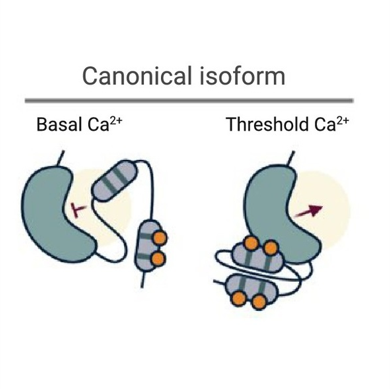
Review: Alternative splicing as conserved mechanism to regulate CDPKs? ($) (TIPS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs/CPKs) are an interesting class of proteins present in plants, algae and some protists that are thought to “sense” and “respond” to spikes in intracellular Ca2+ signaling events. While multiple mechanisms have been proposed to be involved in the regulation…

The secret to leaf forever: Mechanisms controlling simple leaf development (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe final shape of a leaf is a consequence of differential growth at its margins. Simple (or lightly serrated) leaves result from limited growth in the margins, while compound leaves result from a constant initiation of leaflets. A recent work by Challa, Rath, and colleagues dissected the regulatory…

Repeat yourself: A new way to self-express
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellReinar et al. uncover the effects of allelic variation in short tandem repeats across natural populations of Arabidopsis thaliana on gene expression.
By Kjetill Jakobsen1, Melinka Butenko2, and William Reinar1
1Centre for Ecological and Evolutionary Synthesis (CEES), University of Oslo, Department…
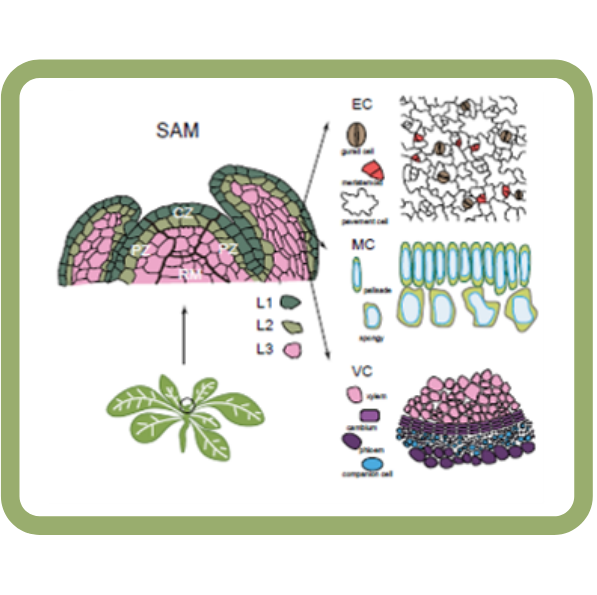
A single-cell analysis of the Arabidopsis vegetative shoot apex (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the most fascinating challenges in developmental biology is to understand how a few stem cells hidden in a microscopic region of the shoot apex give origin to all aerial parts of the plant. Technological advances such as single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) are enabling the comprehensive analysis…
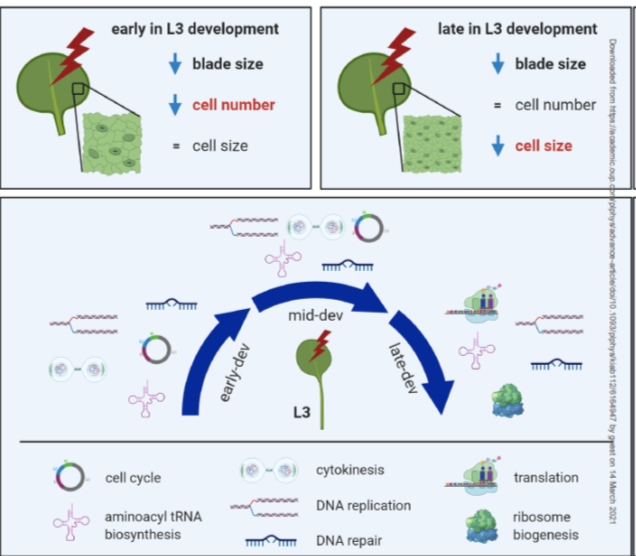
Phytochrome regulates cellular response plasticity and the basic molecular machinery of leaf development (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe effects of light on plant growth are incredibly complex and depend on where it is perceived, light quantity, light quality (wavelength), and when within the circadian cycle it is perceived. Romanowski et al. examined the effect of late-day far-red light perception in Arabidopsis leaves. This treatment…
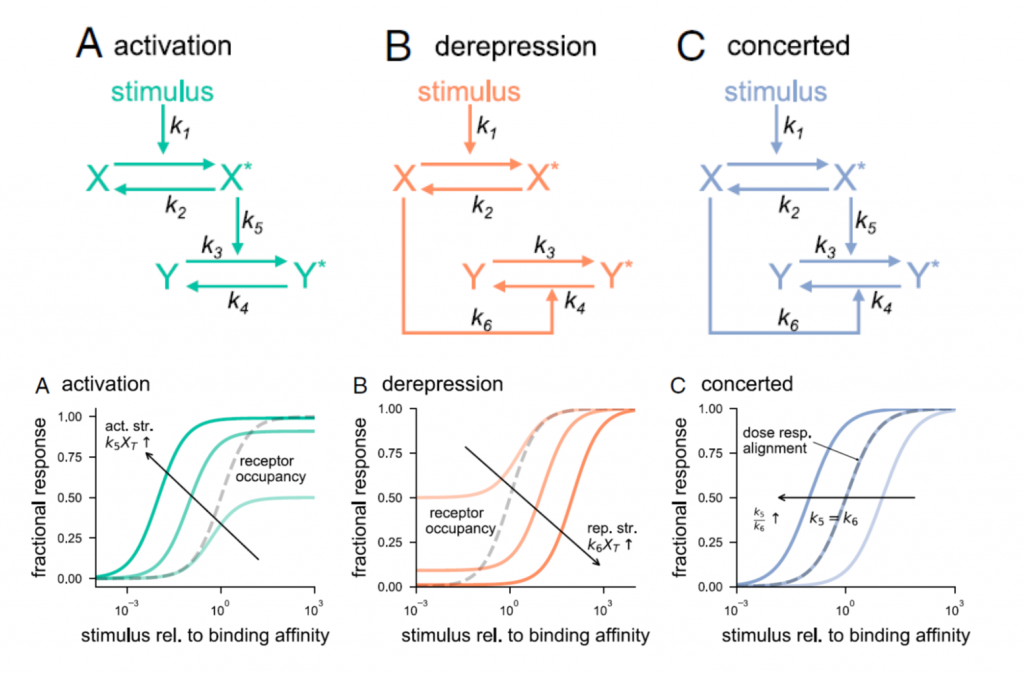
Molecular switch architecture determines response properties of signaling pathways (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenetic studies have provided us with countless examples of regulatory switches that transduce a signal into a response. Mutant analysis is usually sufficient to identify these controlling elements, but often in an all-or-nothing way. Here, Ghusinga et al. have taken a theoretical kinetic approach to…
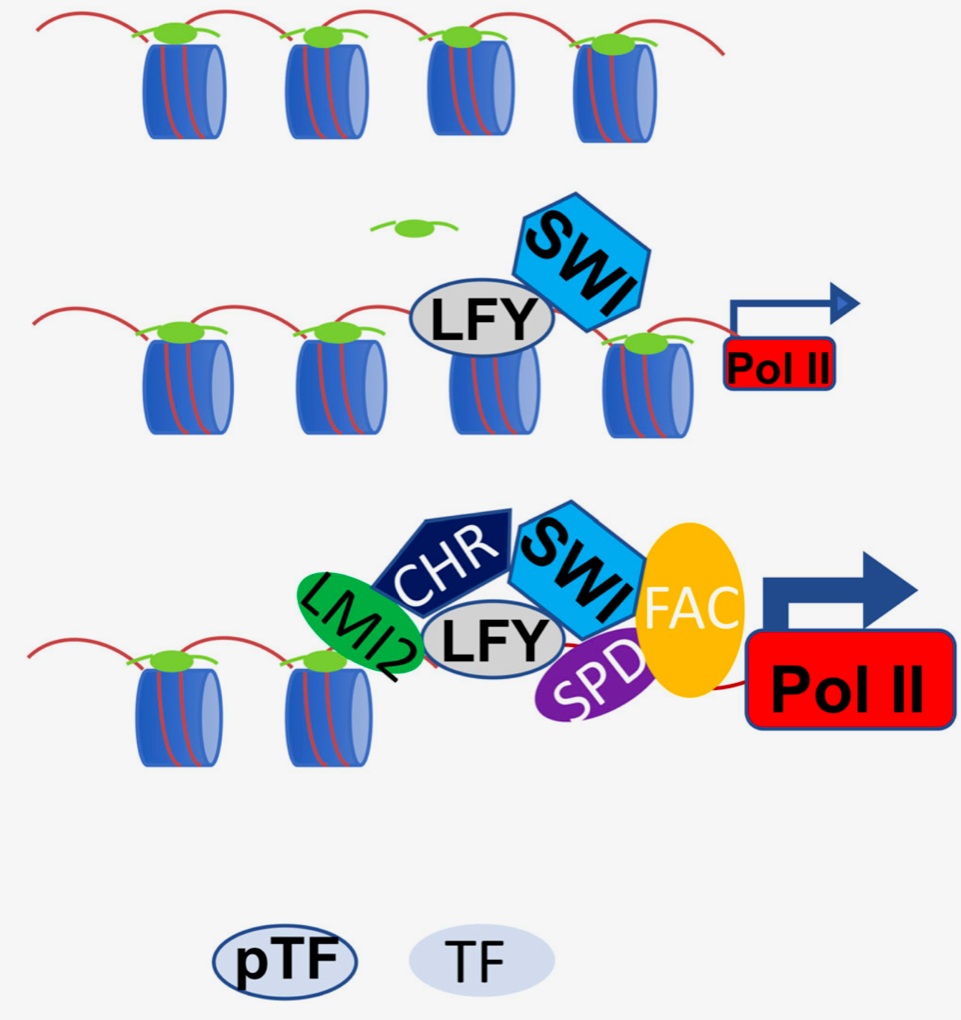
LEAFY is a pioneer transcription factor and licenses cell reprogramming to floral fate (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaster transcription factors (TFs) can activate specific genetic programs to reprogram cellular fate in the context of open chromatin. A special class of these proteins known as pioneer TFs are defined by their ability to trigger cell fate reprogramming by binding their cognate cis motifs in a nucleosome…
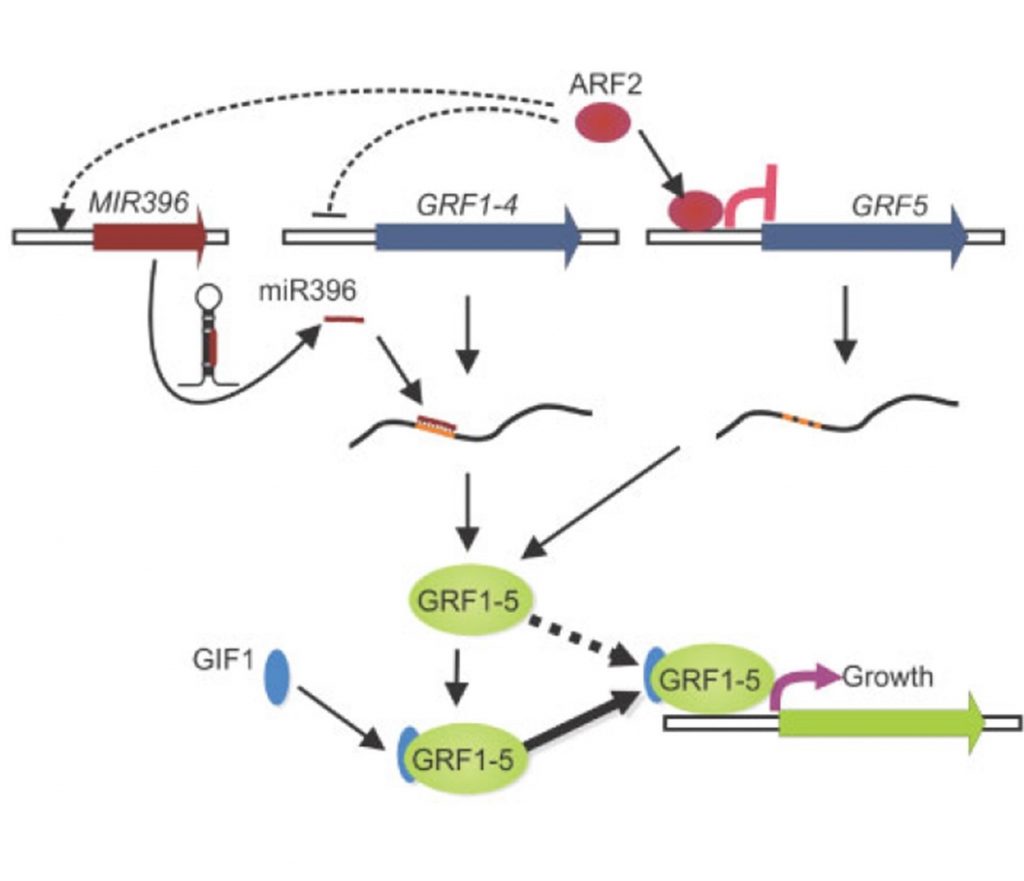
A complementary mechanism to the microRNA-mediated control of leaf size (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants form leaves with highly reproducible sizes and shapes by employing a conserved set of developmental regulators. During early leaf growth, a zone of high cell proliferation is formed towards the proximal end of the lamina. Proliferating cells progressively exit this zone and enter the distal…
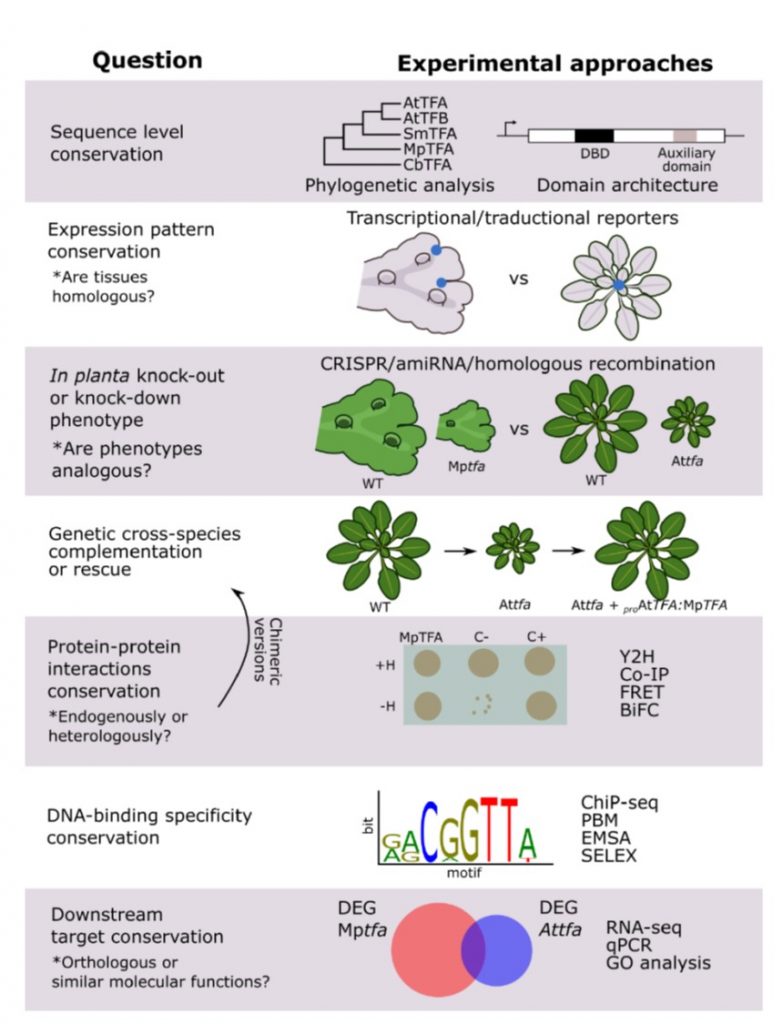
Review: Molecular mechanisms involved in functional macroevolution of plant transcription factors (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTranscription factors (TFs) are very important actors through which evolution can operate. In every organism and system studied, starting with the seminal work of Jacob and Monod, they’ve been shown to be potent regulatory proteins. Here, Romani and Moreno review the contributions of plant transcription…

