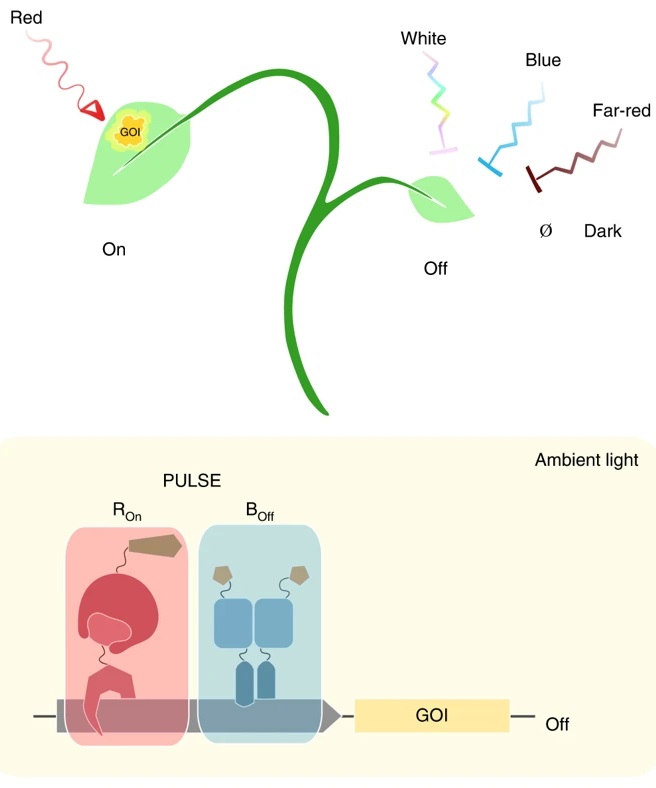
An optogenetic tool for plants grown in ambient light (Nature Methods)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOptogenetics has revolutionized mammalian biology by its ability to fine-tune gene expression in individual cells by pulses of light. However, its application in plants has been challenging because the white light required for plant growth misfires the system. Ochoa-Fernandez et al. solved this problem…

The 3′ processing of antisense RNAs physically links to chromatin-based transcriptional control (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis, multiple genetic pathways control the floral transition in response to external and internal stimuli. Among these, components of the autonomous pathway promote flowering by negatively regulating the central floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Despite the wealth of information on…
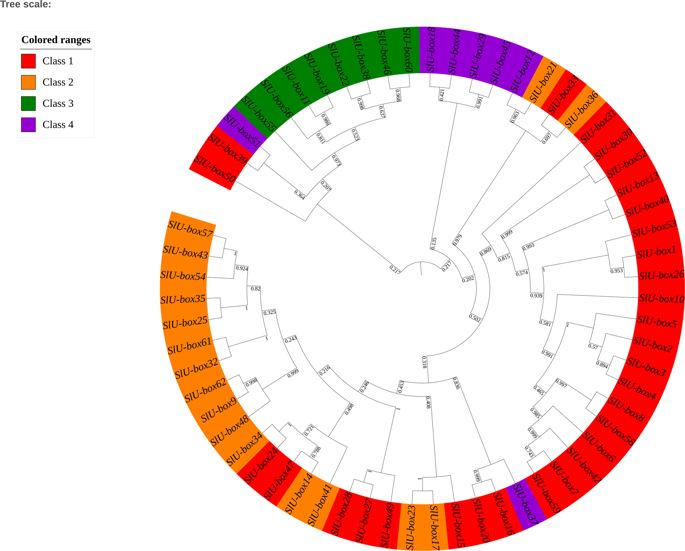
Genome-wide analysis of the U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme gene family in tomato (Sci. Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUbiquitination is a process of adding ubiquitin (a small regulatory protein) to a substrate protein, leading to its degradation. A wide variety of cellular processes necessary for plant growth and development are regulated by ubiquitination. E3 ubiquitin ligases are the largest family of proteins involved…
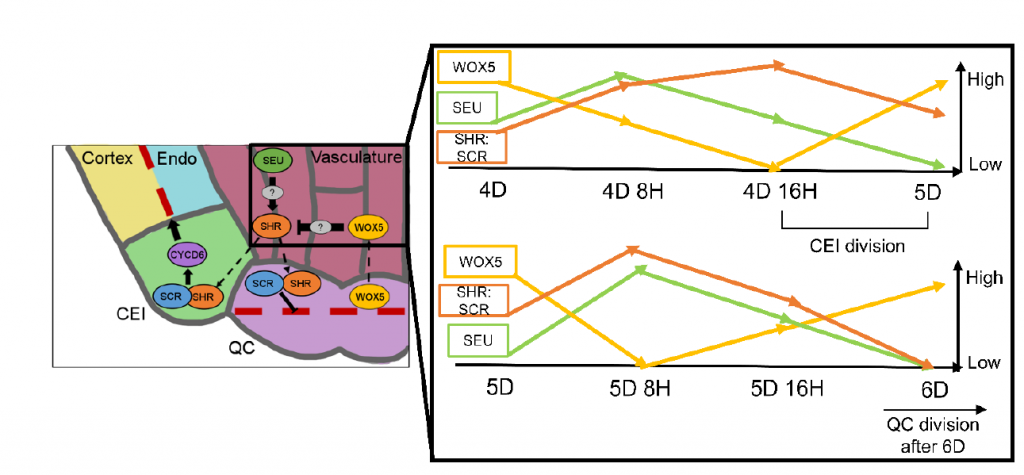
Protein complex stoichiometry and expression dynamics of transcription factors modulate stem cell division (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStem cells are a group of undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate to form new organs. In Arabidopsis roots, the quiescent center (QC: the mitotically inactive group of cells) helps regulate the division of surrounding initials and maintain the stem cell fate. What makes the QC different…
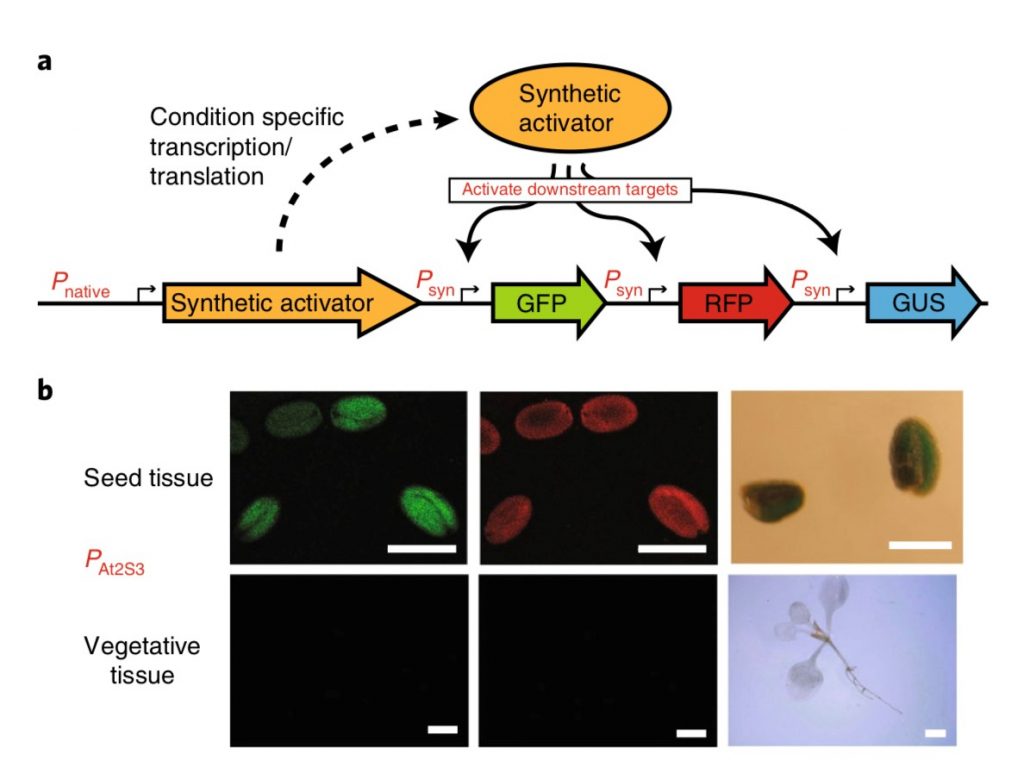
Modulation of gene expression in plants with orthogonal regulatory systems (Nat. Chem. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome of the most promising applications in synthetic biology need precise control of gene expression. For instance, metabolic engineering in plants requires the expression of enzyme-coding genes at a precise time, space, and quantity to ensure correct output. Recently, Belcher, Vuu, and colleagues engineered…
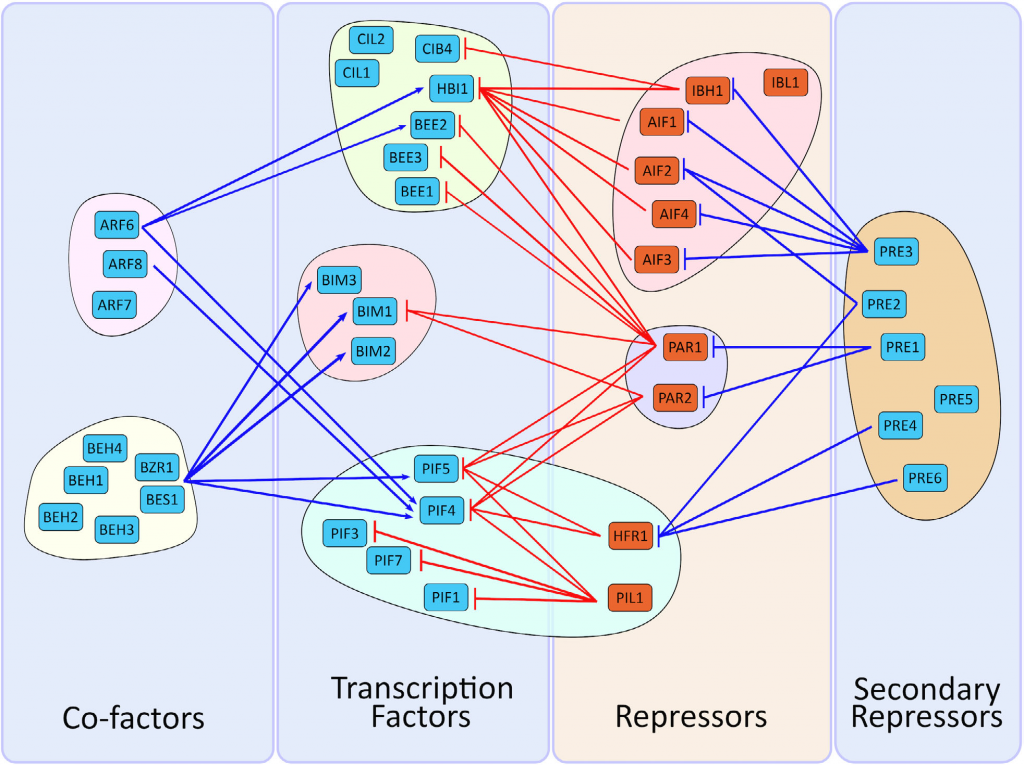
Review: The bHLH network underlying plant shade-avoidance (Physiol. Plant.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyShade avoidance is a complex phenomenon in which plants avoid shade by altering their developmental program in various ways including early flowering, hypocotyl elongation, and more. Many photoreceptors and transcription factors (TFs) are involved in regulating shade avoidance, including the bHLH (basic…

