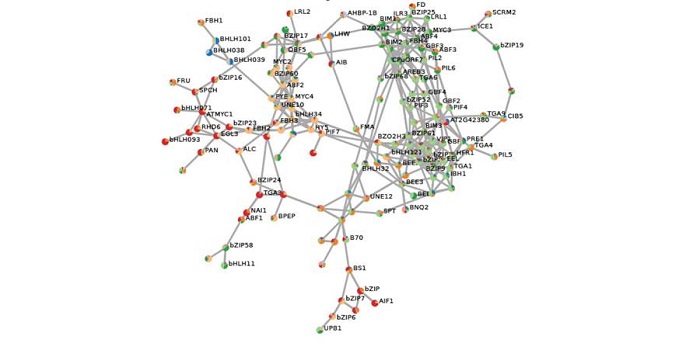
The G-box transcriptional regulatory code in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe G-box (CACGTG) is a DNA element widespread in plant genomes and recognized by two large families of transcription factors (TFs), the basic leucine zipper family (bZIP) and the basic-helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family. Members of these TF families contribute to growth, temperature and light signaling,…
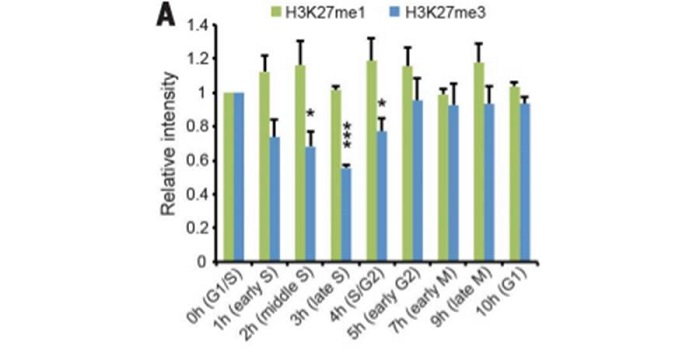
Epigenetic memory restoration and maintenance after cell division
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNucleosomes, composed of histones, pack chromatin and make genes less available for transcription. Methylation of some histone positions is associated with repression of transcription and epigenetic silencing of some genes. After cell division during the cell cycle, maintenance of expression patterns…

Flowering Versus Runnering: A Very Important Decision in Strawberry
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellTenreira et al. find a gene responsible for the differentiation of the stolon in strawberry. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00949
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parents. This process takes many forms in flowering plants, including…
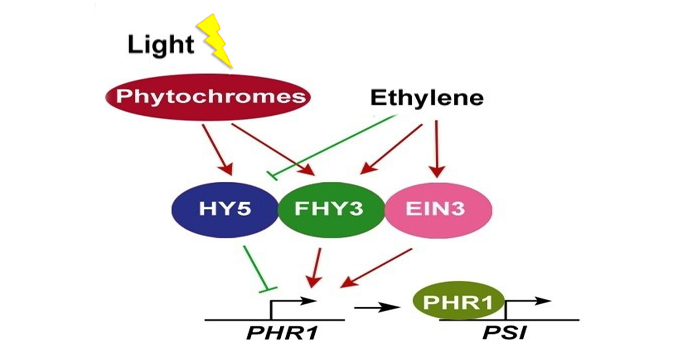
Light Helps Plants Cope with Phosphate Starvation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu et al. focus on transcriptional regulation of PHR1 expression. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00268
Phosphorus (P) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth, development, and metabolism. Phosphate (Pi), the major form of P used by plants, is highly immobile in most soils,…
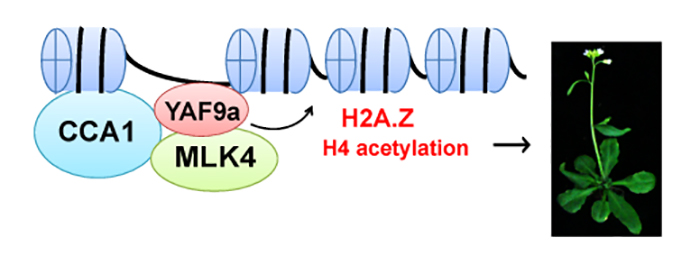
How Does Histone Phosphorylation Affect Flowering Time?
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSu et al. look at chromatin modifications that affect flowering. The Plant Cell 2017. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00266
Plants, unlike animals, begin their lives as seeds that – in flowering plants – develop from flowers. This depends upon proper regulation of flowering time, to ensure pollination,…
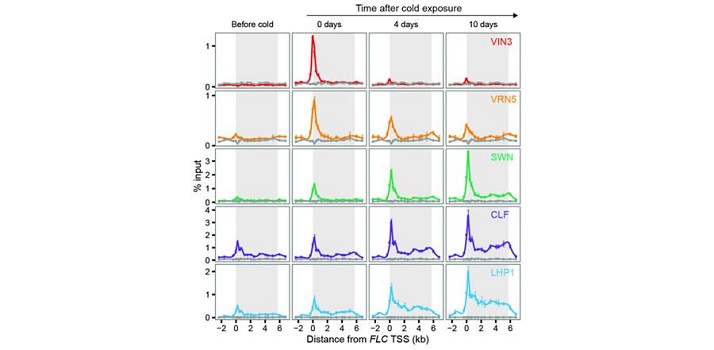
Stages of silencing to hold epigenetic memory
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe gene FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C) is a repressor of flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. It needs to be silenced after exposure to prolonged cold for plants to be able to flower. The memory of winter leads to changes in the methylation state of Histone 3 associated with FLC in two steps: first by recruiting…
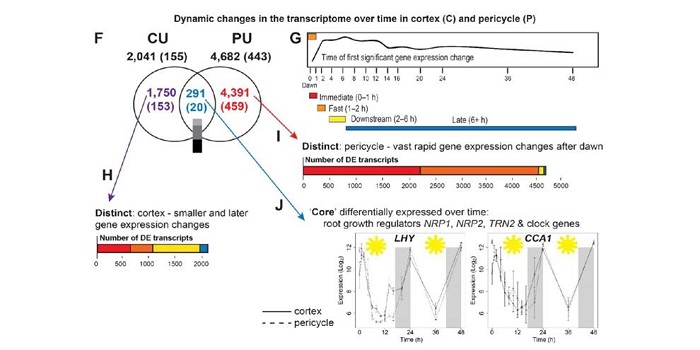
4D root gene expression
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIt becomes more and more clear that regulation of complex traits and processes, such as root growth and lateral root growth, involves not only gene expression quality (which genes are expressed), quantity (how much transcript is present) and space (in which cell-type transcripts are accumulating) but…
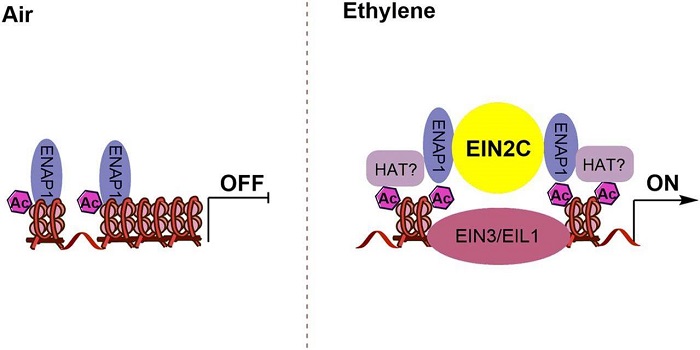
EIN2 mediates direct regulation of histone acetylation in the ethylene response
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPerception of the phytohormone ethylene results in the cleavage of EIN2 and translocation to the nucleus of its C-terminal end, EIN2-C. Zhang et al. showed that EIN2-C is essential for chromatin modification that allows EIN3, the main ethylene signaling transcription factor, to transcriptionally regulate…
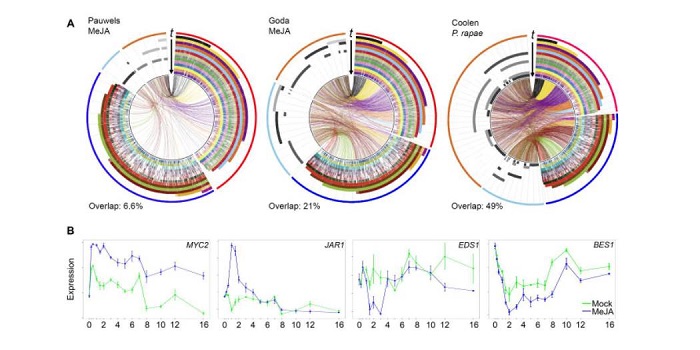
Architecture and dynamics of the jasmonic acid gene regulatory network
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogJasmonic acid (JA) and its derivatives including methyl jasmonate (MeJA) mediate diverse responses to wounding and herbivory and also help to control the growth-defense trade off. JA’s core signaling components have mainly been identified through genetics approaches in Arabidopsis, but gaps remain…

