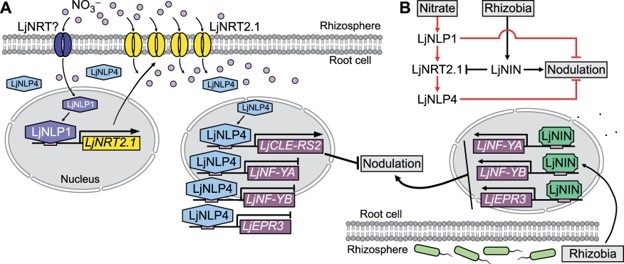
Nitrate transporter NRT2.1 is a determinant of a nitrogen acquisition switch between nitrate uptake and symbiosis in Lotus japonicus (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen nitrogen or nitrate availability is high, symbiotic nodule generation is curtailed to conserve the associated energy cost. But how does the presence of nitrate interfere with nodulation and symbiosis? Previously, genetic studies identified nitrate unresponsive symbiosis (nrsym) mutants in Lotus…
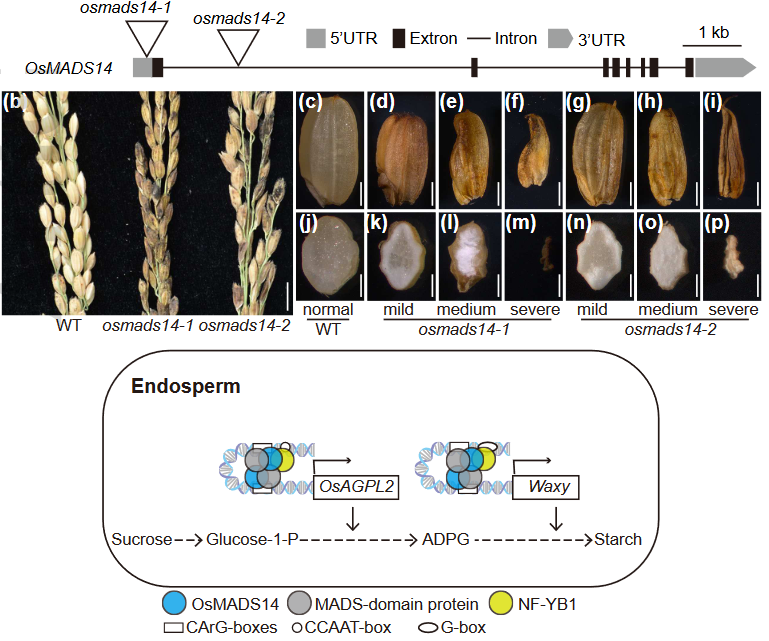
OsMADS14 and NF-YB1 cooperate in the direct activation of OsAGPL2 and Waxy during starch synthesis in rice endosperm (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRice grain is mainly composed of starch, which provides the necessary energy and sugars for successful germination and seedling development. Since rice is the most widely consumed crop, studying the regulators that control starch synthesis is crucial to ensure food security for more than half the world‘s…
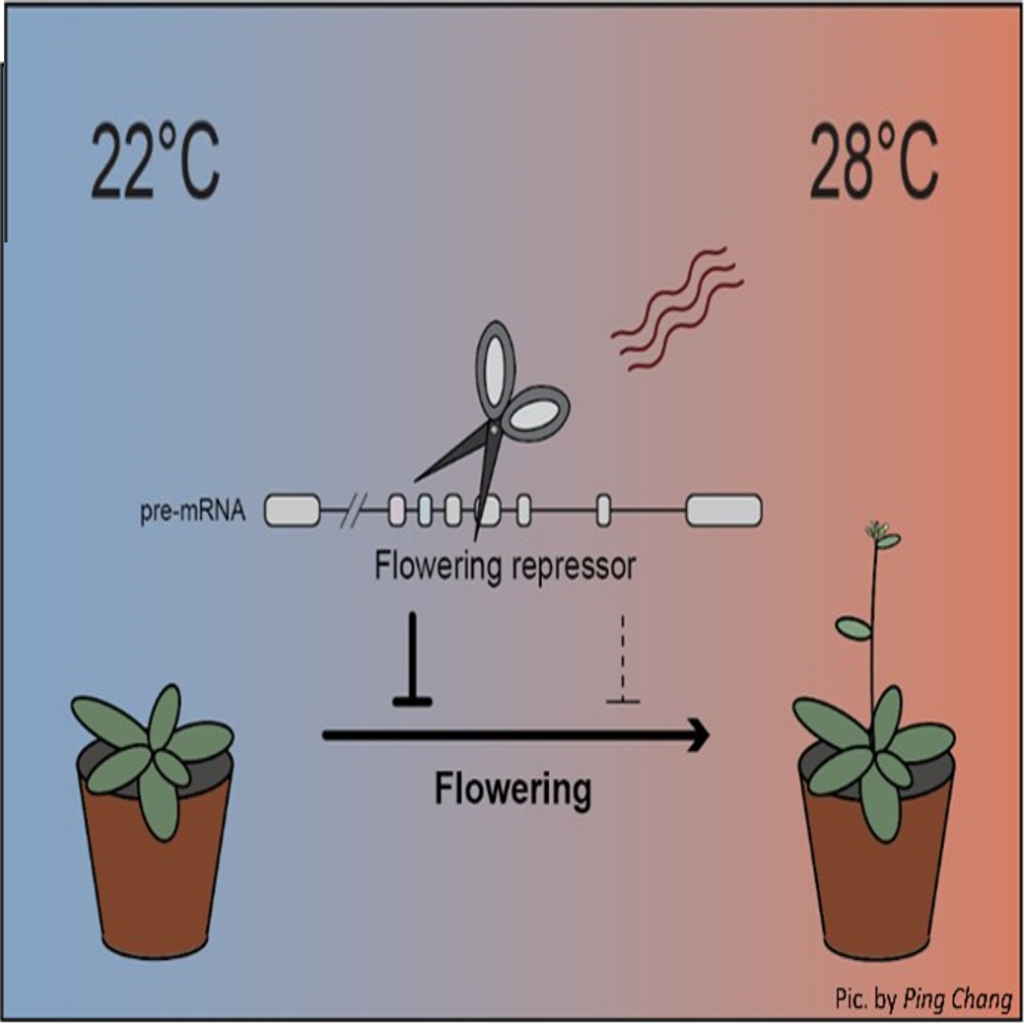
The splicing factor RNA BINDING PROTEIN 45d regulates temperature-responsive flowering (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPosttranscriptional events such as splicing are part of the gene regulation toolbox. Previous studies have demonstrated a role for U-rich small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) such as U1 in the control of splicing. In a recent paper in The Plant Cell, Chang et al. identified a splicing factor, RNA…
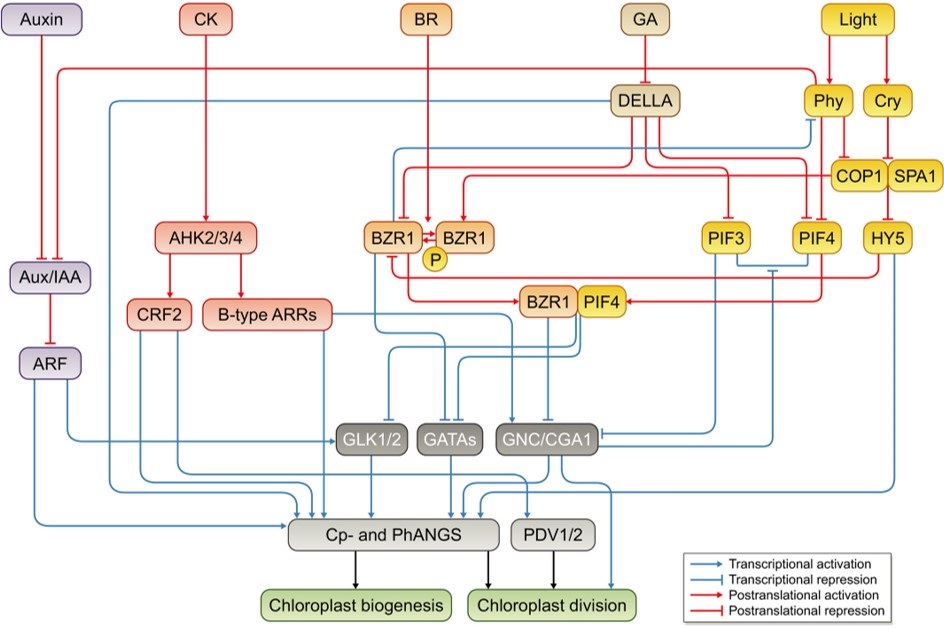
Review. Chloroplast development in green plant tissues: The interplay between light, hormones, and transcriptional regulation (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChloroplasts are indispensable for plant growth and physiological performance; not only for photosynthesis but also for many biochemical processes. Due to the endosymbiont origin of the chloroplast, chloroplast development requires sophisticated machinery to relay the signals between the nuclear and…
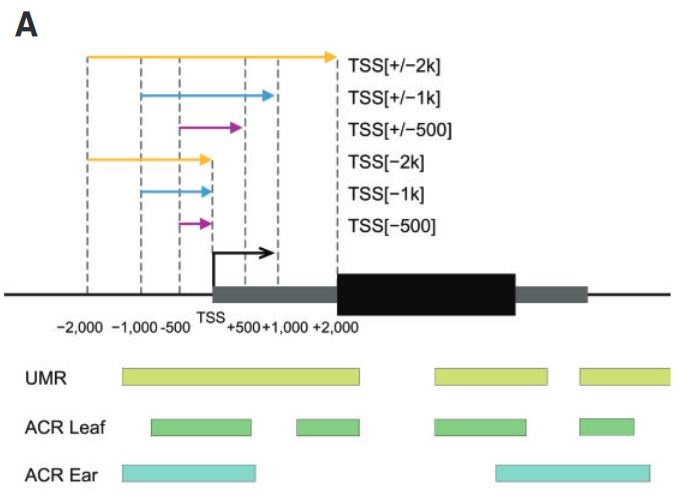
Prediction of conserved variable heat and cold stress response in maize using cis-regulatory information (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeveral transcription factors (TFs) have been identified previously as responsive to cold and heat stresses in maize. Variation in TF binding sites (TFBS) determine changes in the expression of target genes in response to the aforementioned stresses. Traditionally, single varieties were used to study…
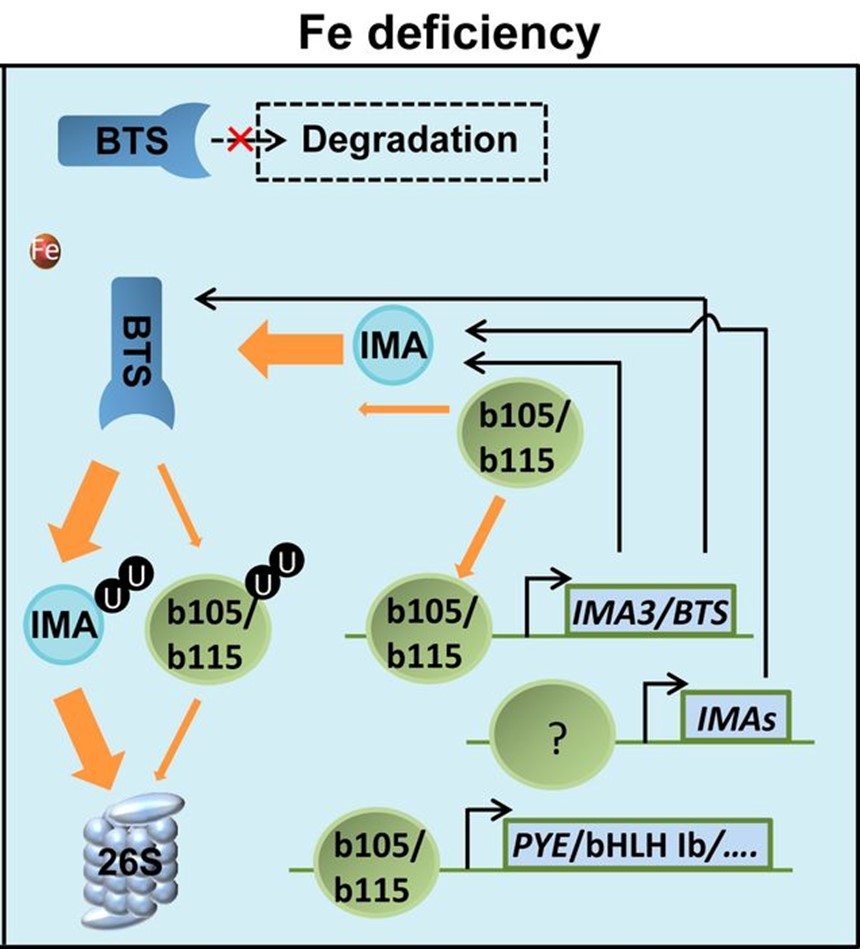
IRON MAN sequesters BTS to activate iron deficiency response (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to maintain an optimum level of iron (Fe) for normal growth and development. Many Fe-responsive molecular players have been identified in Arabidopsis, including the IRON MAN (IMA) peptides. These peptides are induced by Fe deficiency, but their role in maintaining Fe homeostasis remains poorly…
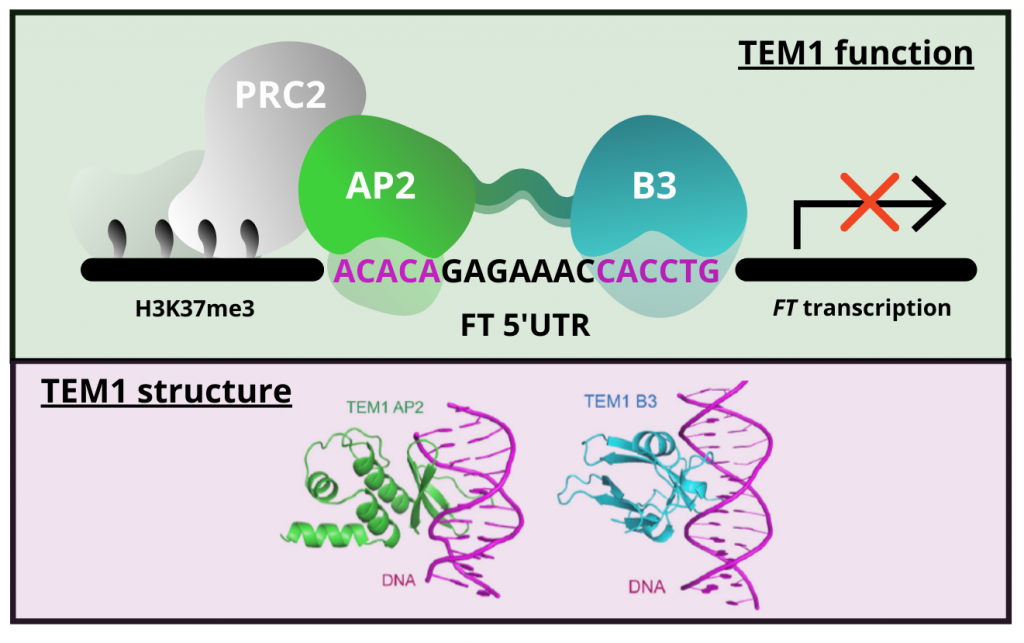
TEM1 combinatorially binds to FLOWERING LOCUS T and recruits a Polycomb factor to repress the floral transition in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene expression is primarily controlled by transcriptional regulatory proteins able to recognize and bind short DNA sequences in downstream targets. Understanding how DNA-binding proteins achieve high precision and switch on/off the transcription of selected genes at a specific developmental stage or…
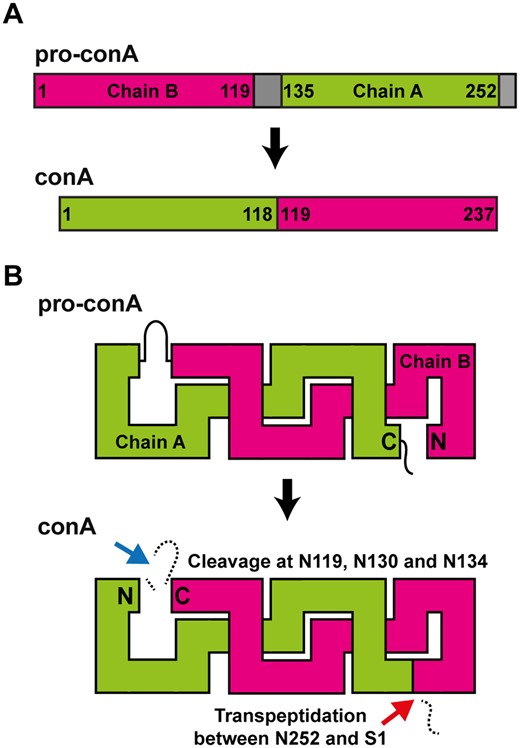
Structural and biochemical analyses of concanavalin A circular permutation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you have heard of concanavalin A (ConA), it probably is because it is a widely-used reagent in carbohydrate science and medical research. ConA is a lectin derived from jackbean (Canavalia ensiformis, hence the name) that binds assorted carbohydrates. It is also a fascinating protein that assembles…
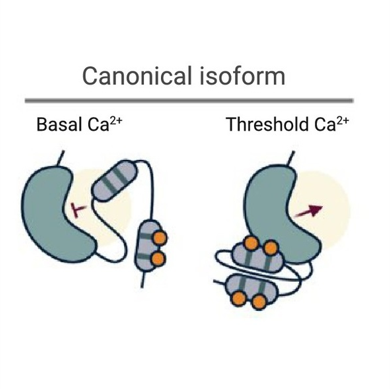
Review: Alternative splicing as conserved mechanism to regulate CDPKs? ($) (TIPS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs/CPKs) are an interesting class of proteins present in plants, algae and some protists that are thought to “sense” and “respond” to spikes in intracellular Ca2+ signaling events. While multiple mechanisms have been proposed to be involved in the regulation…

