
Plantae Presents: Sophien Kamoun and Phil Carella
Blog, Plantae Presents, Research Skills0 Comments
/
Plantae Presents - Sophien Kamoun and Phil Carella
Recorded Wednesday September 16 10am EDT, 4pm CET
Sophien Kamoun: Evolutionary dynamics of NLR immune receptors in plants
Sophien Kamoun is senior scientist at the Sainsbury Laboratory and professor of biology at the University of East Anglia.…

Review: Compartmentalization drives the evolution of symbiotic cooperation (Proc. Roy. Soc.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Many plants take advantage of microbial symbionts to boost their nutrient uptake, with classic examples provided by mycorrhizal fungi and the legume/Rhizobia partnership. Similar symbiotic partners are found in other domains of life, including the coral/dinoflagellate symbiosis, and the symbiosis…
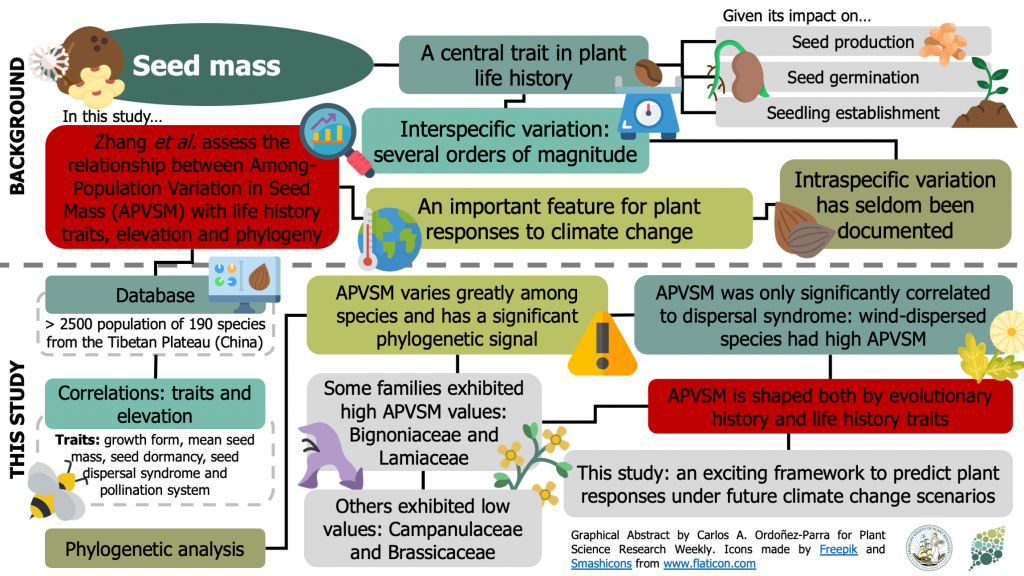
Among-population variation in seed mass for 190 Tibetan plant species: Phylogenetic pattern and ecological correlates (Glob. Ecol. Conserv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed mass is a central trait in plant life history that impacts on seed production, germination, and establishment. Several studies have documented the variation in seed mass between species, but little is known about its variation among populations of the same species. In this paper, Zhang et al. tested…
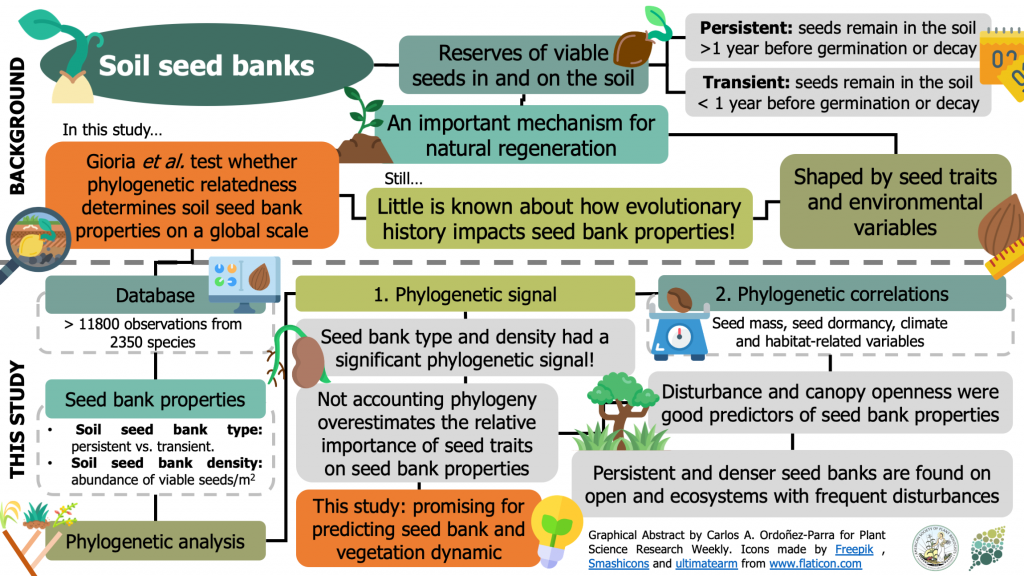
Phylogenetic relatedness mediates persistence and density of soil seed banks ($) (J. Ecol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoil seed banks are classified into two types, depending on how long seeds remain viable in the soil before germination or decay: transient (< 1 year) or persistent (> 1 year). In turn, a species' ability to form a persistent seed bank presumably depends on seed traits and plant habitat. However,…

Cones structure and seed traits of four species of large‐seeded pines: Adaptation to animal‐mediated dispersal (Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDifferent studies show that animal-dispersed pines have particular cone and seed structures to match their dispersers. However, most research has either addressed the changes in cone and seed traits in a single species over an environmental gradient or the differences between wind-dispersed and animal-dispersed…
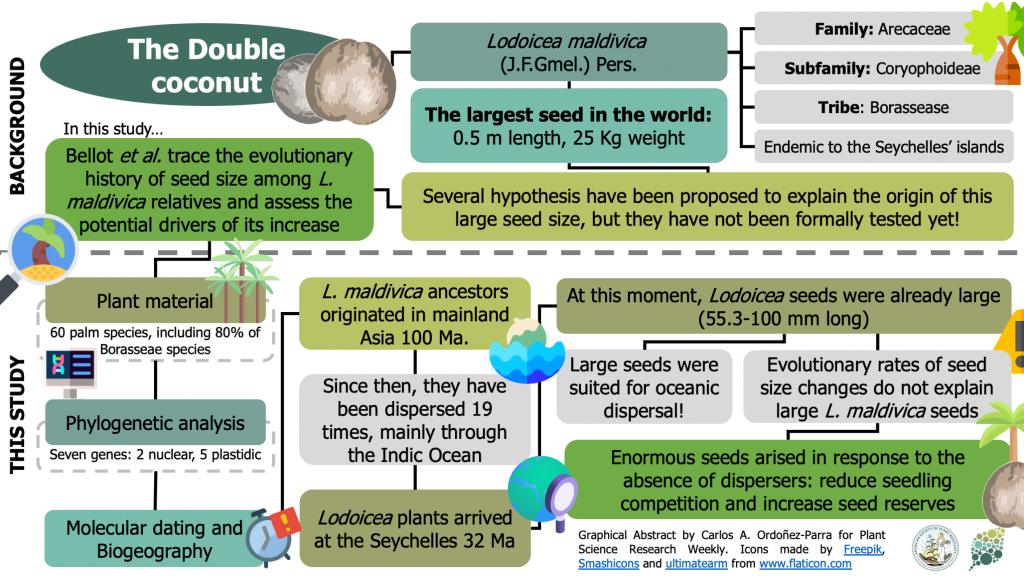
On the origin of giant seeds: the macroevolution of the double coconut (Lodoicea maldivica) and its relatives (Borasseae, Arecaceae) (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe double coconut –Lodoicea maldivica (J.F.Gmel.) Pers. (Arecaceae: Coryophoideae)– is an endemic palm from Seychelles with the largest seed in the world: 0.5 m length and 25 Kg weight. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the origin of this enormous seed, but they have not been formally…
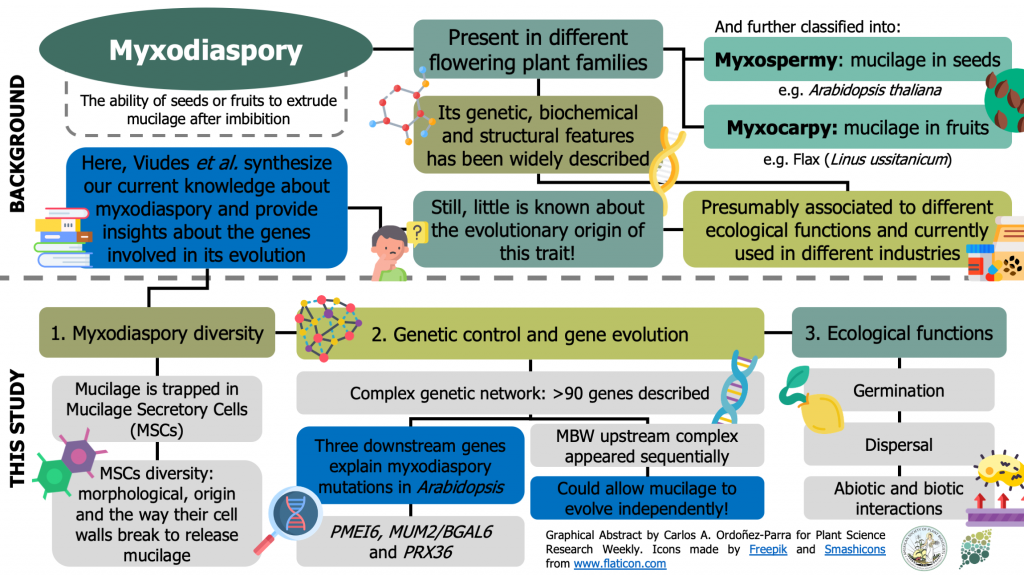
Review: Seed Mucilage Evolution: Diverse Molecular Mechanisms Generate Versatile Ecological Functions for Particular Environments ($) (Plant Cell Environ.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants with myxodiaspory release mucilage upon imbibition of seeds (myxospermy, e.g., Arabidopsis thaliana) or fruits (myxocarpy, e.g., Linum usitatissimum). This ability appears in several angiosperm families, but its evolutionary origin has seldom been studied. In this review, Viudes et al. synthesize our…
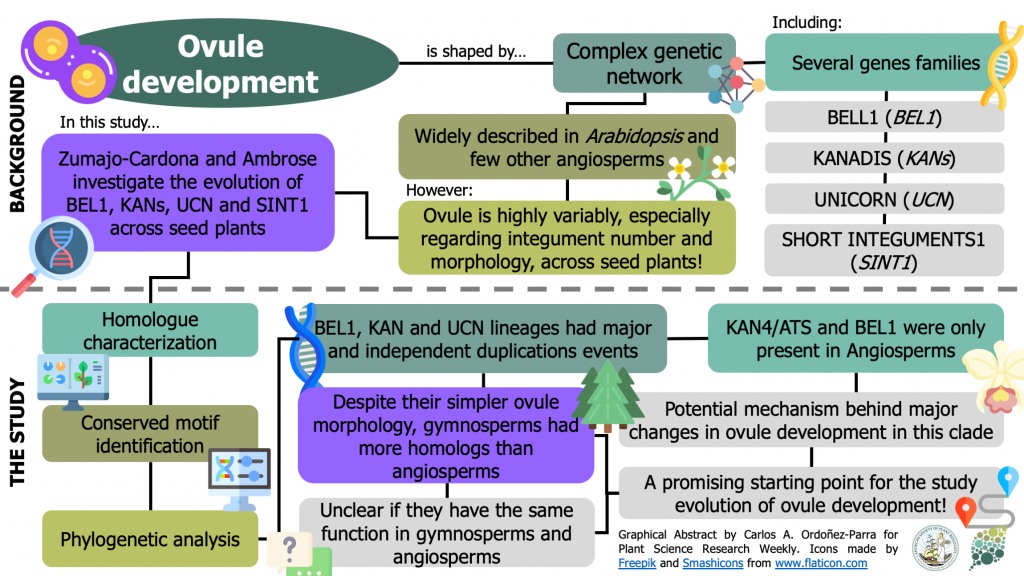
Phylogenetic analyses of key developmental genes provide insight into the complex evolution of seeds ($) (Mol. Phylogenet. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe complex genetic network behind the development of the ovule –the cell that will give place to seeds after fertilization– has been widely described in some model plants. However, ovules hold a high variability in integument number and morphology across seed plants. To understand the genetic mechanism…
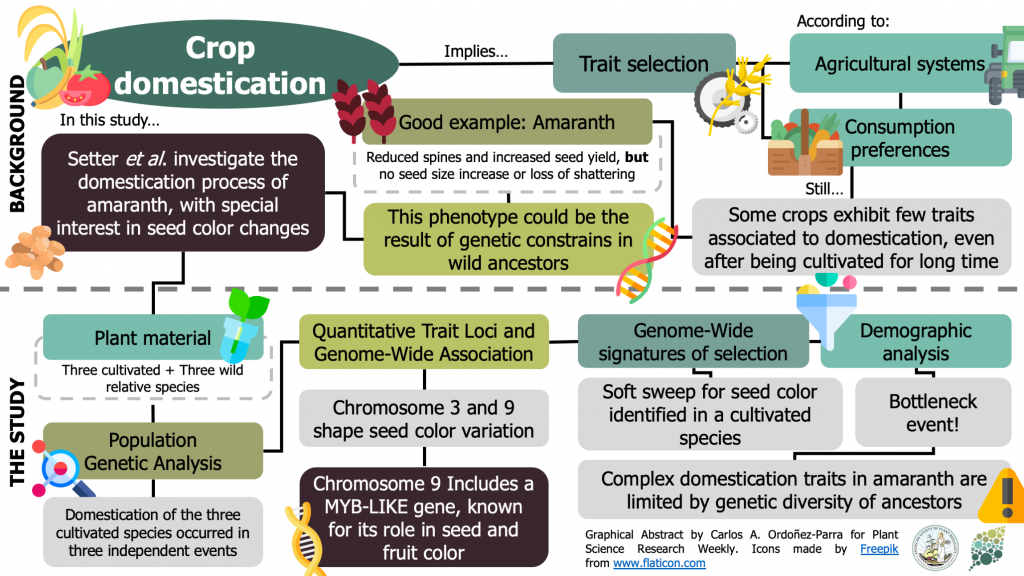
Parallel Seed Color Adaptation during Multiple Domestication Attempts of an Ancient New World Grain ($) (Mol. Biol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmaranth has been cultivated in Central and South America since Pre-Columbian times. Still, it exhibits features that are unexpected in domesticated plants, such as seed shattering and reduced seed size. Here, Setter et al. dissected the genetic signature of this crop’s domestication process, with…

