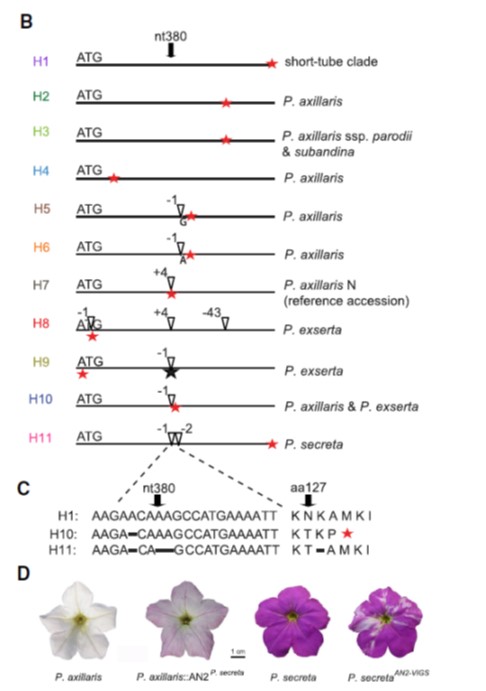
Pseudogenization and resurrection of a speciation gene (Curr. Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany flowers have evolved to attract pollinators through scent, shape, nectar production and color. Small changes in any of these attributes can be sufficient to dramatically shift pollinator preferences and pollination efficiency. Petunia has recently diverged into several species, characterized as…

Archetypal roles of an ABA receptor in drought and sugar responses in liverworts ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of the molecular pathway for ABA response comes from studies on Arabidopsis. Thanks to genomic sequencing efforts, we know that this pathway is largely conserved amongst plants, including mosses. Jahan et al. extend this understanding to liverworts, drawing on the recently sequenced…

Major domestication-related phenotypes in indica rice are due to loss of miRNA-mediated laccase silencing (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRice (Oryza sativa) is derived from breeding of perennial wild ancestors with long stalks and few seeds to short plants with enlarged panicles (inflorescences). Many known domestication changes are due to changes in transcription factors or modulation of enzymatic actions. Recent work by Swetha et al.…
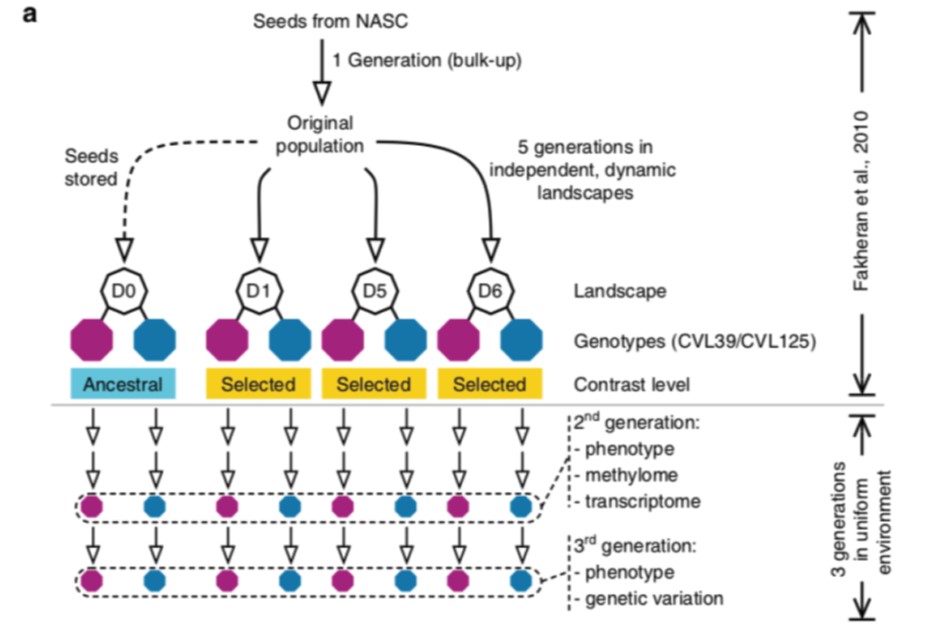
Contribution of epigenetic variation to adaptation in Arabidopsis (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt is known that changes in the epigenetic state can be inherited, but whether the epigenetic changes are subject to natural selection is uncharted territory. Schmid et al. examined the phenomic and epigenomic changes in Arabidopsis accessions that underwent selection to simulated habitat fragmentation.…
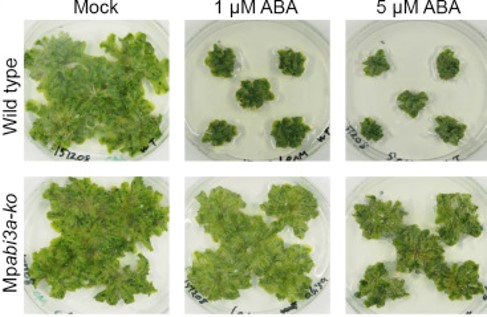
A conserved ABA signaling module regulates dormancy in liverworts (Curr Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can strategically maintain a state of dormancy to prevent germination and growth under unfavorable environmental conditions. In evolutionarily young lineages, dormancy is regulated by a canonical abscisic acid signalling pathway comprised of ABA receptors (PYR/PYL/RCAR), the negative regulator…
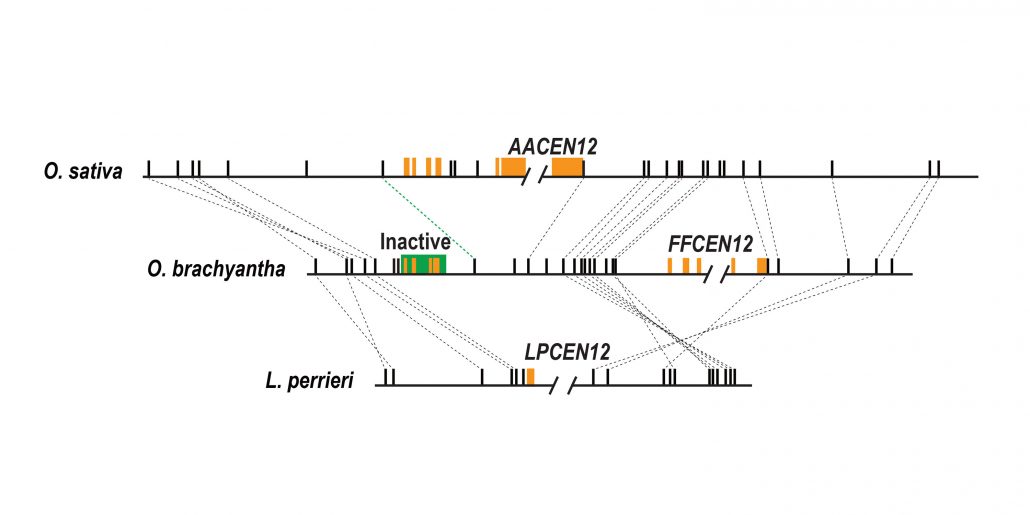
Selection Drives Gene Escape from Centromeres
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiao et al. performed comparative phylogenomic analysis on rice centromeres. Plant Cell (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00163
By Yi Liao and Mingsheng Chen
Background: Centromeres are necessary for faithful chromosome segregation in eukaryotic organisms. The genomic regions conferring centromere…
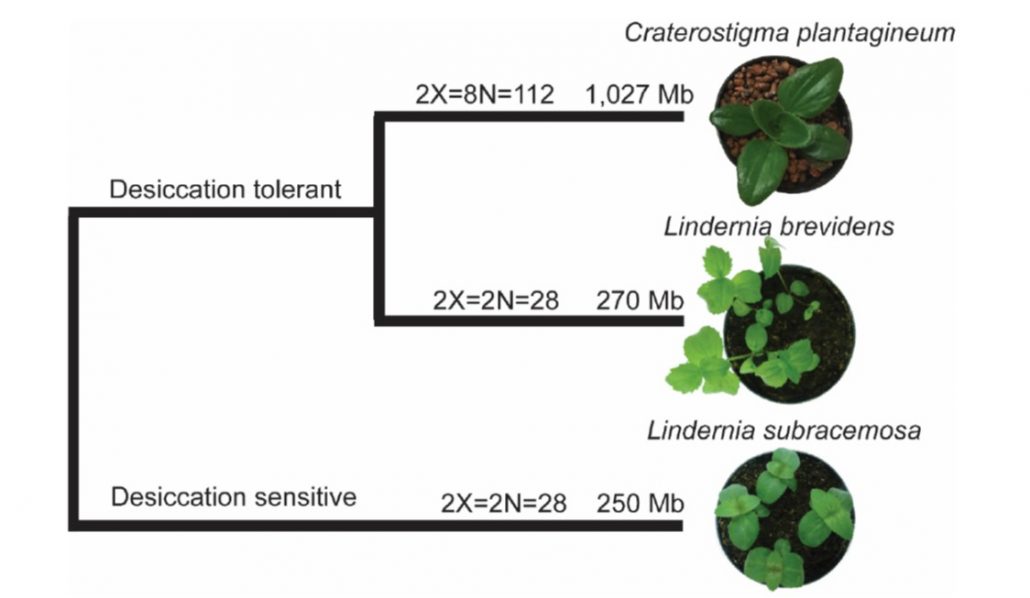
Desiccation tolerance evolved through gene duplication and network rewiring in Lindernia (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDesiccation tolerance is the property of being able to survive and recover from extreme dehydration. Although there are many desiccation-tolerant plant species, efforts to identify the genetic basis of desiccation tolerance have been limited by a lack of closely-related desiccation sensitive species.…
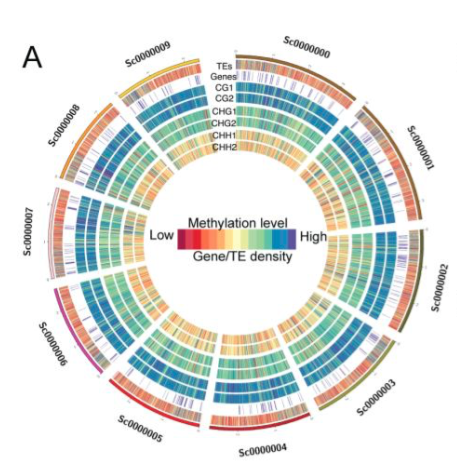
Tea genome expansion linked to TE bursts (Plant Biotechnol. J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyExpansion of plant genomes is thought to be linked to massive bursts of transposable elements activity. This implies consequences on the distribution of epigenetic modifications required for the silencing of the causative transposons. Consequences of transposon bursts have been extensively described…
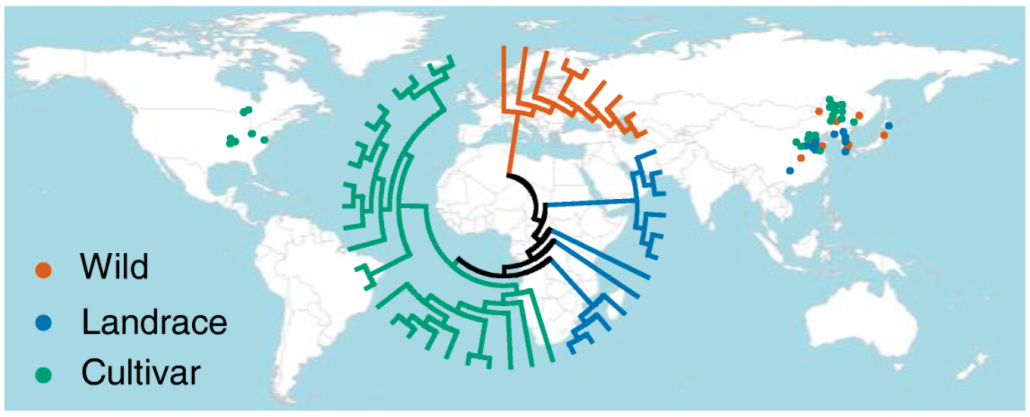
DNA methylation footprints during soybean domestication and improvement (Genome Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop domestication relies on harnessing the natural genomic diversity present in the cultivated population. The contribution of genetic variation for selection and improvement of traits in plants has been extensively studied. Besides this, variation in epigenetic components such as DNA methylation offers…

