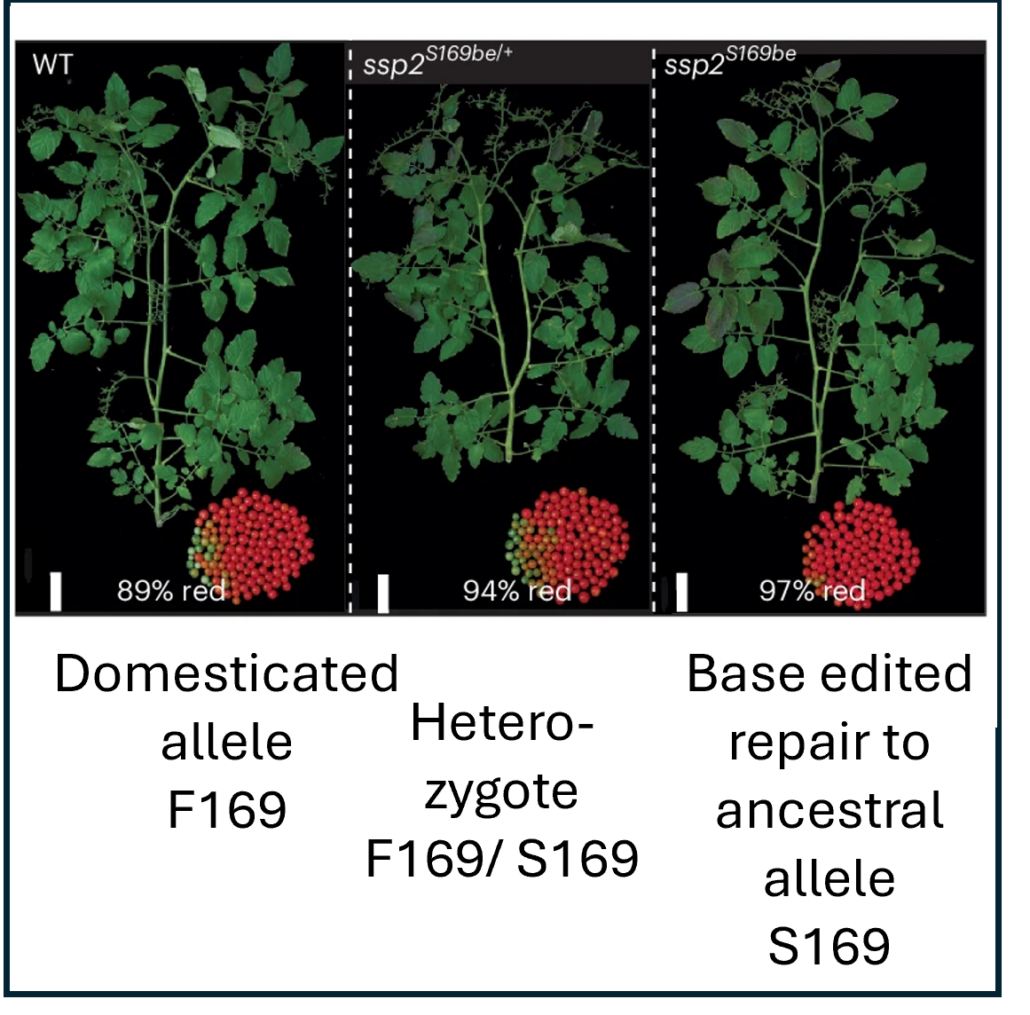
Repairing a detrimental domestication variant improves tomato harvests
Blog, Plant Science Research WeeklyDomesticated plants and animals are remarkable human achievements but were achieved with rather blunt instruments. With the benefit of hindsight, we can now see that some of the genes and alleles that passed through the population bottlenecks and artificial selection process are deleterious. Glaus et…
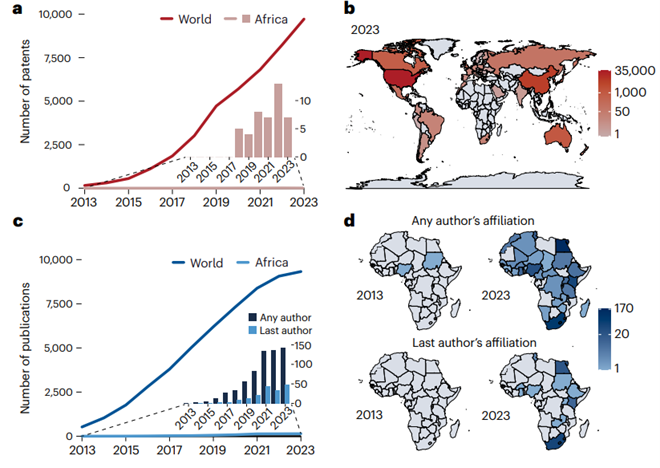
Making genome editing a success story in Africa
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe introduction of CRISPR-Cas technology in 2012 marked a significant advancement in global genome editing, yet its potential remains largely untapped in Africa, where it could address crucial challenges in agriculture, public health, and medicine. However, several obstacles hinder its full realization,…

Commentary: Time to fight the over-hype
Plant Science Research WeeklyA year ago, graduate student Merritt Khaipho-Burch Tweeted a reaction to an article about a gene described as enhancing yield, which led to lively on-line and in-the-lunchroom discussions about how to realistically measure yield, and, maybe more importantly, where to draw the line between potential and…
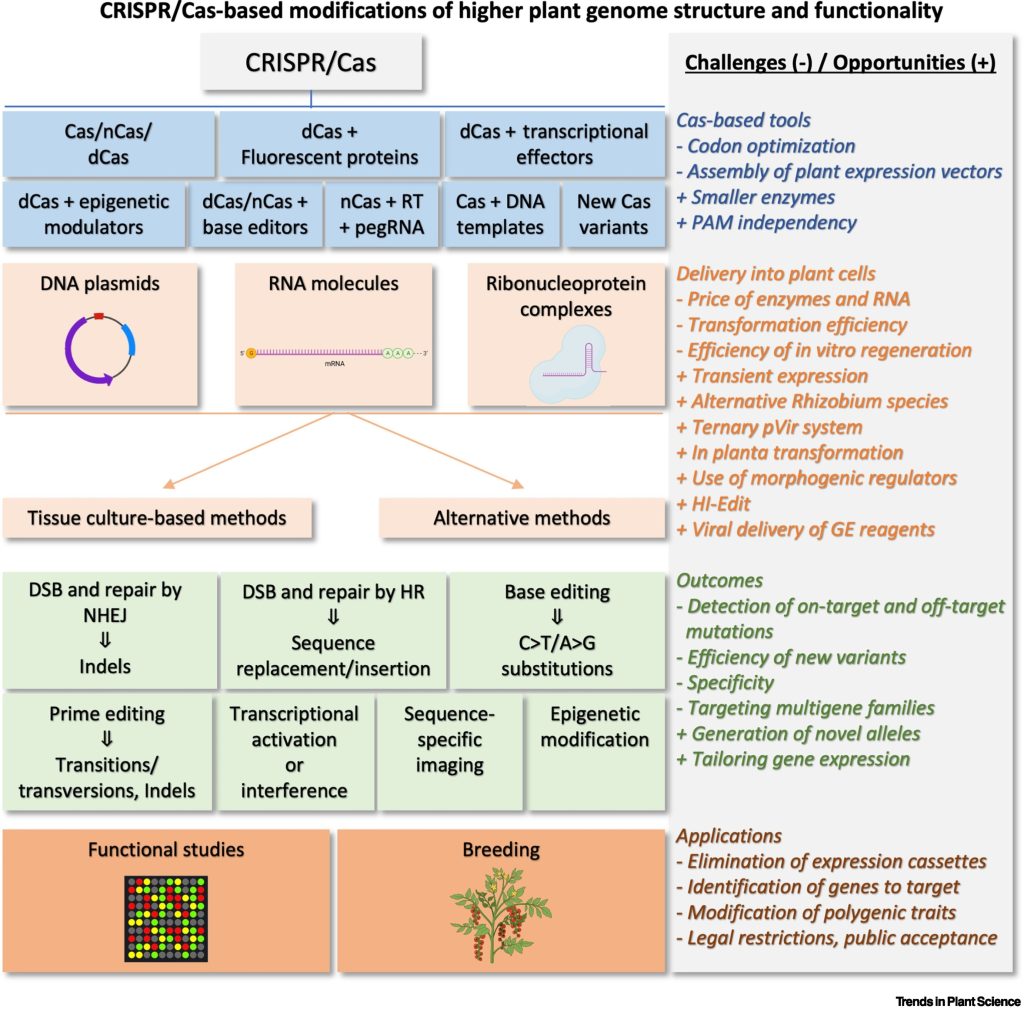
Review: CRISPR/Cas-mediated plant genome editing, a decade after implementation
Plant Science Research WeeklyI’ll be honest, I was surprised to see “a decade after implementation” in this title, but indeed, the first publication describing CRISPR/Cas in plants was in 2013. We’ve learned a lot in the past 10 years and the technology provides many opportunities, but challenges remain, both of which are…
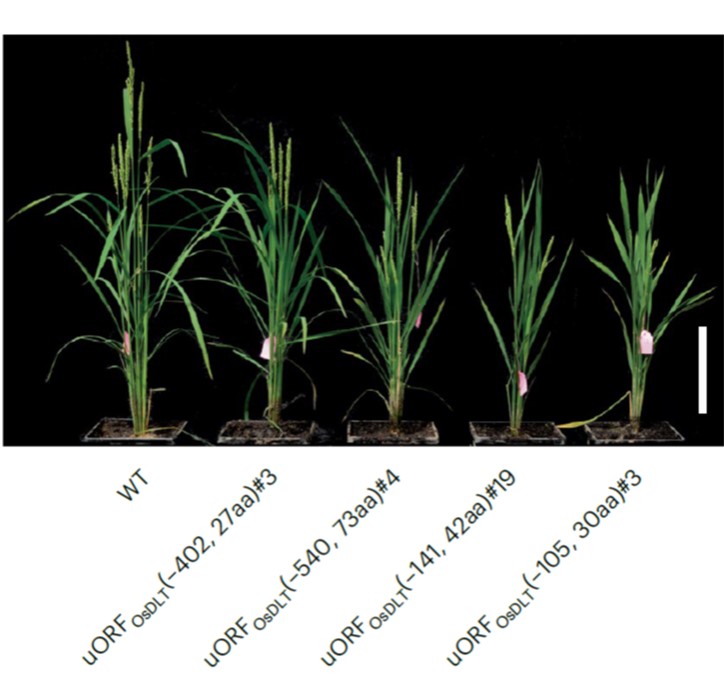

Fine tuning upstream open reading frames allow graded protein downregulation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyRegulatory components called upstream open reading frames (uORFs) are commonly found in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. These uORFs regulate the translation rate of downstream coding sequences. Xue et al. edited uORFs added or edited uORFs in several genes to investigate the effects of adding or extending…

Targeted A-to-G base editing of chloroplast DNA in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe chloroplast has its own genome which encodes proteins needed for chloroplast function. Editing these genes via CRISPR-Cas9 is difficult due to challenges in targeting guide RNAs to the chloroplast. Instead, base editors can be used, but these were originally developed for cytosine to thymine edits…
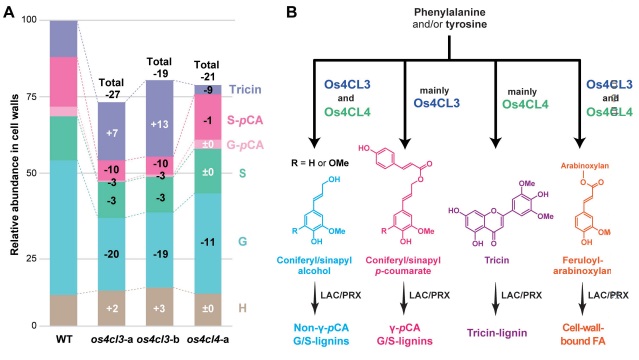
Genome-edited rice deficient in two 4CL genes display diverse lignin alterations (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLignin is one of the most important end-products of the cinnamate/monolignol pathway and it is abundant in the secondary cell wall of vascular plants. In grasses, lignins are derived from monolignols, p-hydroxycinnamates, and a flavonoid tricin. In the proposed cinnamate/monolignol pathway, 4-COUMARATE:COENZYME…
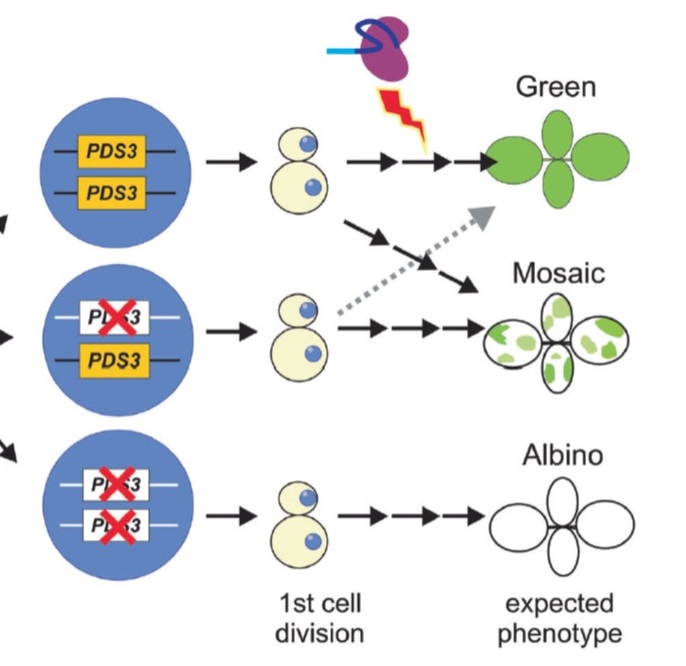
An experimental protocol for teaching CRISPR/Cas9 in a post-graduate plant laboratory course without sequencing (Biochem Mol Biol Educ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyExperience is the best teacher, so hand-on learning is invaluable for students of biology. If you have the opportunity to teach with a laboratory course and haven’t yet incorporated a module that incorporates CRISR/Cas9, you’re in luck! Here, Mayta et al. share the design of the laboratory course…
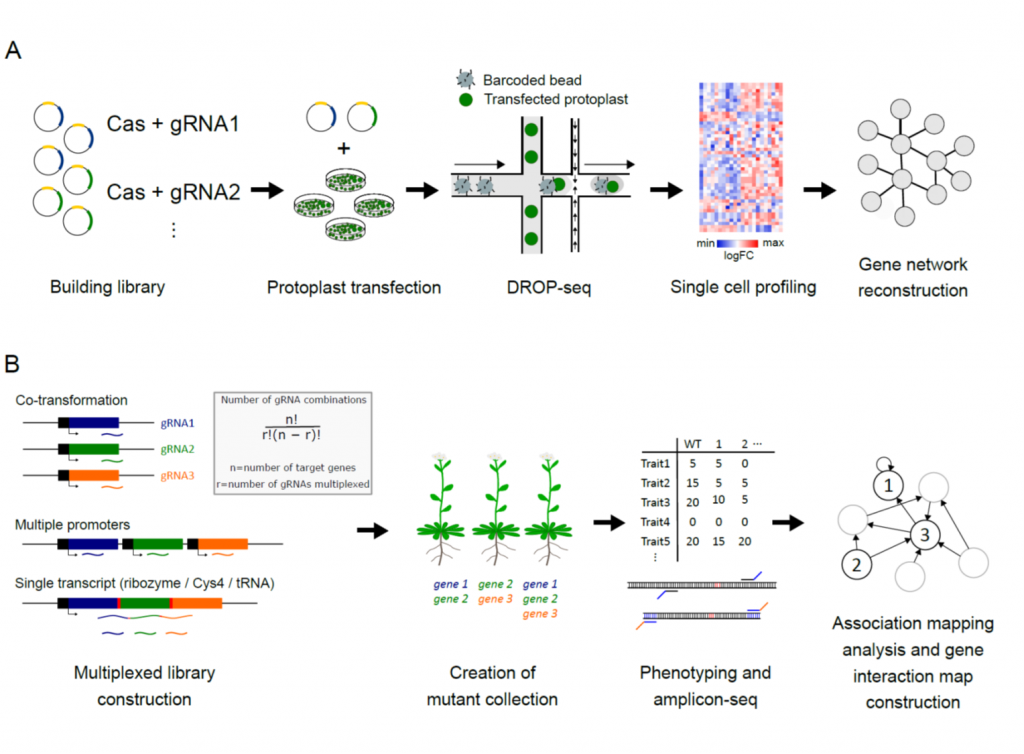
Review: CRISPR screens in plants: Approaches, guidelines, and future prospects (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe don’t need to remind you of the tremendous positive impact that CRISPR-based technologies have had on the life sciences through enabling any gene to be edited precisely. Here, Gaillochet et al. provide an up-to-date review of a lesser-known application of CRISPR, its use in large-scale screening…

